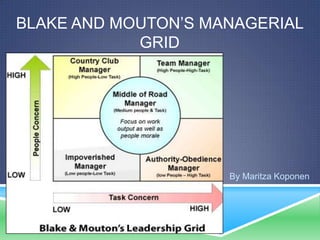
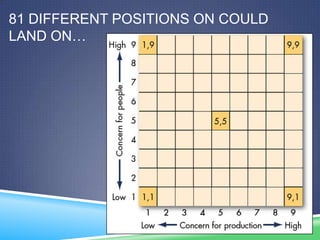
The document summarizes Blake and Mouton's Managerial Grid leadership model. The model depicts two dimensions - concern for people and concern for production - which when plotted on a grid, define five different leadership styles: impoverished management, task management, middle-of-the-road, country club, and team management. Team management, with high concern for both people and production, is considered the most effective style. The grid helps managers analyze their own style and work to improve it. However, the model does not account for external factors that could influence leadership.