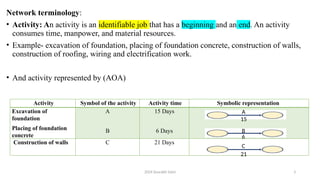
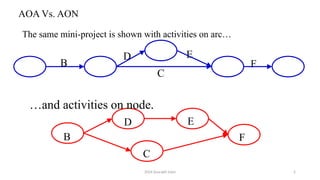
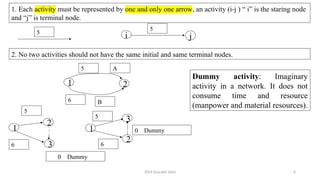
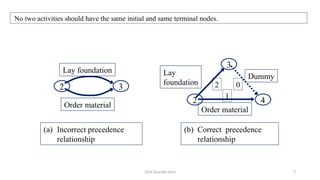
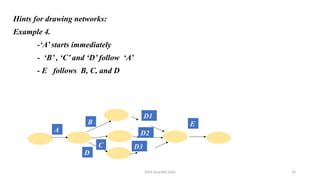
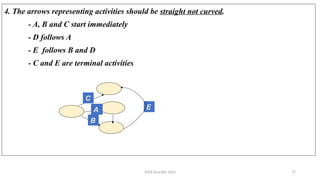
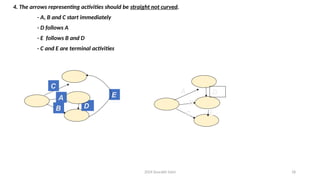
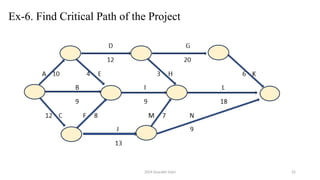
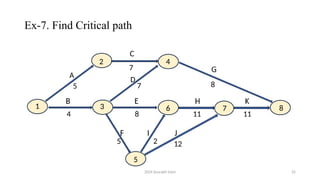
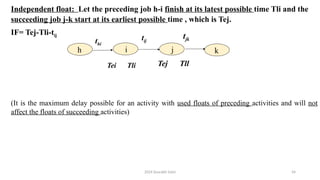
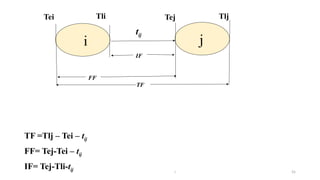
The document outlines project management concepts through network diagrams, focusing on Activity on Arrow (AOA) and Activity on Node (AON) representations. It explains critical path analysis, forward and backward pass computations to determine earliest start and latest finish times, and identifies slack time associated with events in a project. The critical path, which determines project duration, is derived from paths with zero slack, emphasizing the importance of precedence relationships and resource management in project scheduling.


























![2024 Sourabh Saini 58
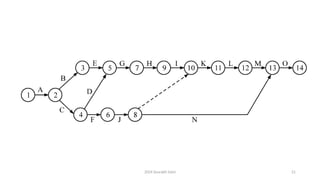
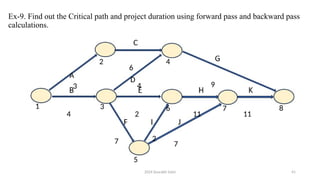
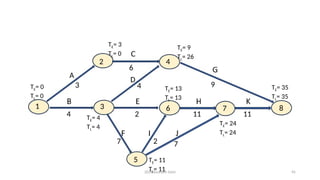
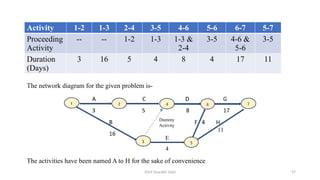
• The activities have been named A to H for the sake of convenience
• [Activity 1-2 is named 'A', activity 1-3 is named 'B' etc.]
