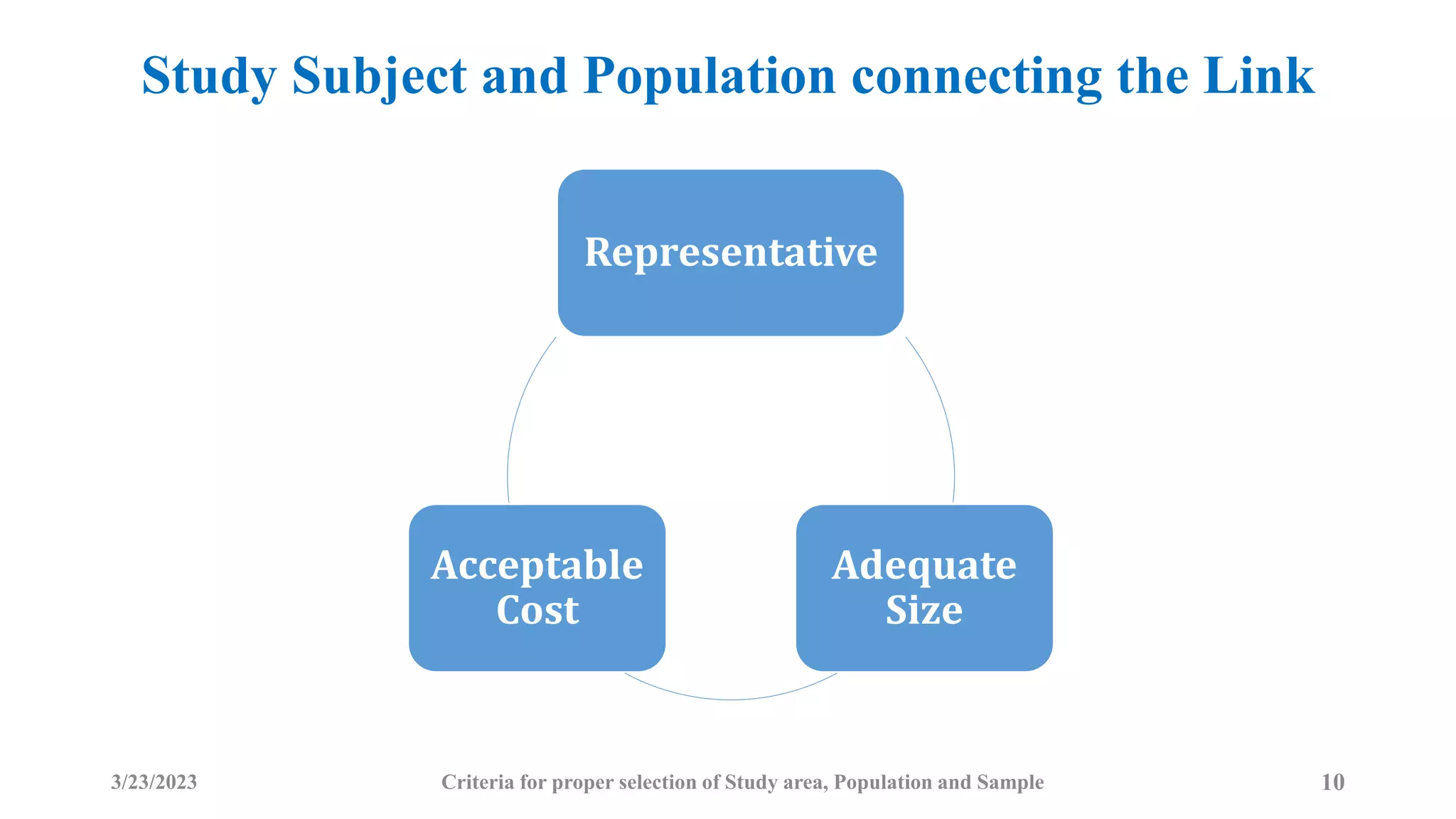
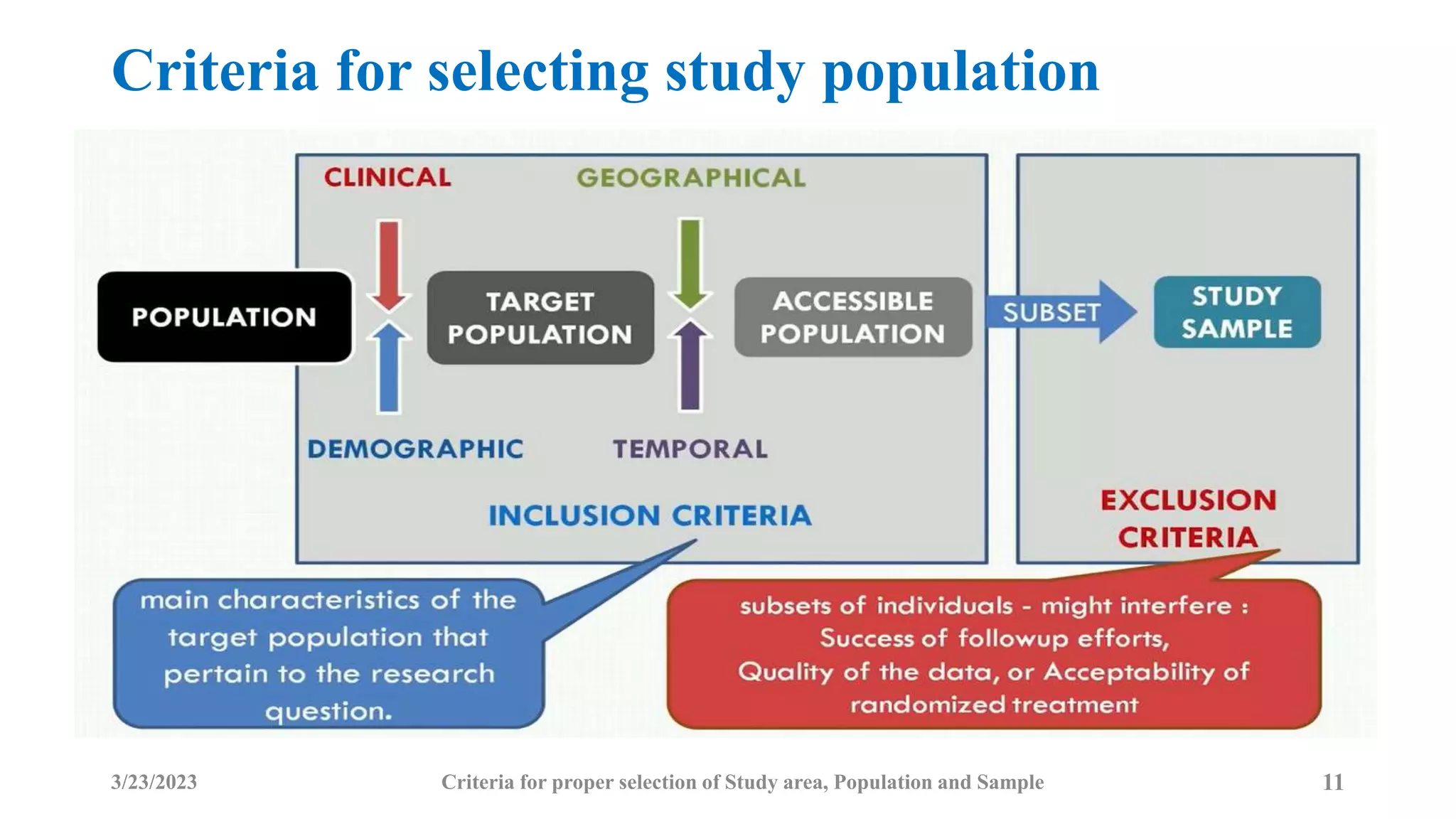
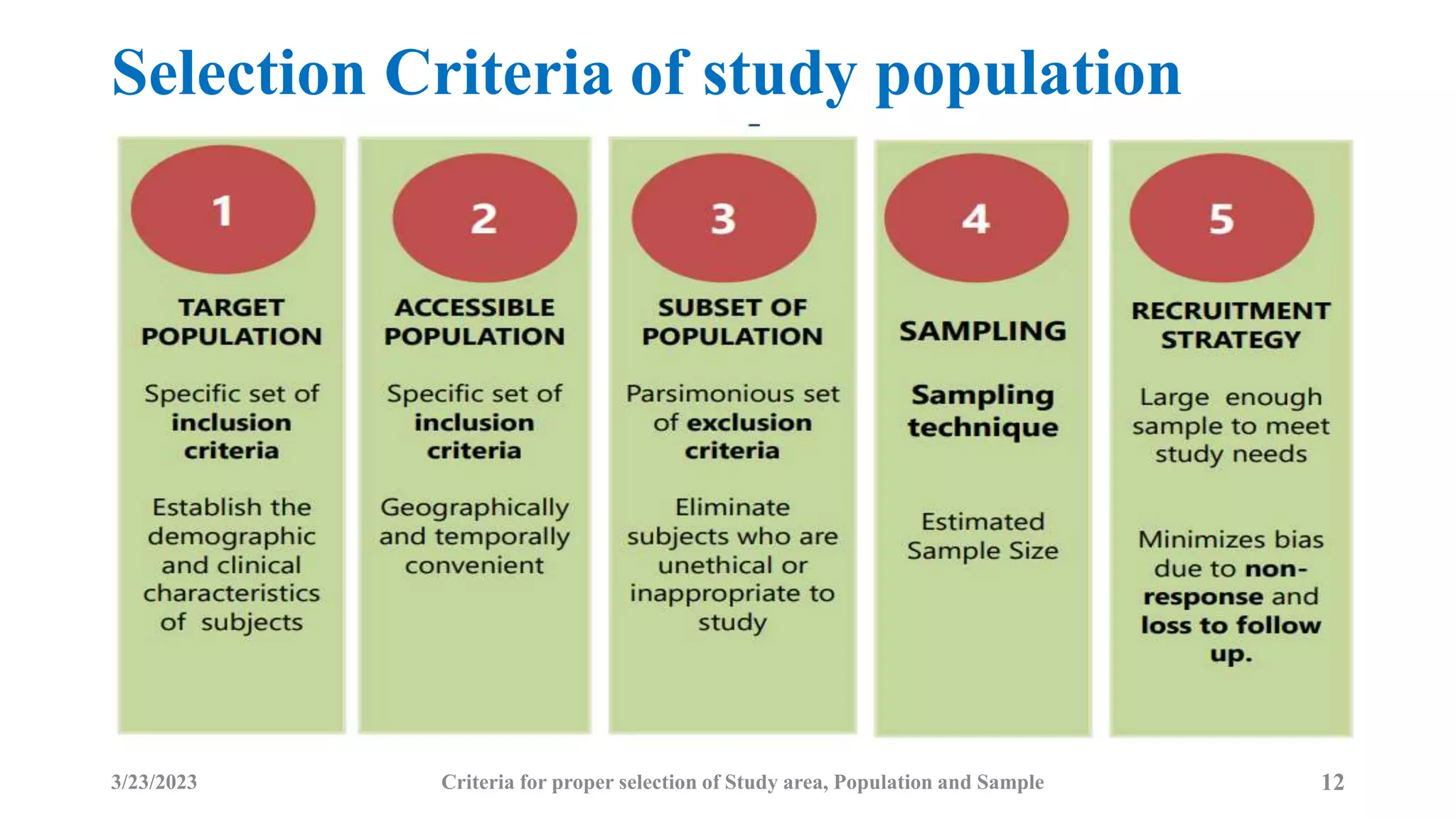
