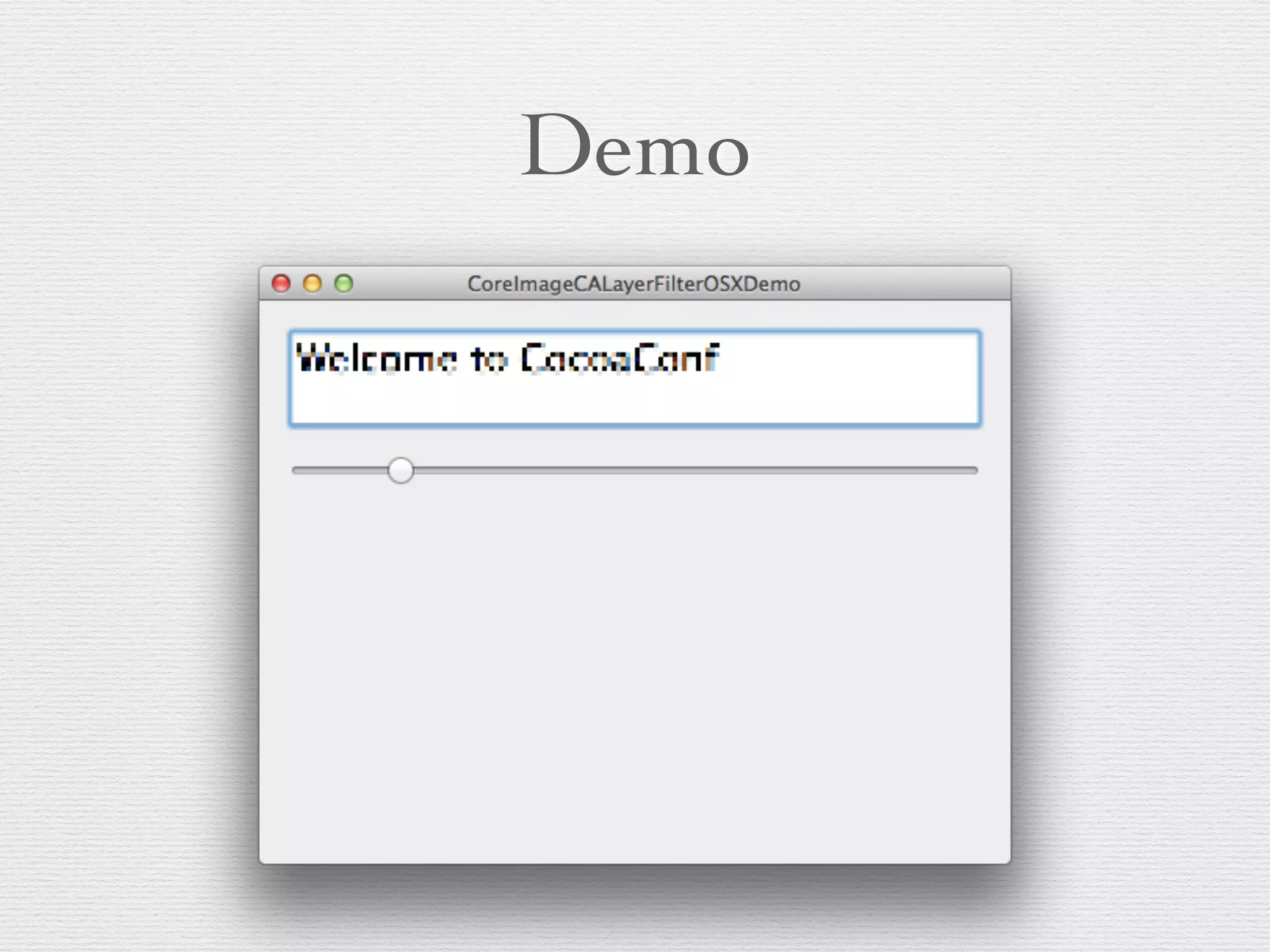
The document discusses Core Image, an Apple framework for image processing that allows near real-time effects for still and video images. It covers core concepts, workflows involving CIImage and CIFilter, various filter categories, and practical demos for applying filters and rendering images. Additionally, it includes advanced usage such as chaining filters and utilizing Core Image in applications using video and custom effects.








![CIContext
• Rendering destination for a CIImage (-
[drawImage:inRect:fromRect:])
• This is where you get pixels (also, this is the processor-
intenstive part)
• On iOS, must be created from an EAGLContext. On
Mac, can be created with CGContextRef
• Can also produce output as a CGImageRef, bitmap data,
or a CVPixelBuffer (iOS only)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-10-2048.jpg)
![CIFilter
• Performs an image processing operation
• Typically takes and produces a CIImage
• All parameters are provided via -[setValue:forKey:]
• Stringly-typed!
