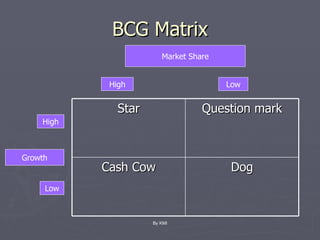
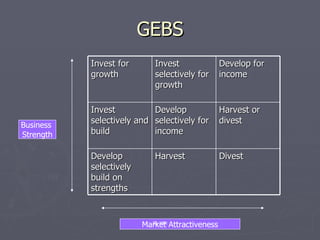
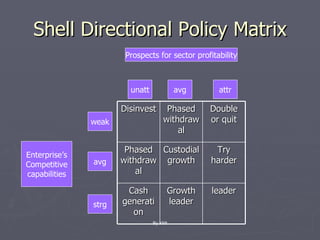
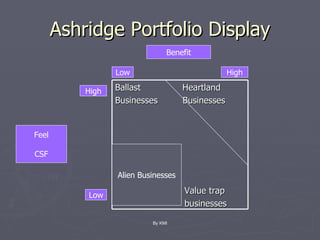
The document discusses various corporate strategies and diversification approaches that large businesses use. It describes how corporate parents oversee business units and can create or destroy value. It also summarizes different types of diversification like related, horizontal, vertical, and unrelated diversification as well as international diversification approaches. Finally, it outlines strategies for business units like cost leadership, differentiation, and discusses various growth methods.