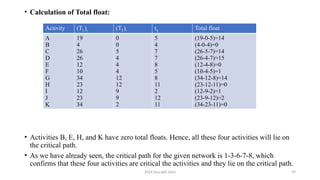
Forward pass Computations Backward pass Computations
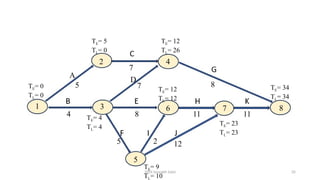
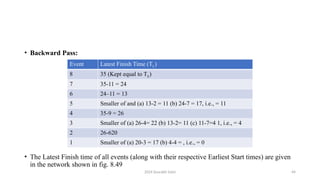
Event TE Event TL
1 0 7 41
2 0+3=3 6 41-17 = 24
3 0+16=16 5 Minimum of (a) 24-2 = 22 and (b) 41-
11 = 30, i.e., = 22
4 Maximum of (a) 3+5 = 8 and (b) 16+0 =
16, i.e., = 16
4 24-8 = 16
5 16+4=20 3 Minimum of (a) 16-0= 16 and (b) 22-2
= 18, l.e., = 16
6 Maximum of (a) 16 +8 = 24 and (b) 20 + 2
= 22 i.e., = 24
2 16-5 = 11
7 Maximum of (a) 24 + 17 = 41 (b) 20+11=
31., = 41
1 Minimum of (a) 11-3=8 (b) 1616 = 0,
i.e., = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkanalysis-250103074503-6a195fb7/85/Network-analysis-pptxbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb-58-320.jpg)
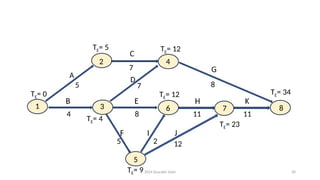
![2024 Sourabh Saini 59
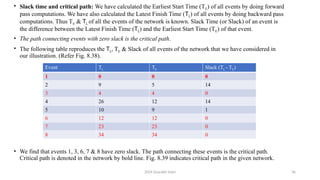
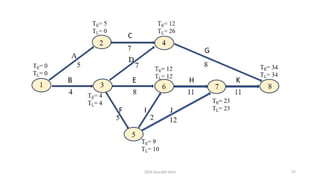
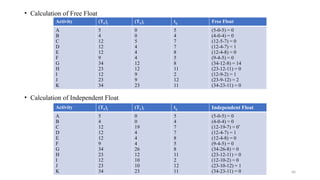
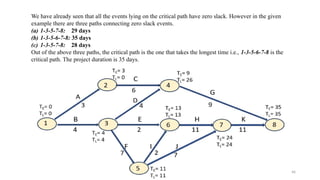
• Nodes 1, 3, 4, 6, 7 have zero slacks.
• There is only one critical path, which is B→ (Dummy) →D→ G.
• The project completion time is (16+0+8+17) = 41 days. [Observation: Critical path can also pass
through dummy activity.]
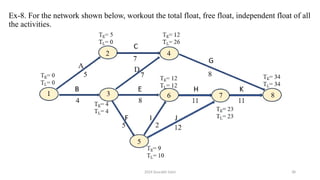
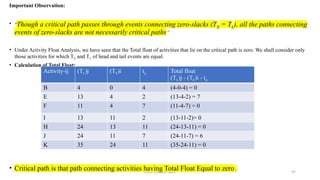
• Let us find out the total floats of all the activities lying on the critical path and check up if they are
all zero.
• As expected, the total floats of all the activities lying on the critical path is zero.
Activity-ij (TL)j (TE)i tij Total float: (TL)j-(TE)i -tij
B
Dummy
D
G
16
16
24
41
0
16
16
24
16
0
8
17
16-0-16=0
16-16-0=0
24-16-8=0
41-24-17=0
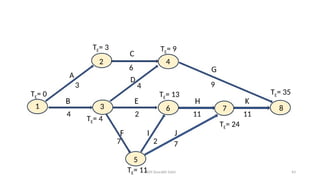
TE= 0
TL= 0
TE= 24
TL= 24
TE= 16
TL= 16
TE= 3
TL= 11
TE= 20
TL= 20
TE= 16
TL= 16
TE=41
TL= 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkanalysis-250103074503-6a195fb7/85/Network-analysis-pptxbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb-59-320.jpg)


