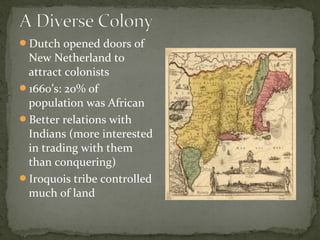
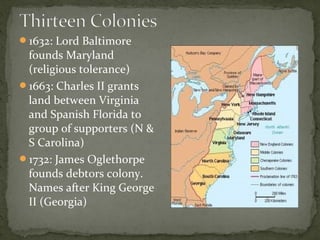
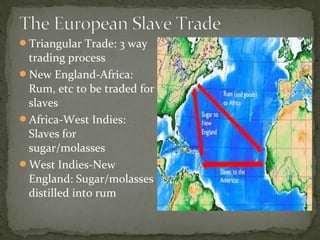
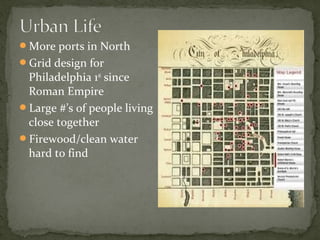
The document provides an overview of the early history of English colonization in North America, including:
1) It discusses the founding of Jamestown in 1607 by the Virginia Company and the early struggles the colony faced, including a "starving time" period.
2) It then covers the establishment of other English colonies along the east coast, including the Puritan founding of Massachusetts Bay Colony for religious freedom in the 1630s.
3) The document also summarizes the growth of the slave trade and rise of the plantation economy in the southern colonies during the 1600s, which became centered around cash crops like tobacco.