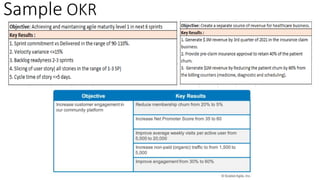
This document discusses OKR (Objectives and Key Results), a goal setting framework used by companies to define, align, and track measurable goals. It consists of an objective, which is significant, concrete, action-oriented, and inspirational, and key results which are specific, time-bound, aggressive yet realistic, and measurable. The document provides examples of OKRs, advantages like exceptional focus and alignment, and steps for adoption such as getting top management buy-in and running a pilot. Reasons for failure include using it only for KPIs rather than strategy or tying it to bonuses. OKRs differ from MBOs in being quarterly rather than annual, bottom-up rather than top-down, looking forward