This document discusses various methods for evaluating the effectiveness of corrosion inhibitors, including wheel tests, bubble tests, static tests, and rotating electrode methods. Key evaluation steps include laboratory testing under simulated field conditions to screen inhibitors, evaluating compatibility factors like cost and environmental impact, and final field testing. Laboratory tests measure corrosion rates through weight loss or electrochemical techniques. Rotating electrode methods like the rotating cylinder electrode can model turbulent flow conditions and are well-suited for studying corrosion under pressure and temperature. The document also provides examples of corrosion inhibitor formulations and testing methods.




![Corrosion Page 7
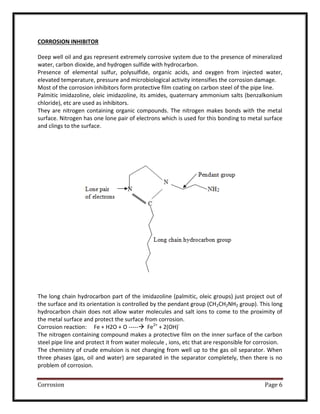
So a nitrogen compound which can make coating on the metal surface quickly and stable
against the attacks of gas, oil and water will be a three phase corrosion inhibitor.
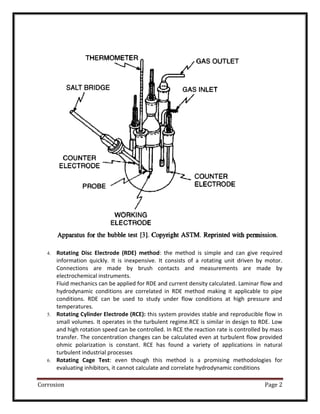
Pendant group play role in locking the hydrocarbon tail in position.
Reaction:
Diethylene triamine + oleic acid
NH (CH2CH2NH2)2 + CH3 (CH2)7CH=CH (CH2)7COOH
In the reaction two molecules of water are eliminated to form ringed structure.
Some Corrosion Inhibitor Formulations
All the below formulations are diluted by 45% with heavy aromatic solvent for supply and
performance evaluation
Formulations
S/N Ingredients
Formulations
1 2 3 4 5
1 Crude Tall Oil (fatty acid) 70.99 65.99 44.99 34.99 30.99
2 C18 Trimer Unsat Fatty acid 0.0 4.0 28.0 28.0 20.0
3 2[(2-Dimethyl amino) ethoxy] ethanol 27.0 10.0 6.0 5.0 3.0
4 Dimethyl amino ethanol 2.00 2.00 1.5 1.5 1.0
5 Antifoam 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01
6 Alcohol solvent (IPA/IBA) - 18.0 19.5 25.5 20.0
7 Aromatic solvent - - - - 17.0
8 Oxylate Polymer - - - - 2.0
9 Alkylated sulfonic acid - - - 5.0 6.0
Method of preparation
1. Weigh 1Lt RB flask and add C18 trimer acid
2. Add crude tall oil
3. Fit a stirring device and mix the content
4. Add alkanol amines drop wise ( reaction is exothermic)
5. Cool the flask to maintain around 25-35o
C
6. Continue stirring for another r 1 hr after addition of amines
7. When the temperature at ambient add diluting solvent (alcohol/aromatic solvent)
Note: in the case of F4 and F8,
8. Add sulfonic acid slowly (reaction is exothermic)
9. Maintain low temperature
10. Add diluting aromatic solvent followed by polymer.
Testing: comparative testing
Wheel box method-coupon testing
1. Weigh test coupons to 4 decimals
2. Add the required brine and oil mixture to test bottles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/412e968d-374d-47a3-a2ef-df85a306f2fb-150803113400-lva1-app6892/85/corrosion-introduction-7-320.jpg)