• Output is retrieved with -[valueForKey:]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-12-2048.jpg)
















![Other output options
• Use a CIContext
• -[drawImage:inRect:fromRect:] draws pixels to
the EAGLContext (iOS) or CGContextRef (OS
X) that the CIContext was created from.
• CIContext can also render to a void* bitmap
• On iOS, can create a CVPixelBufferRef, typically
used for writing to a file with AVAssetWriter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-32-2048.jpg)







![Working with Video
• AVFoundation AVCaptureVideoDataOutput and
AVAssetReader deliver CMSampleBuffers
• CMSampleBuffers have timing information and
CVImageBuffers/CVPixelBuffers
• +[CIImage imageWithCVPixelBuffer:]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-41-2048.jpg)


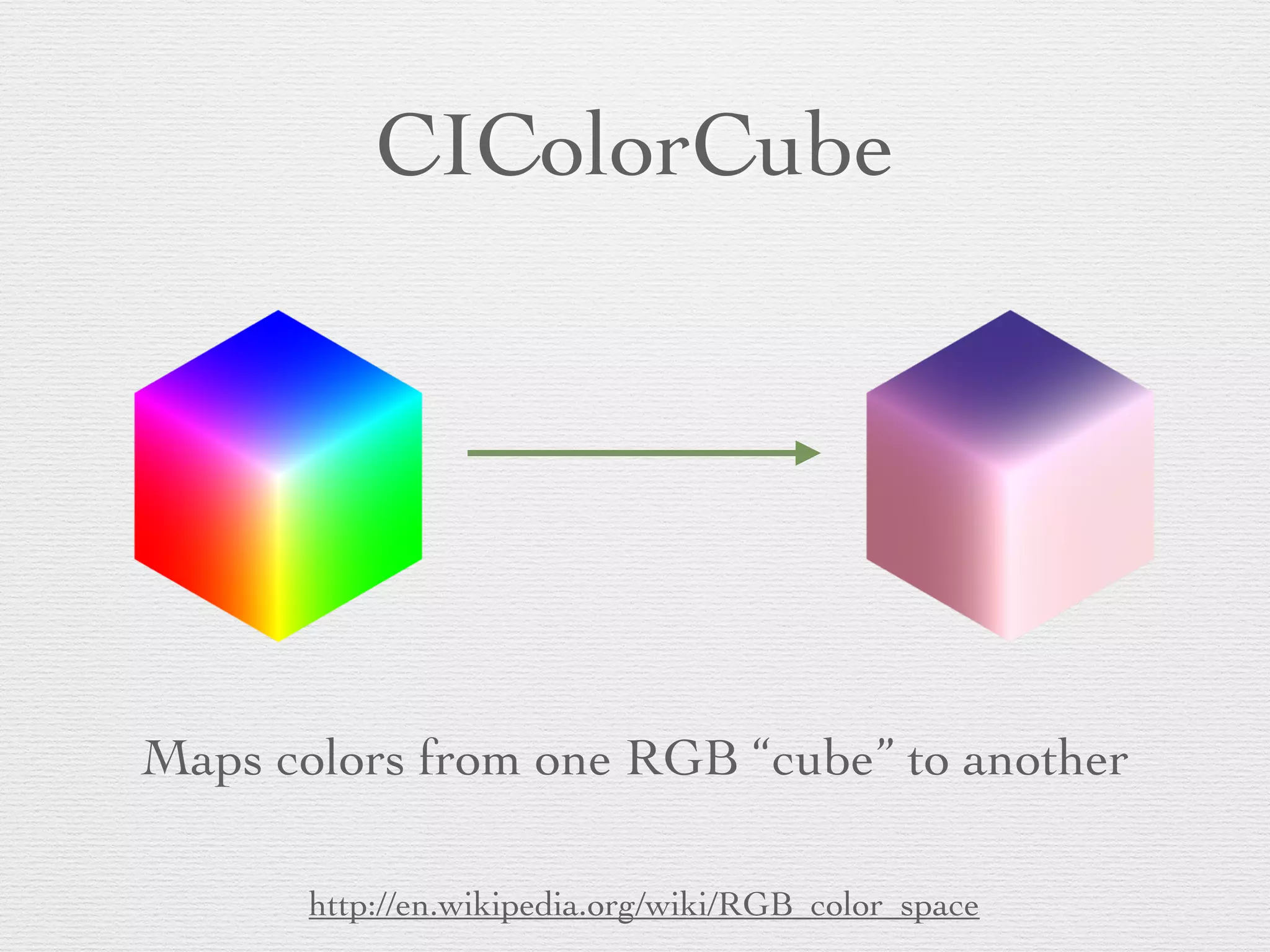


![CIColorCube Dataconst unsigned int size = 64;!
size_t cubeDataSize = size * size * size * sizeof (float) * 4;!
float *keyCubeData = (float *)malloc (cubeDataSize);!
