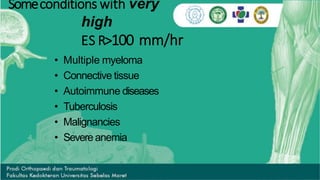
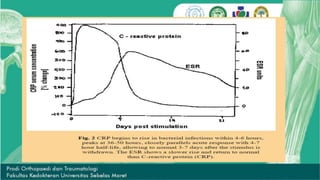
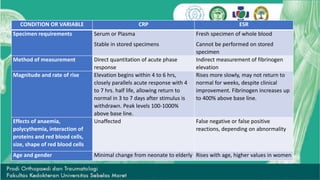
CRP and ESR are common markers of inflammation. CRP is a protein in the blood that levels rapidly rise within 6 hours of inflammation or infection, peaking at around 48 hours, and then fall quickly once the stimulus is removed. In contrast, ESR rises more slowly and can remain elevated for weeks despite clinical improvement. ESR is measured by how fast red blood cells sediment in a tube, which is increased when inflammatory proteins cause clumping. While not specific, ESR is used as a screening tool along with other tests to detect increased inflammatory activity associated with various conditions.