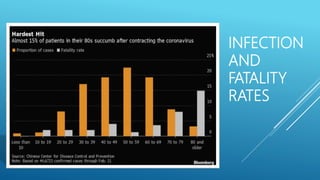
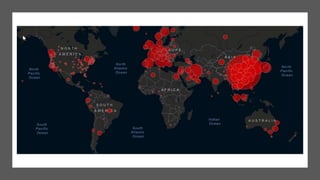
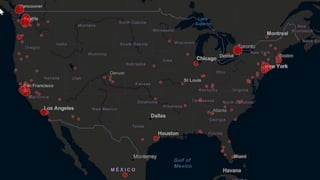
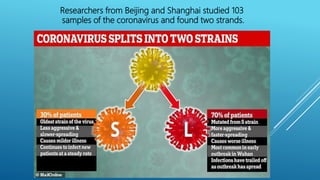
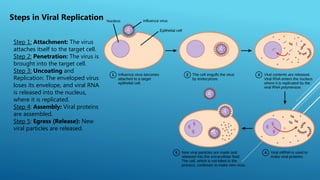
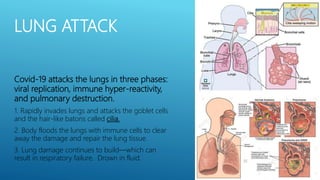
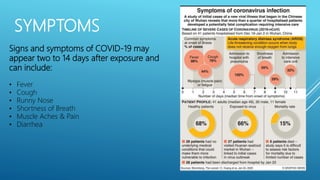
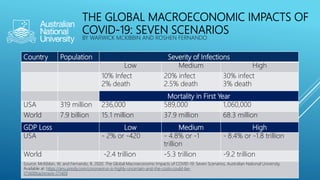
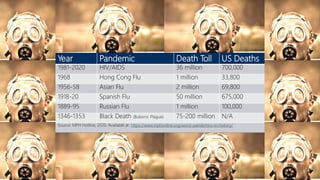
The document summarizes information about the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) including where it is present, symptoms, how it spreads, comparisons to the flu, economic impacts, and pandemic history. It notes that as of March 10, 2020 there were over 118,000 cases and over 4,000 deaths globally, with the virus present in over 100 countries. The virus can spread through droplets from coughs or sneezes within 6 feet, or by touching contaminated surfaces. Proper hand washing and avoiding contact with infected individuals are recommended.