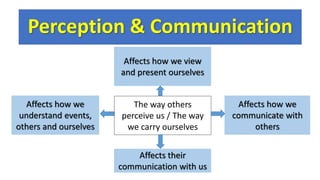
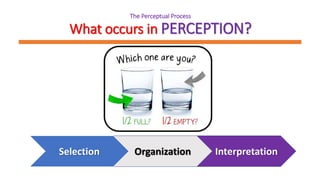
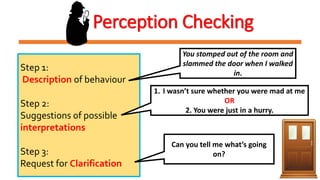
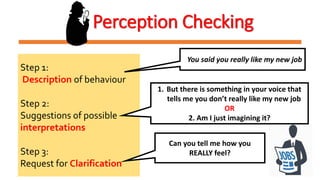
This document discusses perception and its role in communication. It defines perception as the process of using senses to acquire information from the environment. Key points include:
- Perception involves selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory information
- Differences in perception can arise from physiological, experiential, emotional, and cultural factors
- Errors in perception include stereotyping, first impressions, and self-serving biases
- Perception checking involves describing behaviors, suggesting interpretations, and seeking clarification to understand others' perspectives
- Understanding perception is important for effective communication