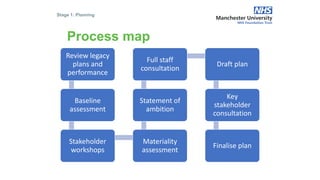
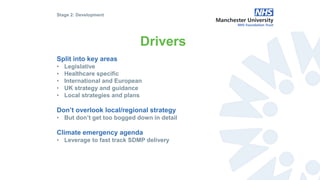
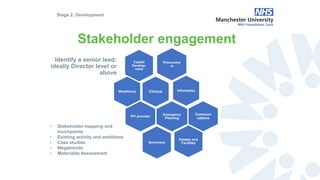
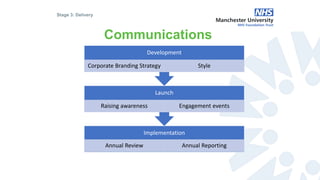
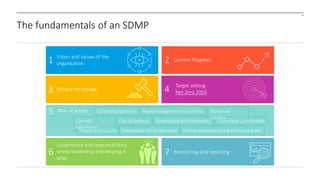
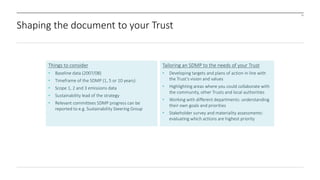
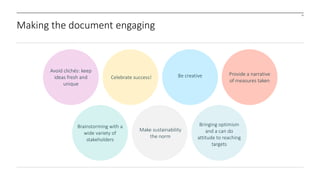
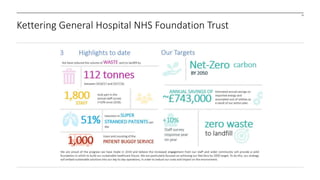
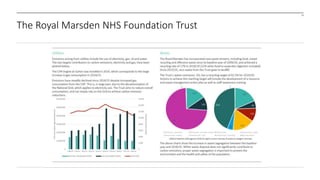
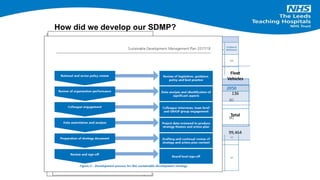
The document outlines the development and implementation of a Sustainable Development Management Plan (SDMP) for NHS trusts, highlighting the improvement in support from senior management and the need for creating mandatory SDMPs. It discusses the strategic context of the Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust’s merger, the planning and development stages of the SDMP, and emphasizes the importance of stakeholder engagement, performance metrics, and a focus on sustainability across various areas. The document also presents examples of progress made in sustainability efforts and suggests further improvements needed for effective reporting and governance.