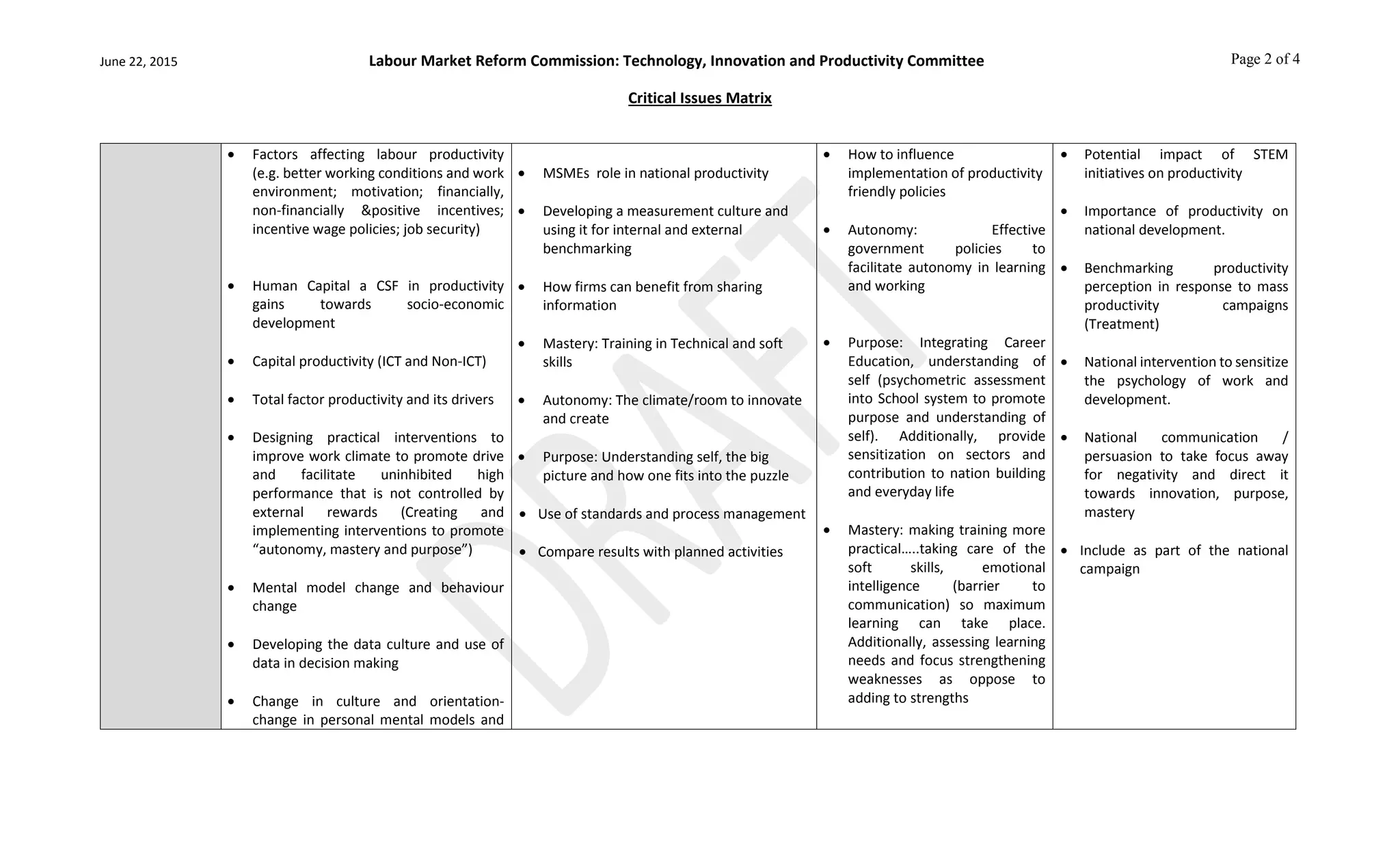
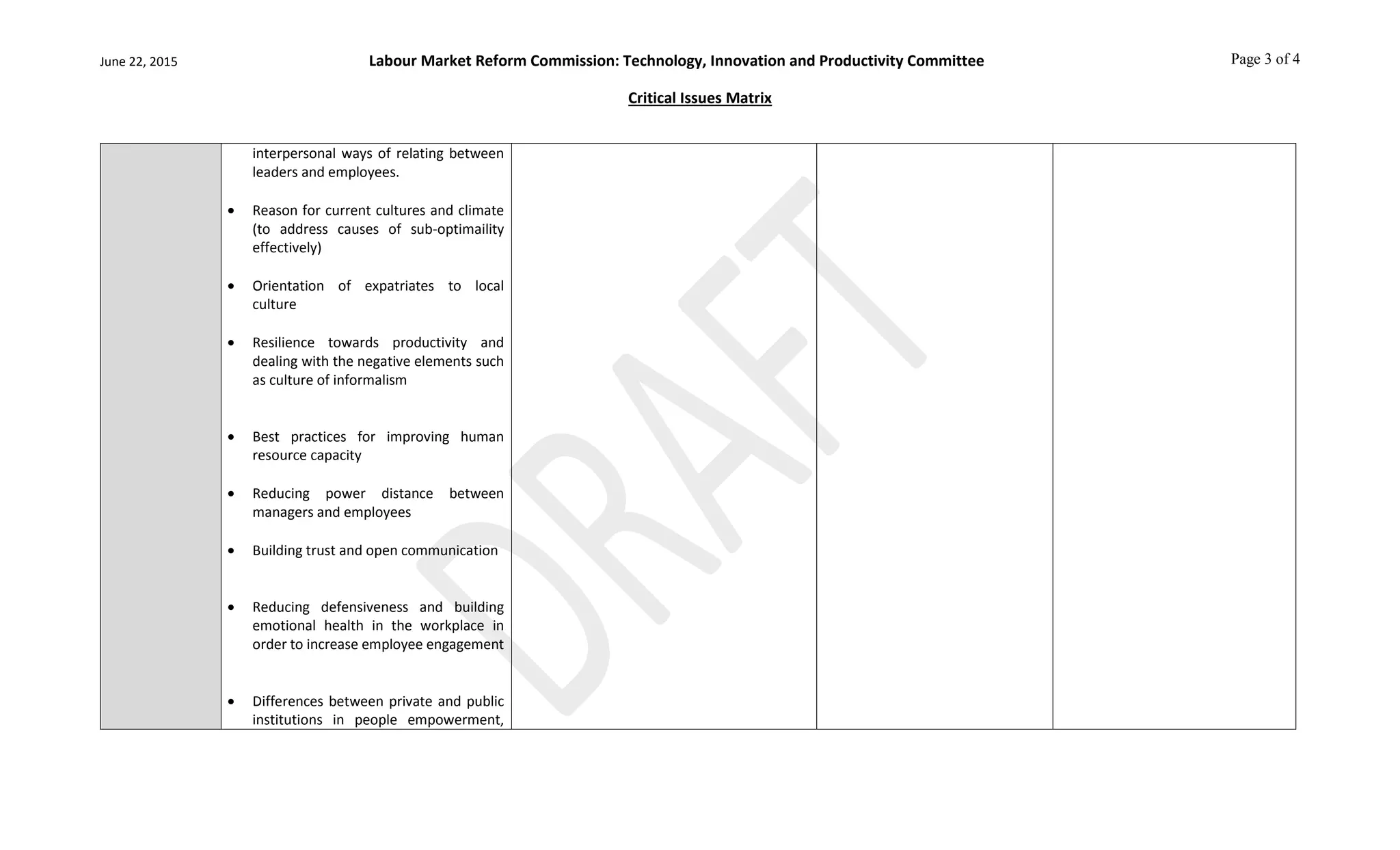
This document outlines a critical issues matrix for a Labour Market Reform Commission's Technology, Innovation and Productivity Committee. The matrix identifies key issues related to human capital, technology, innovation, productivity, competitiveness, and their relation to small and medium enterprises, government policies, and national development. Issues addressed include fostering creativity, technology adoption, research and development, workforce skills, productivity measurement, and creating an environment that promotes competitiveness. The goal is to inform the committee's work in developing strategies and policies to advance technology, innovation and productivity in Jamaica.