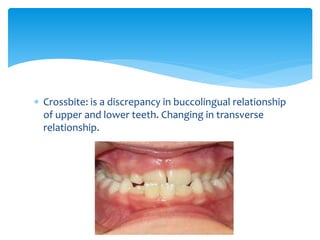
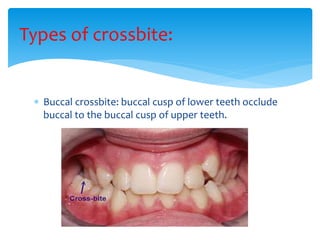
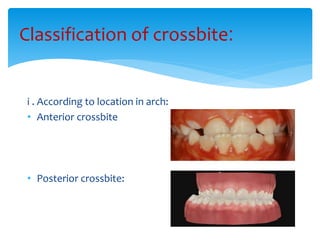
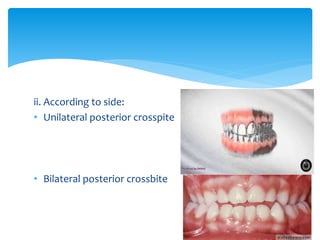
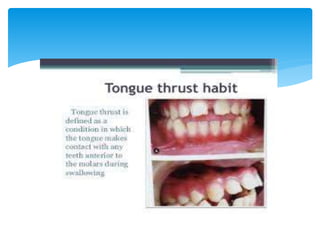
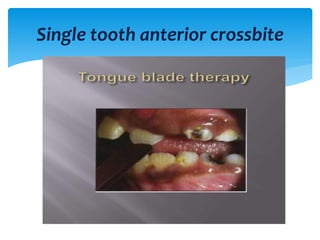
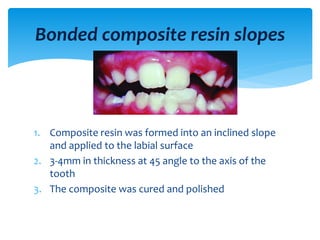
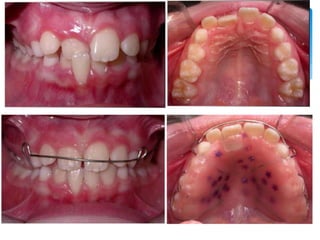
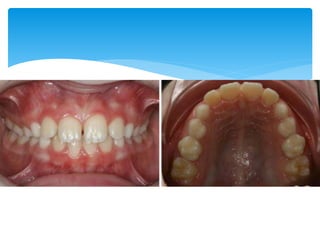
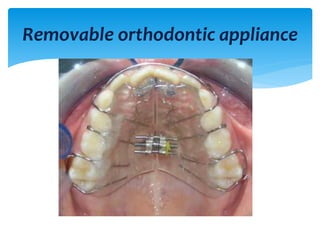
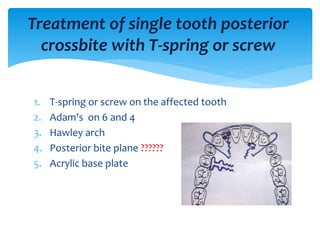
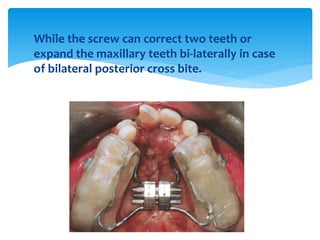
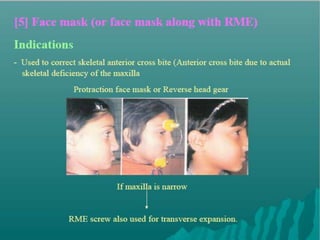
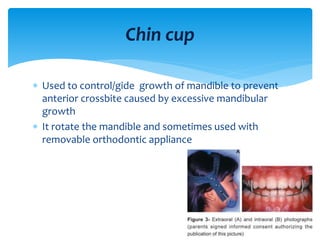
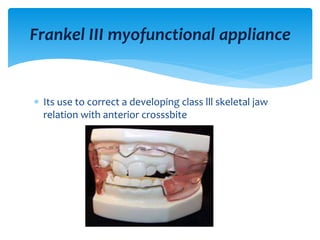
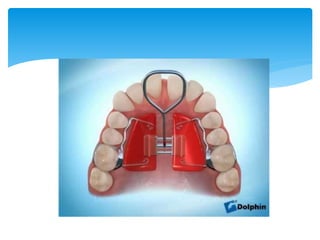
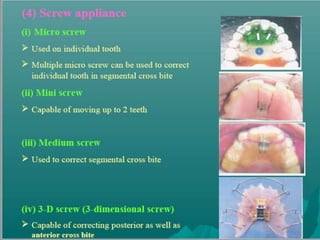
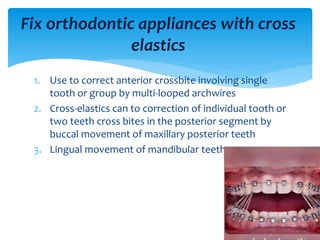
This document discusses different types of crossbite, including buccal, lingual, unilateral, bilateral, dental, skeletal, and functional. Crossbite can be caused by dental anomalies, soft tissue habits like digit sucking, heredity, congenital issues like cleft lip and palate, and trauma. Treatment for crossbite is urgent to prevent TMJ dysfunction, asymmetric growth, gingival recession, and esthetic issues. Various appliances can be used depending on the location and severity of the crossbite, including removable plates with springs, composites, Catalan's appliance, chin cups, myofunctional appliances, quad helix, rapid maxillary expansion, and fixed braces with elastics