//! float *alphaMatteCubeData = (float *)malloc (cubeDataSize);!
//! float rgb[3], hsv[3], *keyC = keyCubeData, *alphaC = alphaMatteCubeData;!
float rgb[3], hsv[3], *keyC = keyCubeData;!
// Populate cube with a simple gradient going from 0 to 1!
for (int z = 0; z < size; z++){!
! rgb[2] = ((double)z)/(size-1); // Blue value!
! for (int y = 0; y < size; y++){!
! ! rgb[1] = ((double)y)/(size-1); // Green value!
! ! for (int x = 0; x < size; x ++){!
! ! ! rgb[0] = ((double)x)/(size-1); // Red value!
!
! ! ! // Convert RGB to HSV!
! ! ! // You can find publicly available rgbToHSV functions on the Internet!
!
! ! ! RGBtoHSV(rgb[0], rgb[1], rgb[2],!
! ! ! ! ! &hsv[0], &hsv[1], &hsv[2]);!
!
! ! ! // RGBtoHSV uses 0 to 360 for hue, while UIColor (used above) uses 0 to 1.!
! ! ! hsv[0] /= 360.0;!
! ! ! !
! ! ! // Use the hue value to determine which to make transparent!
! ! ! // The minimum and maximum hue angle depends on!
! ! ! // the color you want to remove!
! ! ! !
! ! ! bool keyed = (hsv[0] > minHueAngle && hsv[0] < maxHueAngle) &&!
! ! ! (hsv[1] > minSaturation && hsv[1] < maxSaturation) &&!
! ! ! (hsv[2] > minBrightness && hsv[2] < maxBrightness);!
! ! ! !
! ! ! float alpha = keyed ? 0.0f : 1.0f;!
! ! ! !
! ! ! // re-calculate c pointer!
! ! ! keyC = (((z * size * size) + (y * size) + x) * sizeof(float)) + keyCubeData;!
! ! ! !
! ! ! // Calculate premultiplied alpha values for the cube!
! ! ! keyC[0] = rgb[0] * alpha;!
! ! ! keyC[1] = rgb[1] * alpha;!
! ! ! keyC[2] = rgb[2] * alpha;!
! ! ! keyC[3] = alpha;!
! ! ! ! ! ! ! !
! ! }!
! }!
}!
See “Chroma Key Filter Recipe” in Core Image Programming Guide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-47-2048.jpg)
![Create CIColorCube from
mapping data
// build the color cube filter and set its data to above!
self.colorCubeFilter = [CIFilter filterWithName:@"CIColorCube"];!
[self.colorCubeFilter setValue:[NSNumber numberWithInt:size]!
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! forKey:@"inputCubeDimension"];!
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithBytesNoCopy:keyCubeData!
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! length:cubeDataSize!
! !! ! ! ! ! freeWhenDone:YES];!
[self.colorCubeFilter setValue:data forKey:@"inputCubeData"];!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-48-2048.jpg)
![Create CISourceOverCompositing
// source over filter!
self.backgroundImage = [UIImage imageNamed:!
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! @"img_washington_small_02.jpg"]; !
self.backgroundCIImage = [CIImage imageWithCGImage:!
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! self.backgroundImage.CGImage];!
self.sourceOverFilter = [CIFilter filterWithName:!
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! @"CISourceOverCompositing"];!
[self.sourceOverFilter setValue:self.backgroundCIImage !
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! forKeyPath:@"inputBackgroundImage"];!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-49-2048.jpg)
![Apply Filters in Capture Callback
CIImage *bufferCIImage = [CIImage imageWithCVPixelBuffer:cvBuffer];!
!
[self.colorCubeFilter setValue:bufferCIImage !
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! forKey:kCIInputImageKey];!
CIImage *keyedCameraImage = [self.colorCubeFilter valueForKey:!
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! kCIOutputImageKey];!
!
[self.sourceOverFilter setValue:keyedCameraImage !
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! forKeyPath:kCIInputImageKey];!
!
CIImage *compositedImage = [self.sourceOverFilter valueForKeyPath:!
