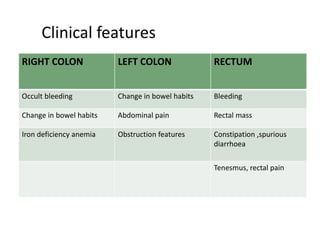
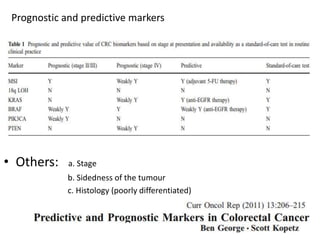
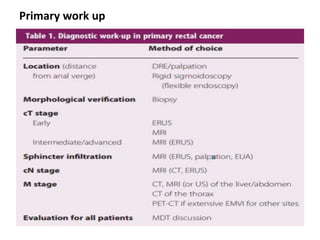
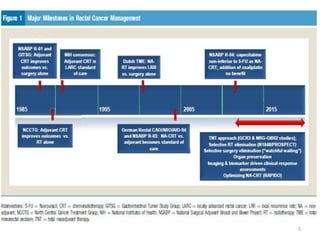
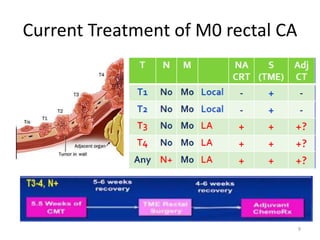
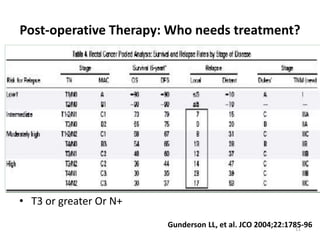
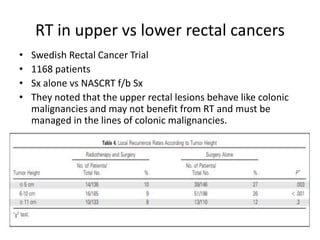
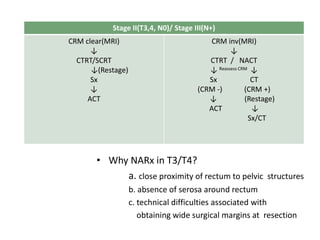
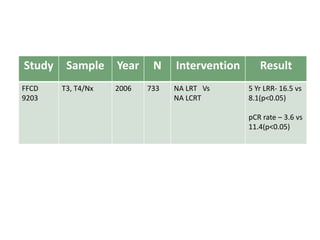
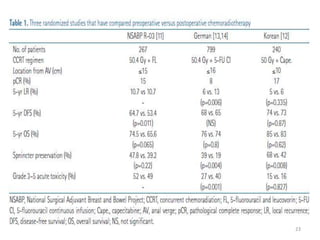
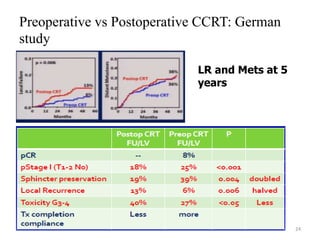
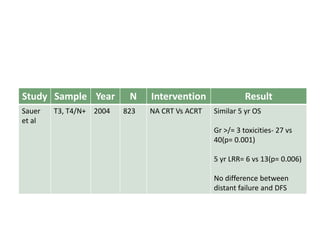
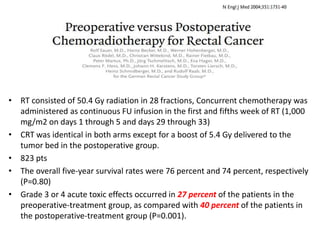
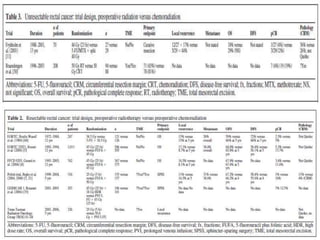
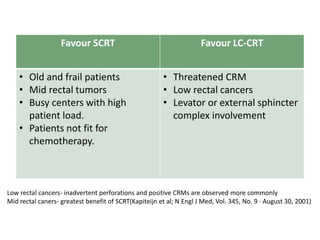
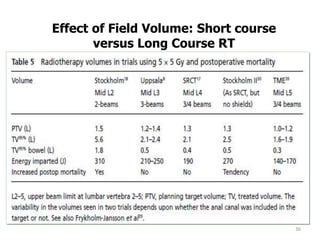
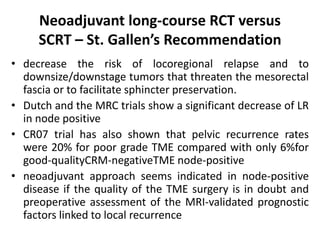
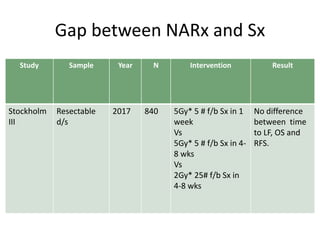
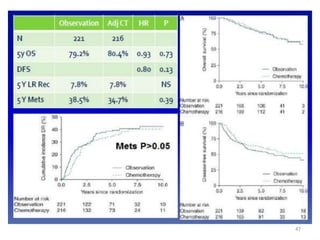
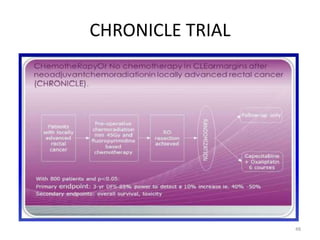
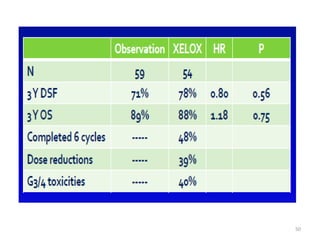
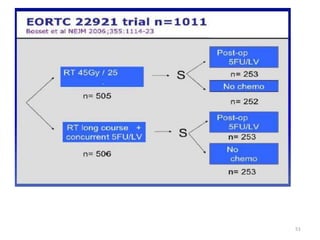
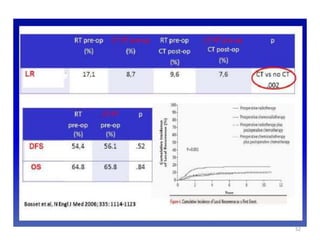
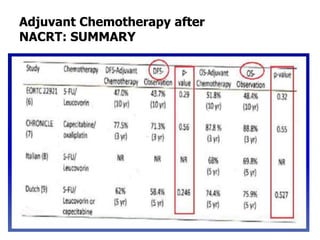
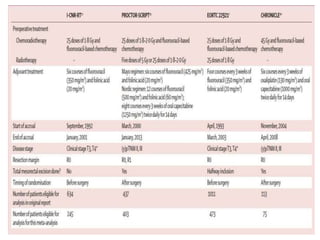
