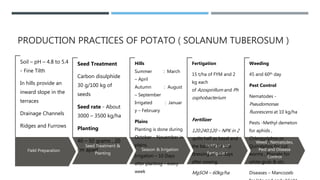
The document discusses crop improvement techniques for potatoes (Solanum tuberosum), including field preparation, seed treatment, planting schedules, irrigation, and pest management. It highlights the use of true potato seeds (TPS) to combat issues like high seed cost and virus infiltration, while also addressing challenges such as soil quality and labor availability. Additionally, it mentions notable potato facts and provides insights into germplasm collections for breeding resistant varieties.