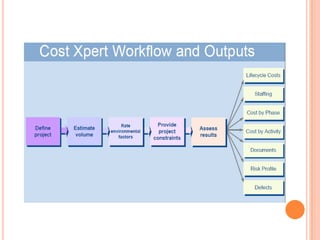
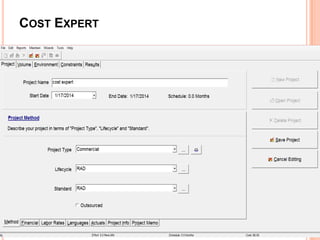
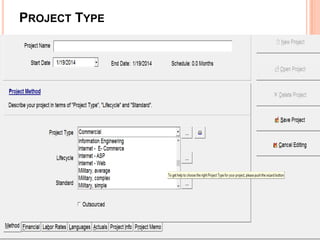
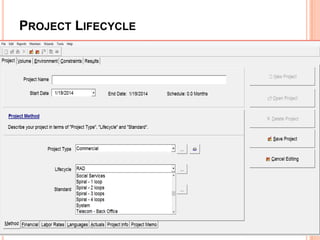
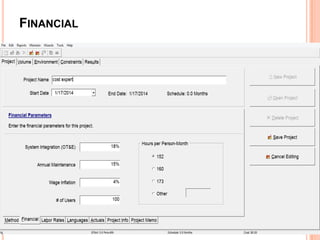
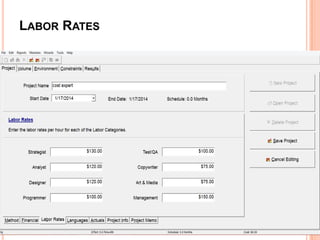
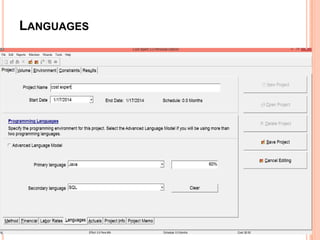
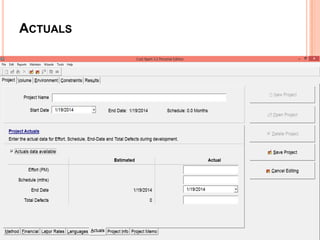
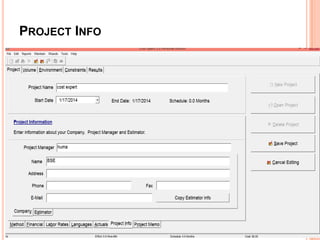
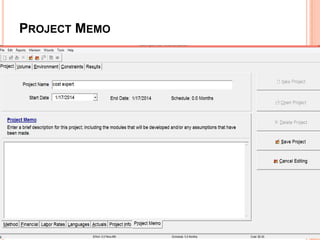
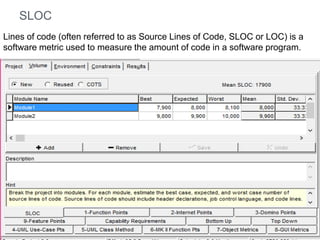
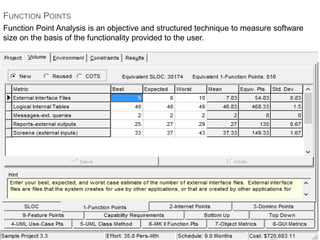
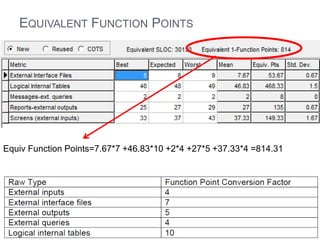
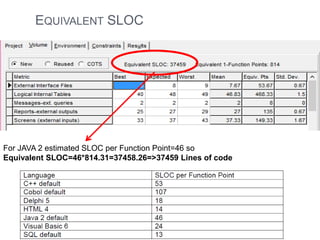
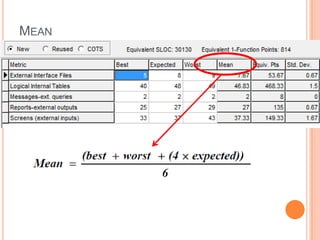
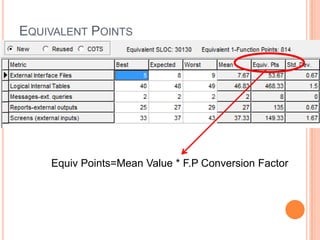
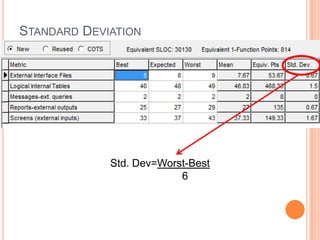
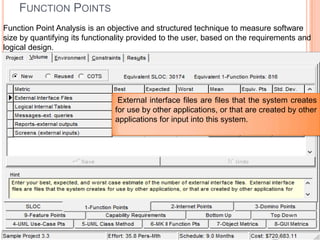
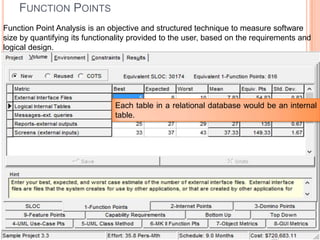
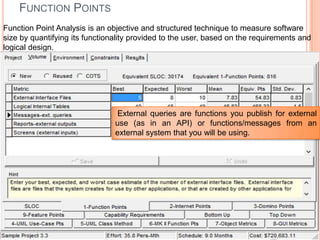
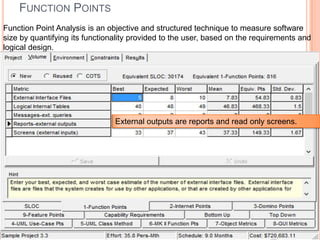
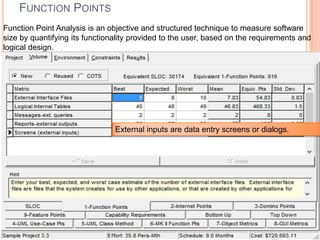