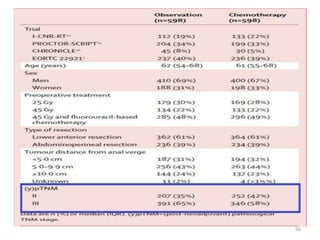
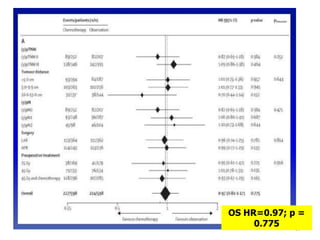
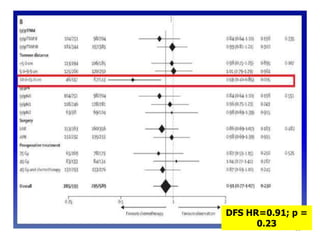
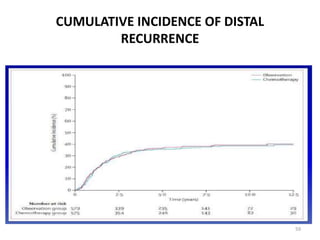
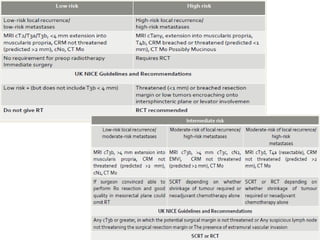
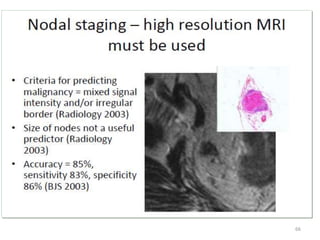
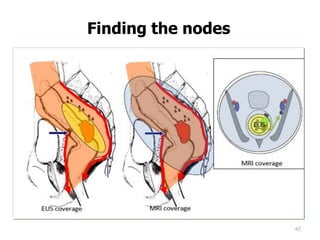
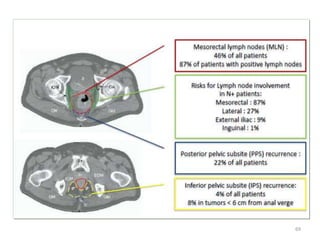
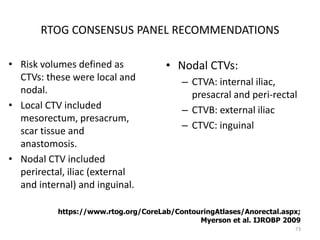
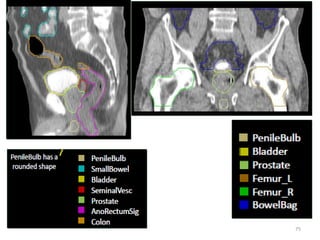
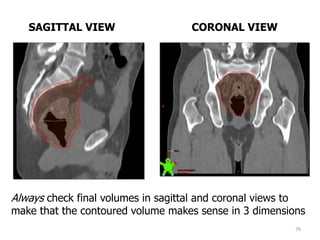
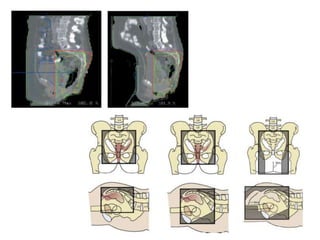
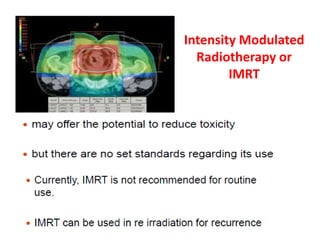
This document discusses updates in radiation therapy for colorectal cancers. It covers clinical features and prognostic markers for different locations of colorectal cancer. It discusses the goals and need for a multidisciplinary approach in treating rectal cancers. It compares pre-operative vs postoperative chemoradiation and short course vs long course radiation. It also discusses omitting adjuvant chemotherapy for some patients and contouring guidelines for radiotherapy planning.