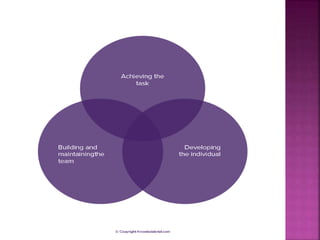
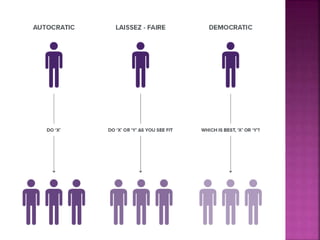
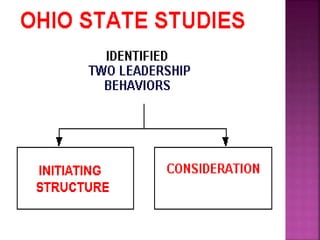
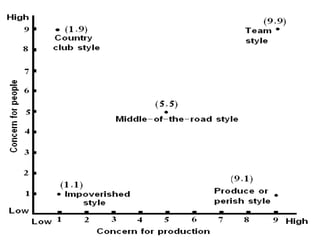
This document discusses various theories of leadership, including trait theory and behavioral theory. It describes behavioral theory as assuming that leadership can be learned rather than inherent. Two major behavioral leadership studies are discussed: the Michigan Leadership Studies, which looked at job-centered and employee-centered leadership, and the Ohio State Leadership Studies, which examined initiating structure behavior and consideration behavior. Blake and Mouton's Managerial Grid is also summarized, outlining five leadership styles based on concern for production and people.