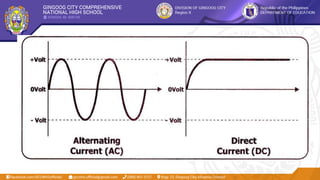
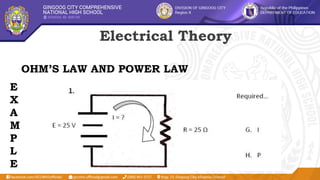
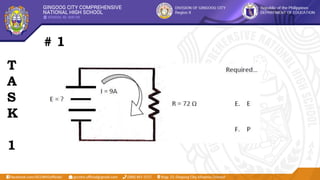
This document provides information about terminating and connecting electrical wiring and electronic circuits. It begins with learning objectives for the lesson, which are to plan and prepare wiring/circuits for termination and connection, perform the terminations and connections, and test the terminated and connected wiring/circuits. It then lists objectives for students to select proper tools, prepare wiring/circuits correctly according to instructions, and follow safety procedures. The document continues with explanations of electrical theory, including direct current, alternating current, and Ohm's law. It identifies components of a simple circuit such as power sources, fuses, wires, switches, and loads. Tasks and examples are provided to demonstrate the concepts.