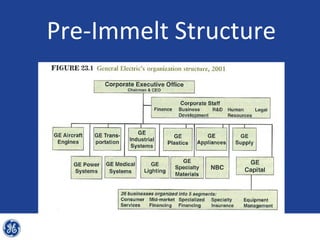
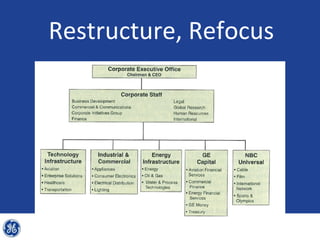
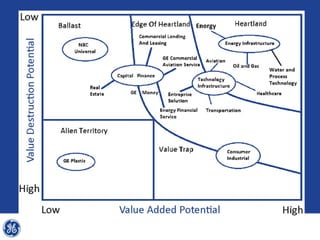
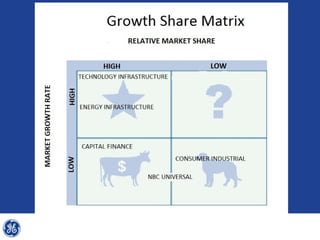
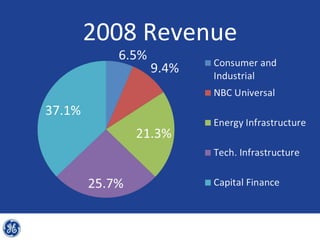
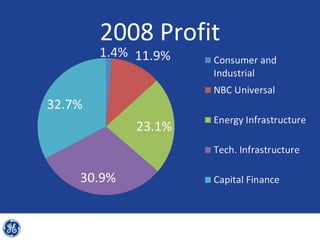
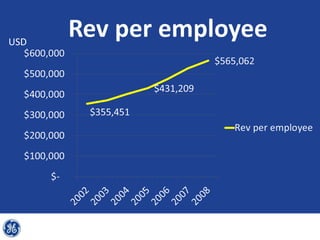
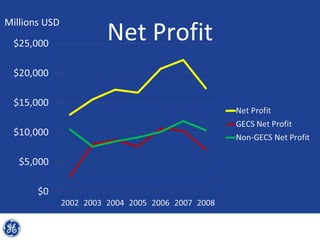
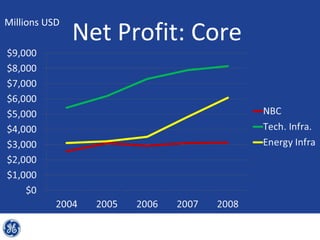
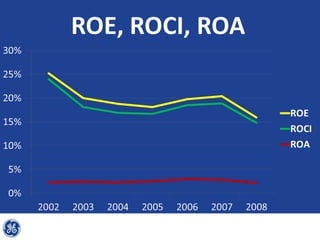
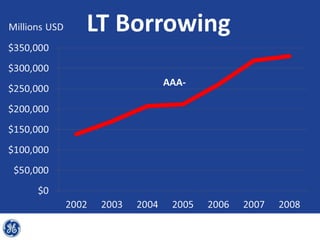
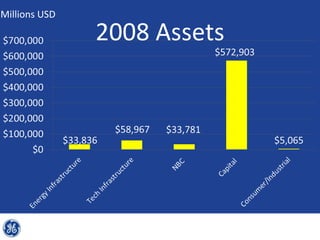
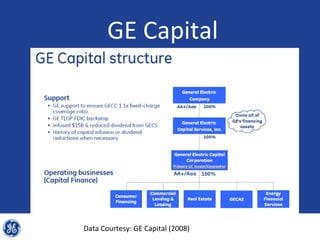
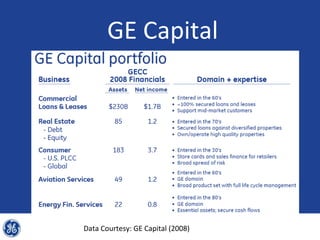
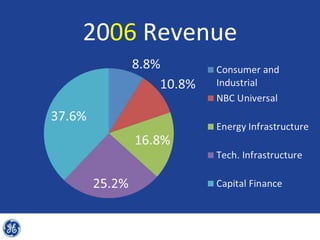
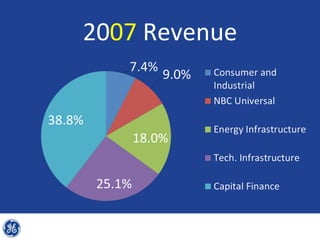
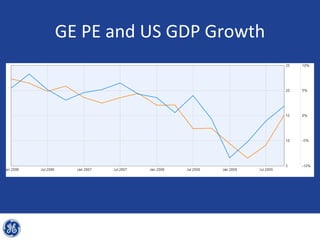
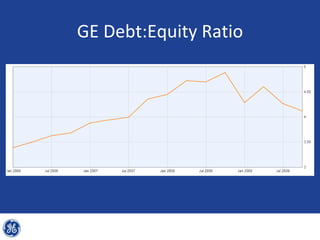
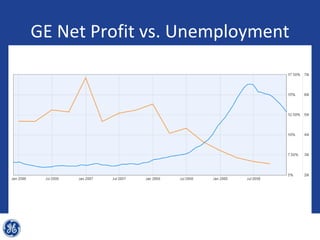
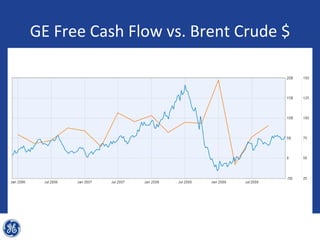
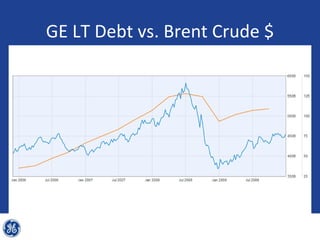
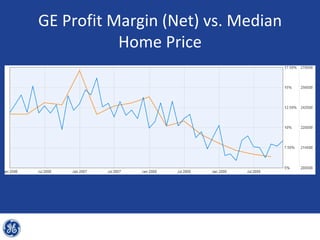
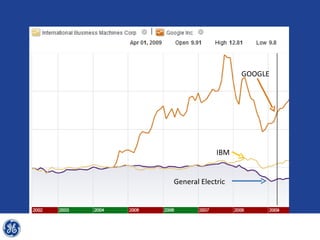
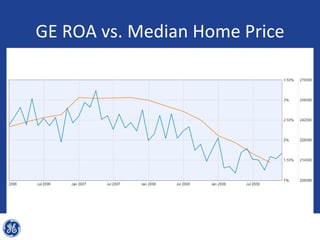
This document provides an overview and analysis of General Electric's strategies under CEO Jeffrey Immelt from 2001-2009. It discusses Immelt's core strategies of growth, integration, and value creation. It analyzes GE's financial performance and portfolio from 2008 including revenues, profits, assets and debt. It recommends reducing reliance on GE Capital, increasing renewable energy investment, and selling NBC Universal while continuing international expansion.