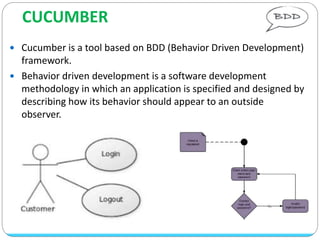
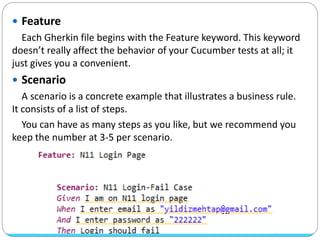
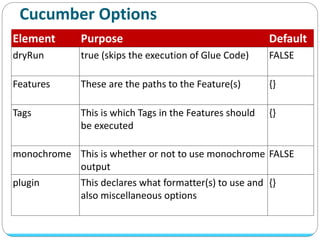
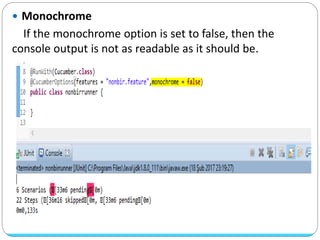
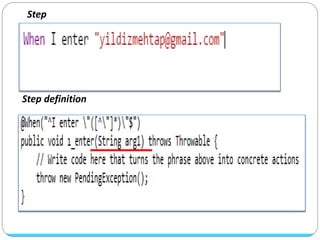
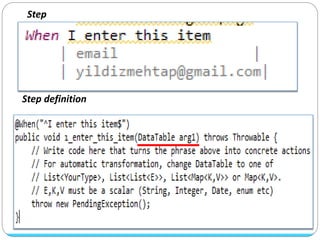
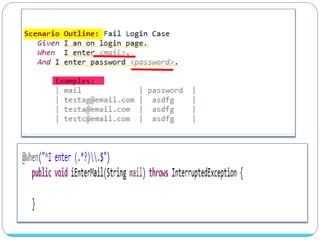
Cucumber is a tool that supports behavior-driven development (BDD). It allows test cases to be written in a simple language called Gherkin that both programmers and non-programmers can understand. Gherkin features are made up of scenarios with steps using keywords like "Given", "When", and "Then" to describe preconditions, actions, and expected outcomes. Cucumber supports many programming languages and can integrate with frameworks like Selenium for browser automation.