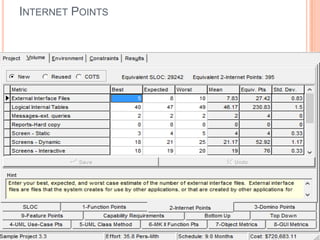
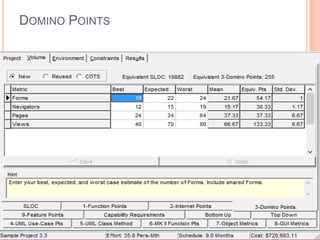
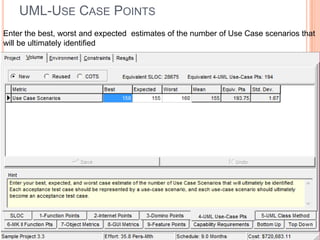
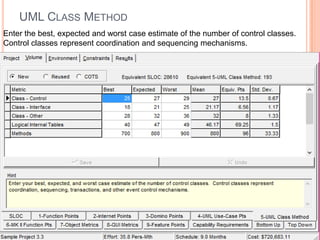
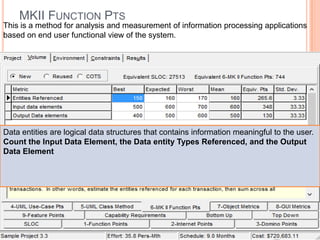
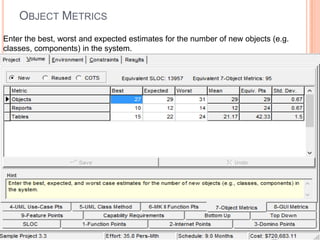
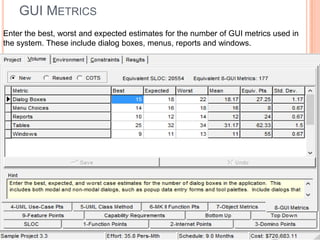
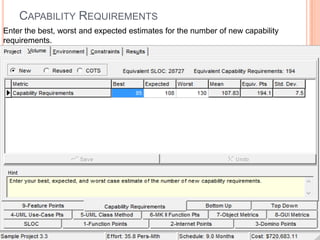
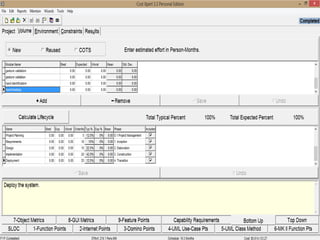
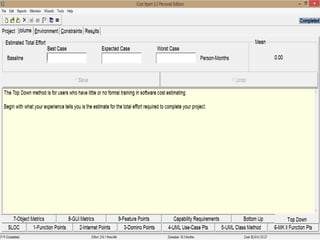
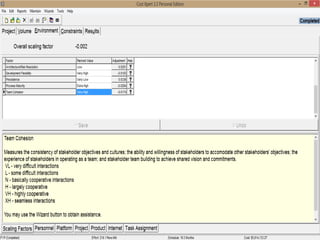
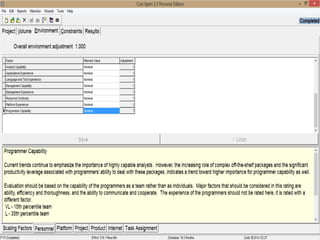
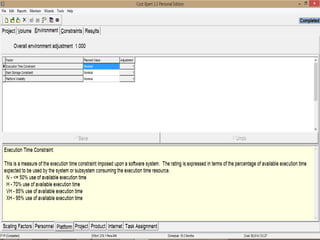
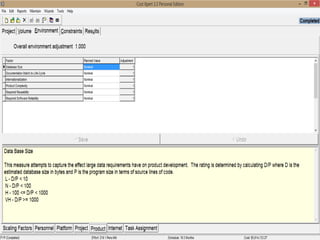
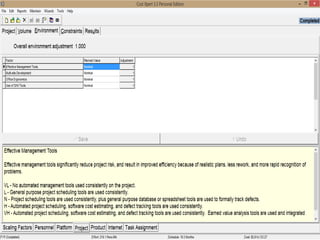
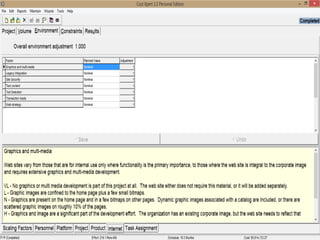
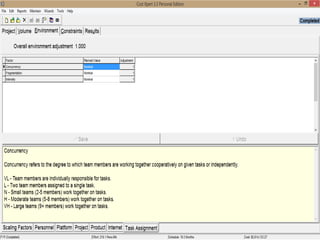
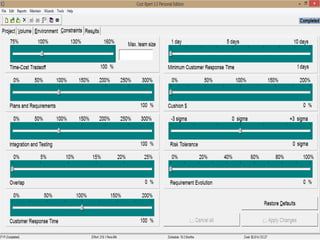
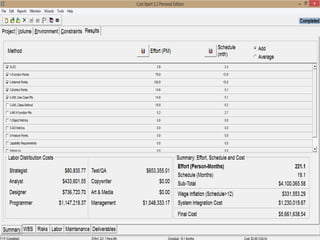
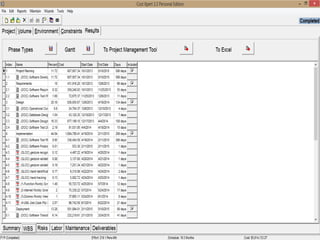
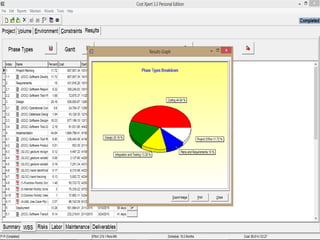
