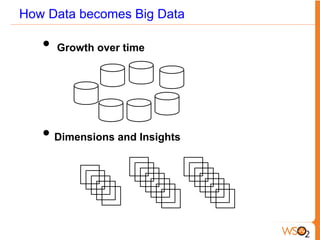
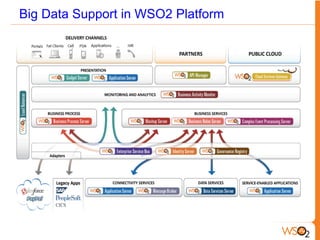
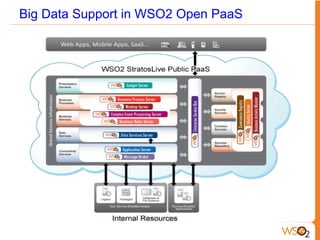
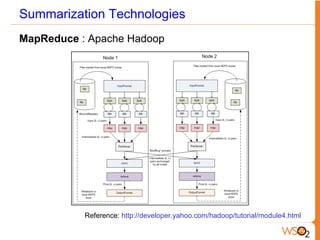
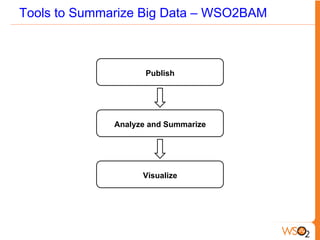
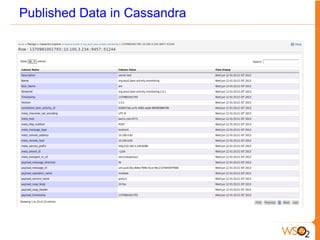
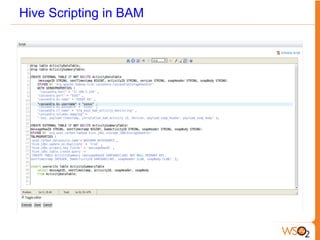
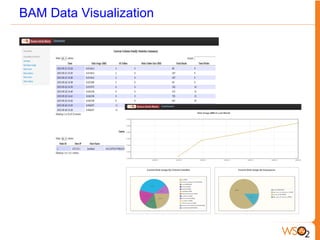
This document discusses big data storage challenges and solutions. It describes the types of data that need to be stored, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Optimal storage solutions are suggested based on data type, including using Cassandra, HBase, HDFS, and MongoDB. The document also introduces WSO2 Storage Server and how the WSO2 platform supports big data through features like clustering and external indexes. Tools for summarizing big data are discussed, including MapReduce, Hive, Pig, and WSO2 BAM for publishing, analyzing, and visualizing big data.