! !! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! kCIOutputImageKey];
Then draw compositedImage to CIContext as before](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-50-2048.jpg)


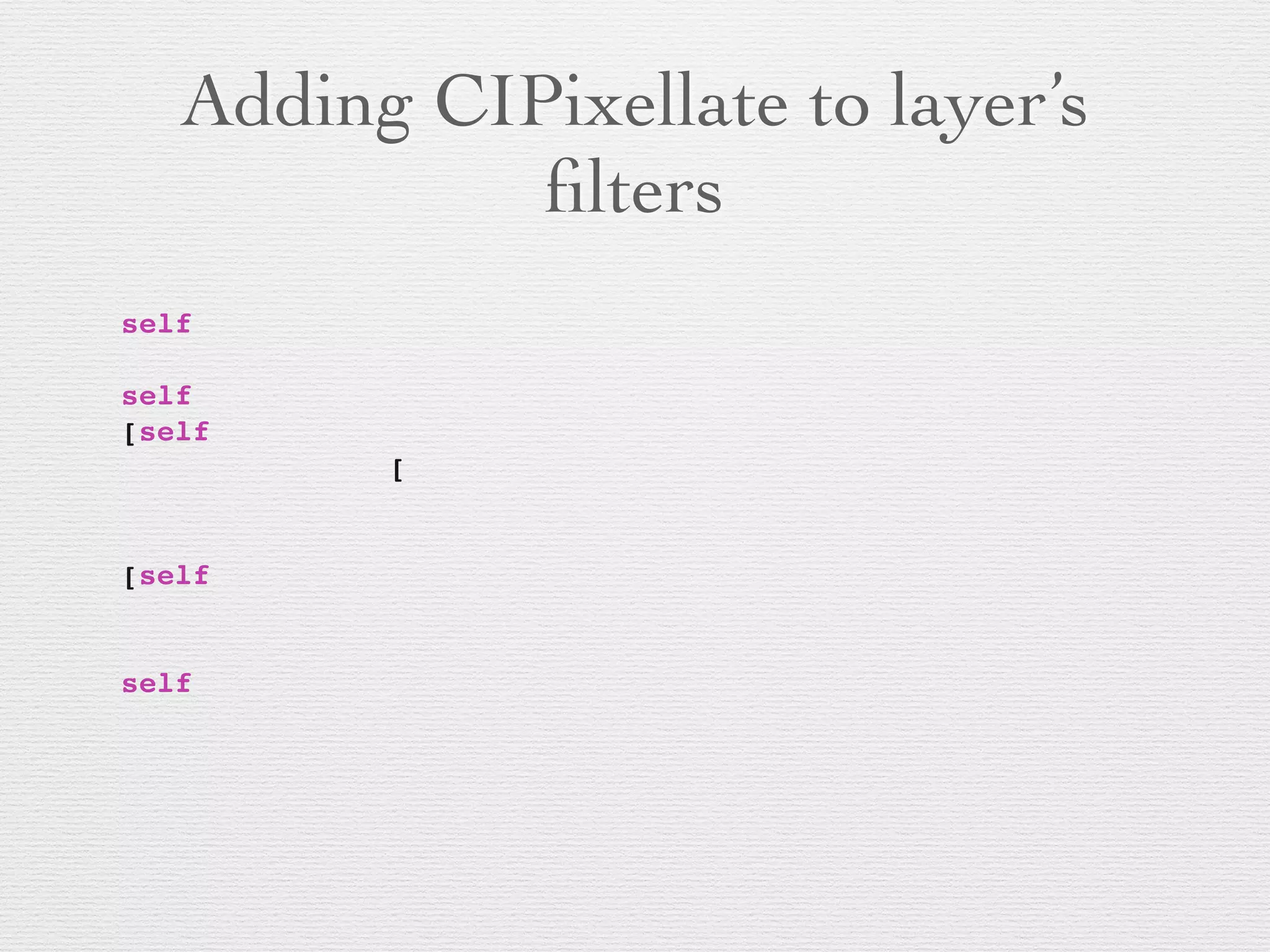
![CALayer Filters on OS X
• Views must be layer-backed (obviously)
• Must also call -[NSView
setLayerUsesCoreImageFilters:] on 10.9+
• CALayer has properties: filters, compositingFilter,
backgroundFilters, minificationFilter,
magnificationFilter
• These exist on iOS, but do nothing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/core-image-columbus-14-140817194610-phpapp02/75/Core-Image-The-Most-Fun-API-You-re-Not-Using-CocoaConf-Columbus-2014-53-2048.jpg)