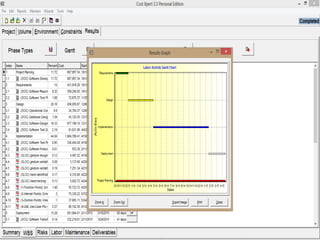
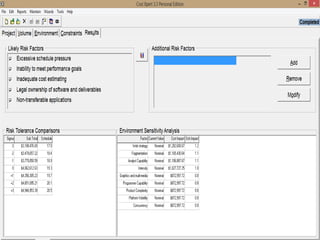
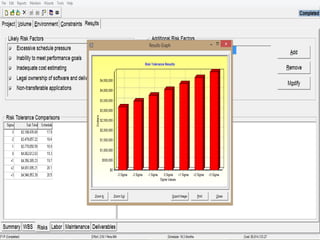
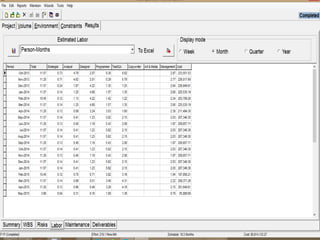
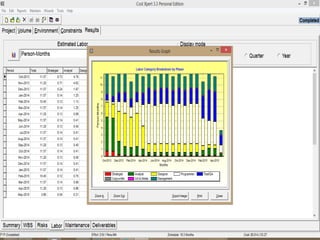
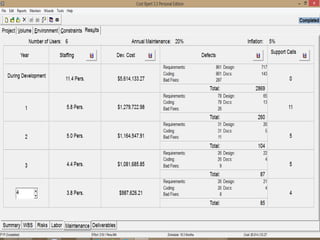
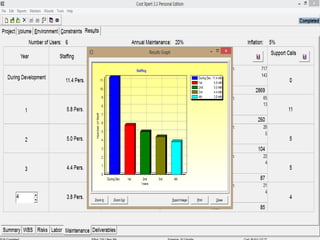
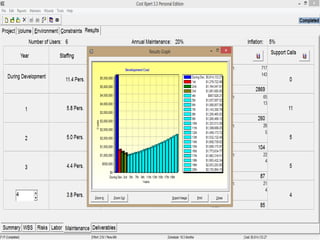
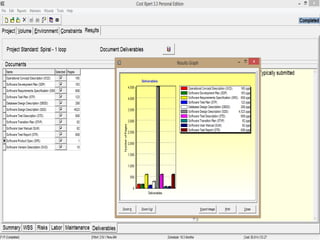
The document discusses a software project management group presenting on cost estimation. The group includes Ayesha Saeed, Huma Shabir, Amna Rehman, Iqra Qasim, and Madeha Arif. Ayesha Saeed introduces the topic of Cost Xpert, a software cost estimation tool. Various members then discuss features of Cost Xpert and methods for estimating project costs, effort, and schedules using metrics like source lines of code and function points. Iqra Qasim and Madeha Arif later discuss limitations of creating highly extensive estimates.