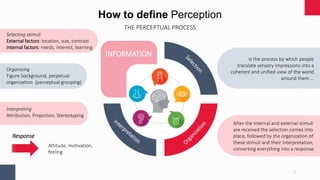
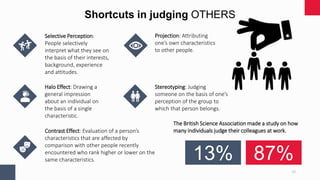
This document discusses various aspects of critical thinking, including perception and presuppositions, cognitive biases, logical fallacies, types of reasoning, problem deconstruction, and building strong arguments. It provides information on how perception is formed through a perceptual process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting external and internal stimuli. Factors that influence perception, like the target object and perceiver characteristics, are examined. Methods for increasing perception through critical thinking and awareness of thinking patterns are presented. The document also explores concepts like attribution theory, perceptual grouping, shortcuts in judging others, and working to identify presuppositions.