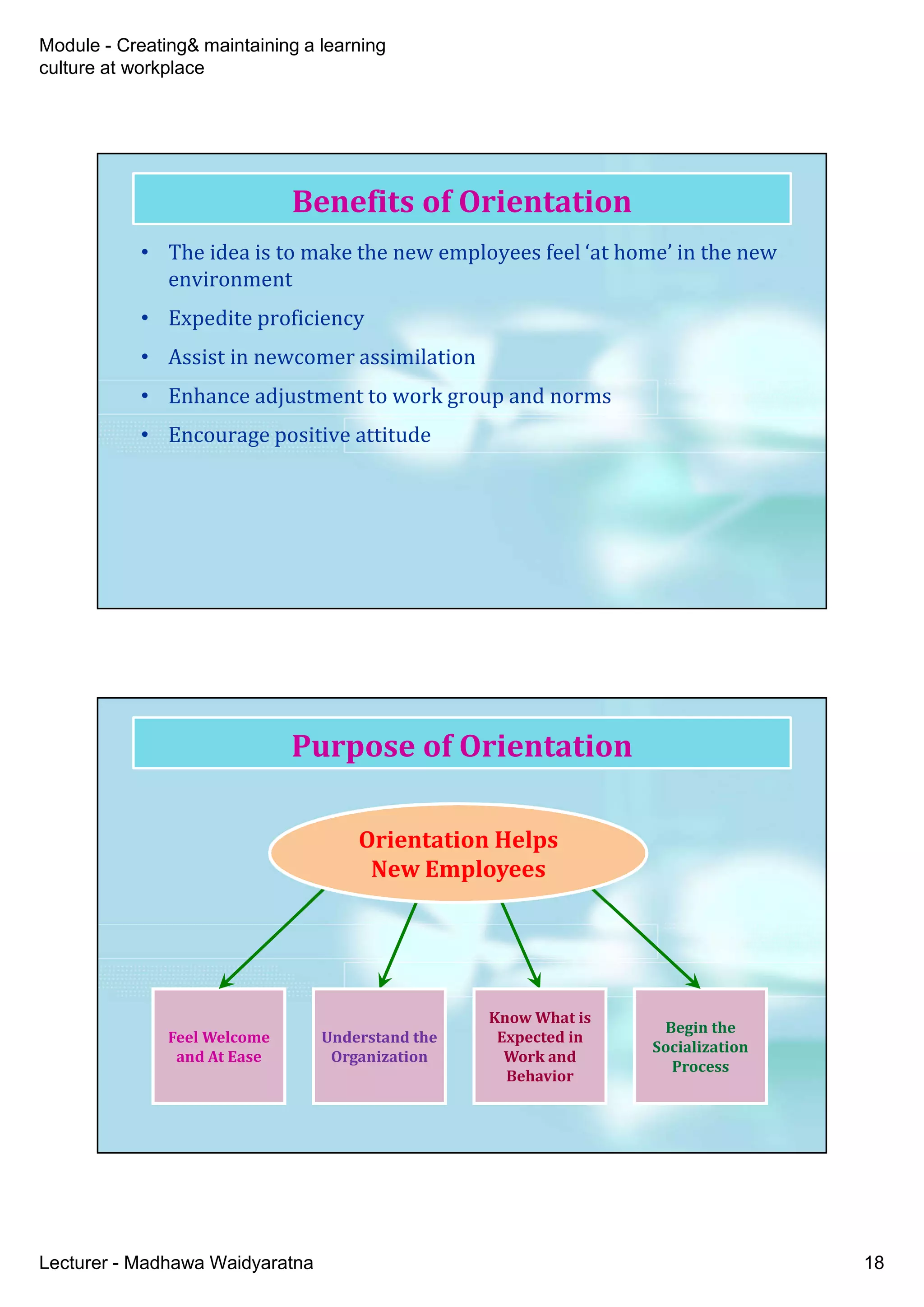
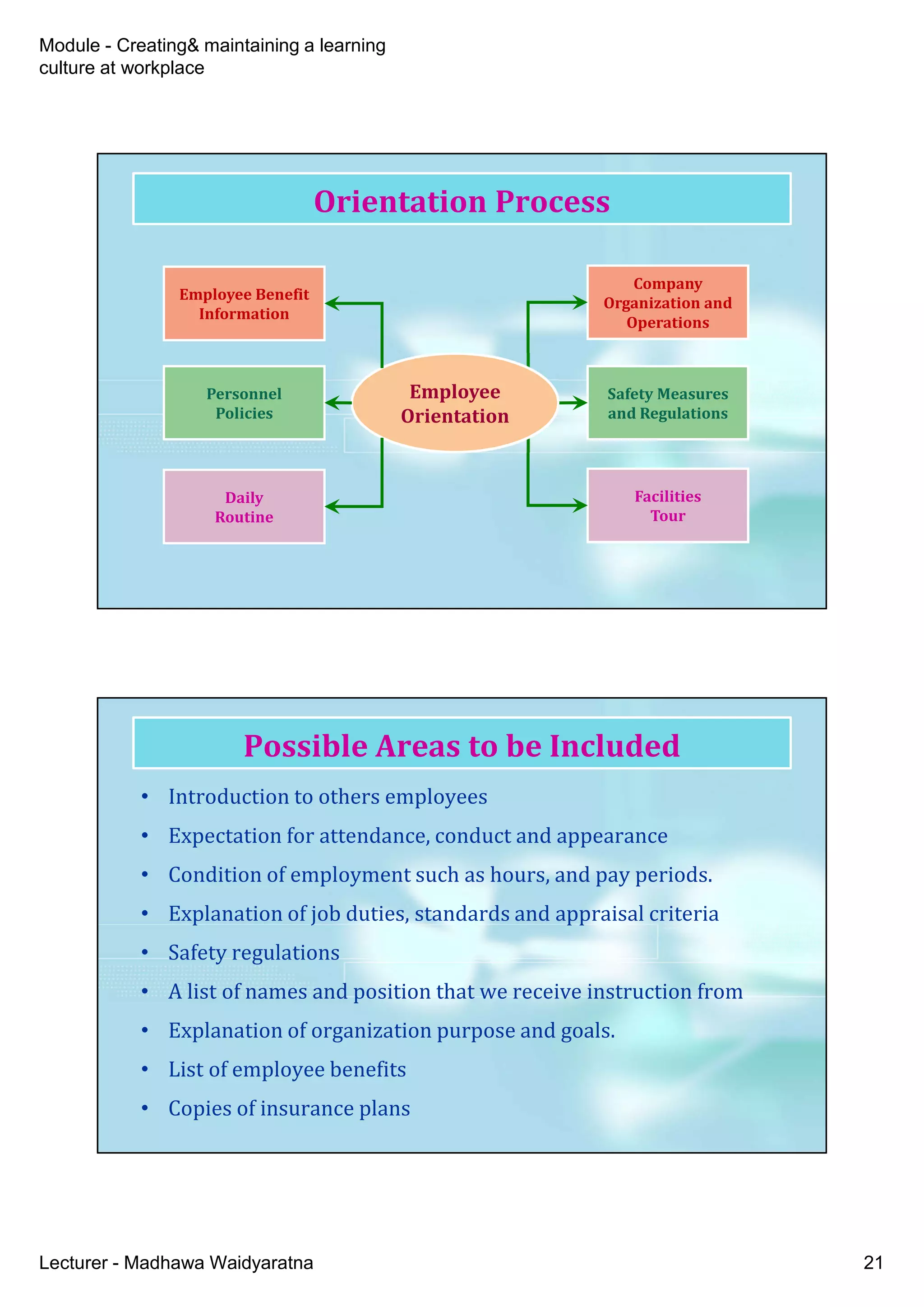
The document discusses creating and maintaining a learning culture in the workplace, emphasizing the importance of continuous employee learning, personal mastery, and shared vision. It highlights the benefits of training and onboarding, as well as the need for effective communication and structure to promote a culture of learning. Additionally, the document addresses the challenges of orientation programs and recommends evaluation methods to improve their effectiveness.