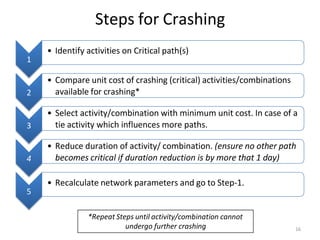
This document discusses crashing vs fast-tracking construction projects and the relationship between activity duration and cost. It provides an example of crashing the duration of a sample ABCD project:
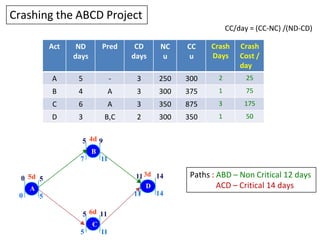
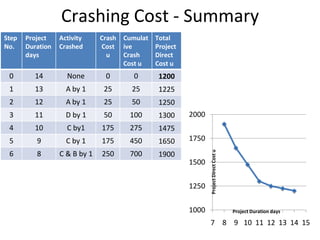
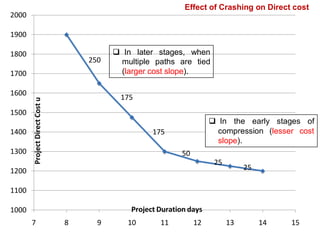
1) The initial critical path is ACD at 14 days. Crashing A by 1 day reduces duration to 13 days at a cost of 25 units.
2) Further crashing A and crashing D reduces the duration to 12 days and 11 days respectively.
3) Crashing C reduces the critical path to 10 days at a cost of 175 units.
4) Continued crashing of C, B, and A reaches the minimum duration of 8 days at a total crashing cost of 700 units.