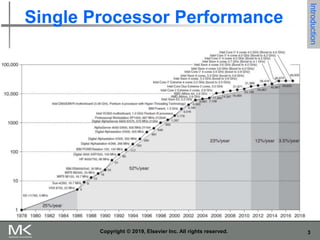
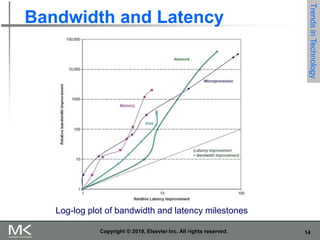
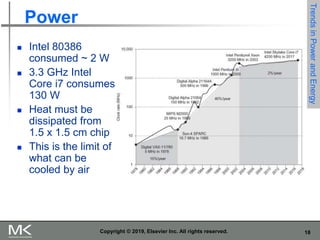
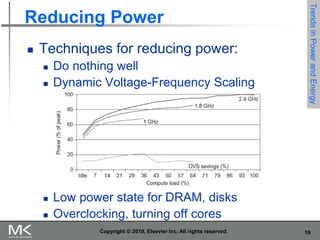
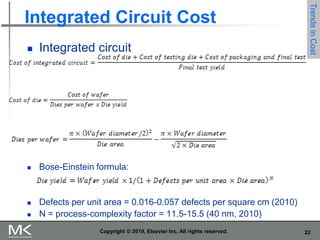
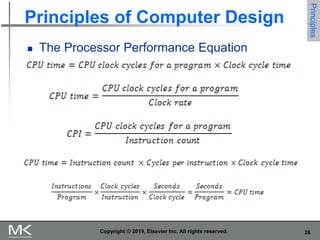
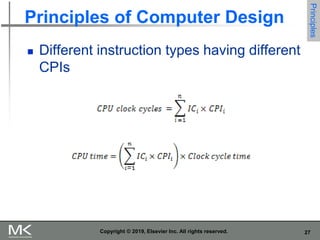
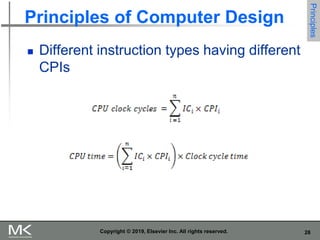
The document discusses key trends in computer technology and architecture over recent decades. It notes that improvements in semiconductor technology and computer architectures have enabled significant performance gains. However, single processor performance improvements ended around 2003. New approaches like data, thread, and request level parallelism are now needed. The document also covers trends in different classes of computers, parallelism techniques, Flynn's taxonomy of computer architectures, factors that define computer architecture like instruction sets, and important principles of computer design like exploiting parallelism and locality.