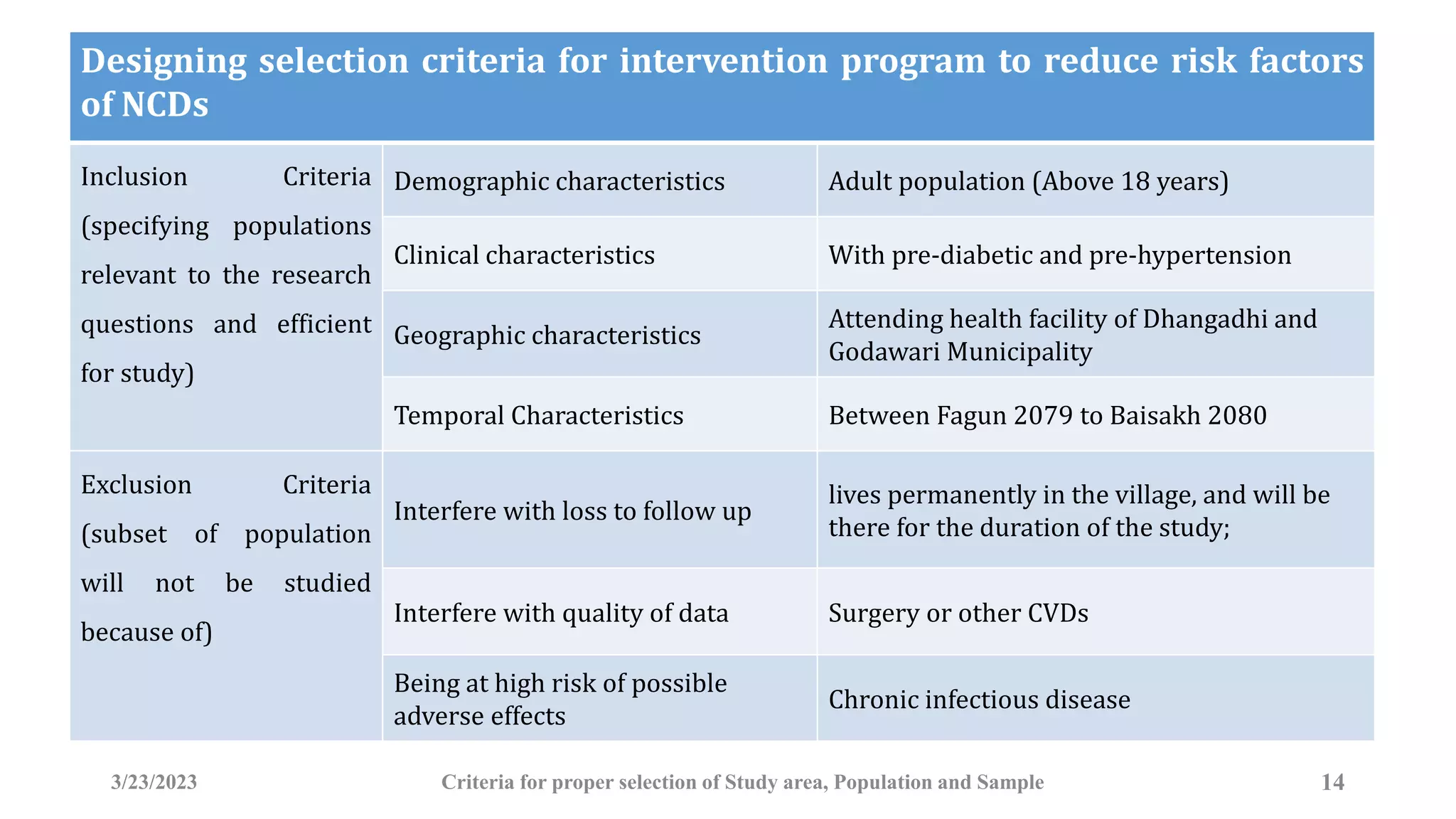
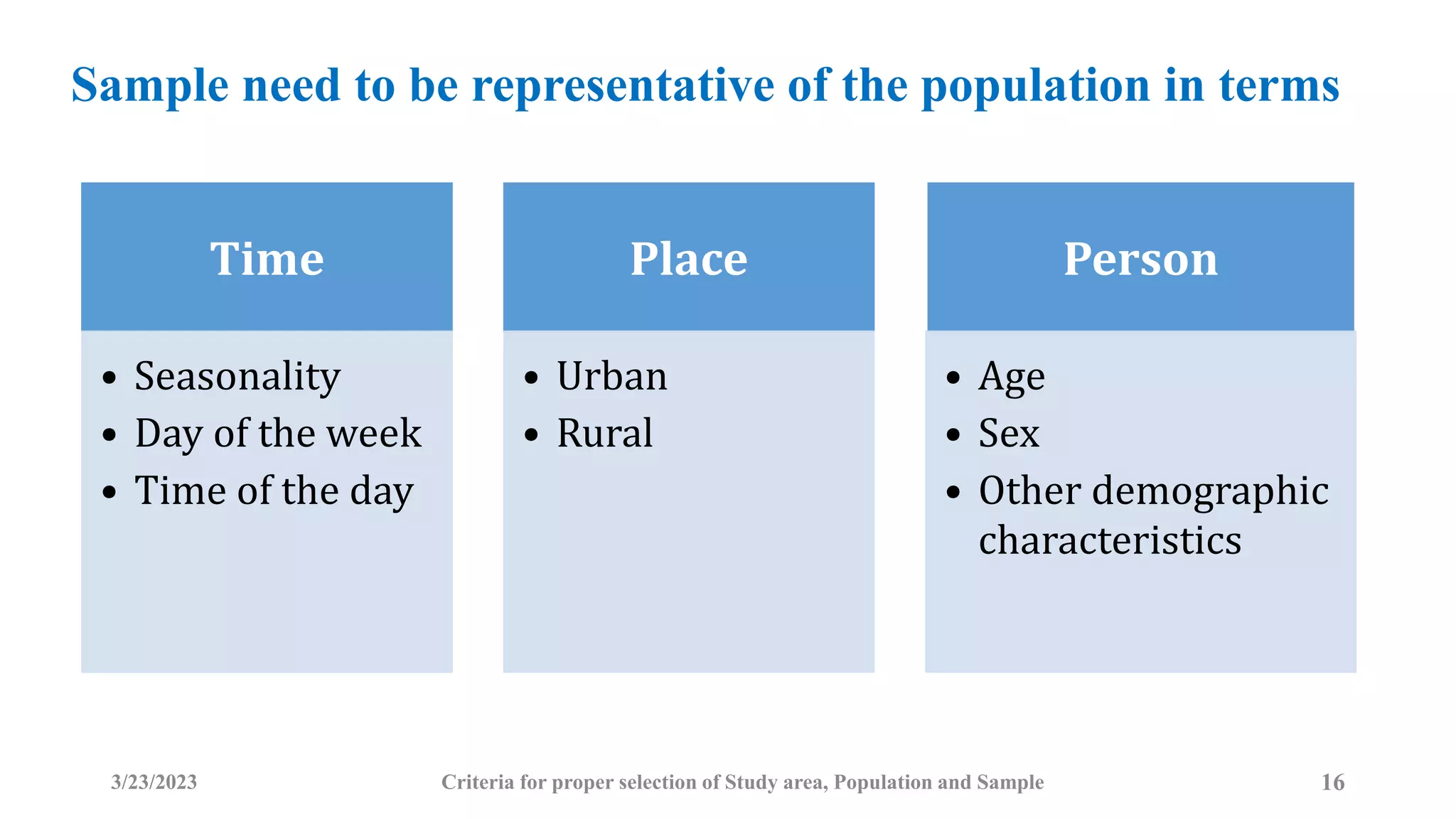
The document outlines the criteria for selecting study areas, populations, and samples in research. It emphasizes the importance of problem specificity, feasibility, and cultural acceptance in selecting study areas and populations, and it details the characteristics and selection processes for samples to ensure representativeness. Additionally, it discusses the significance of understanding the broader research area and the research question in the context of public health and epidemiology.