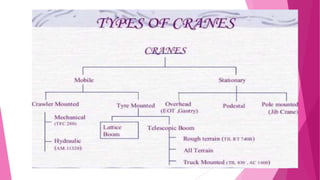
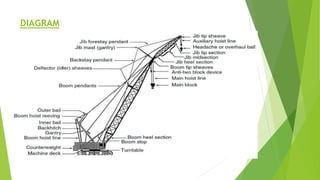
Crawler mounted cranes have tracks that allow them to operate on any ground surface. They consist of a rotating crane structure, hoist, boom, optional jib, and counterweights. Major components were described along with advantages like increased stability from tracks. Accidents can occur from exceeding weight limits, improper assembly/training, mechanical failures, or contacting power lines. Proper planning, inspections, and safety precautions are needed when using crawler cranes for lifting operations in construction, demolition, and cargo loading. Examples of crawler crane applications and images from construction sites were also provided.