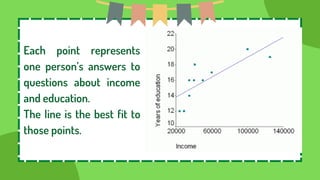
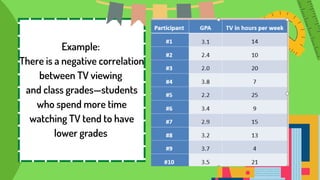
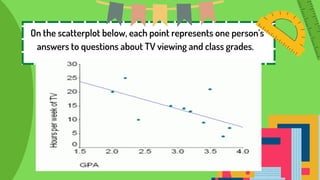
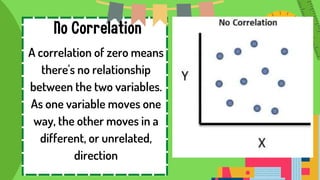
This document defines and provides examples of correlational research. It discusses the three types of correlation: positive correlation, where two variables increase or decrease together; negative correlation, where one variable increases as the other decreases; and zero correlation, where the variables are unrelated. Examples are given of positive correlations between income and education, and negative correlations between TV viewing and grades. Correlational research examines relationships between existing variables to better understand cause and effect relationships.