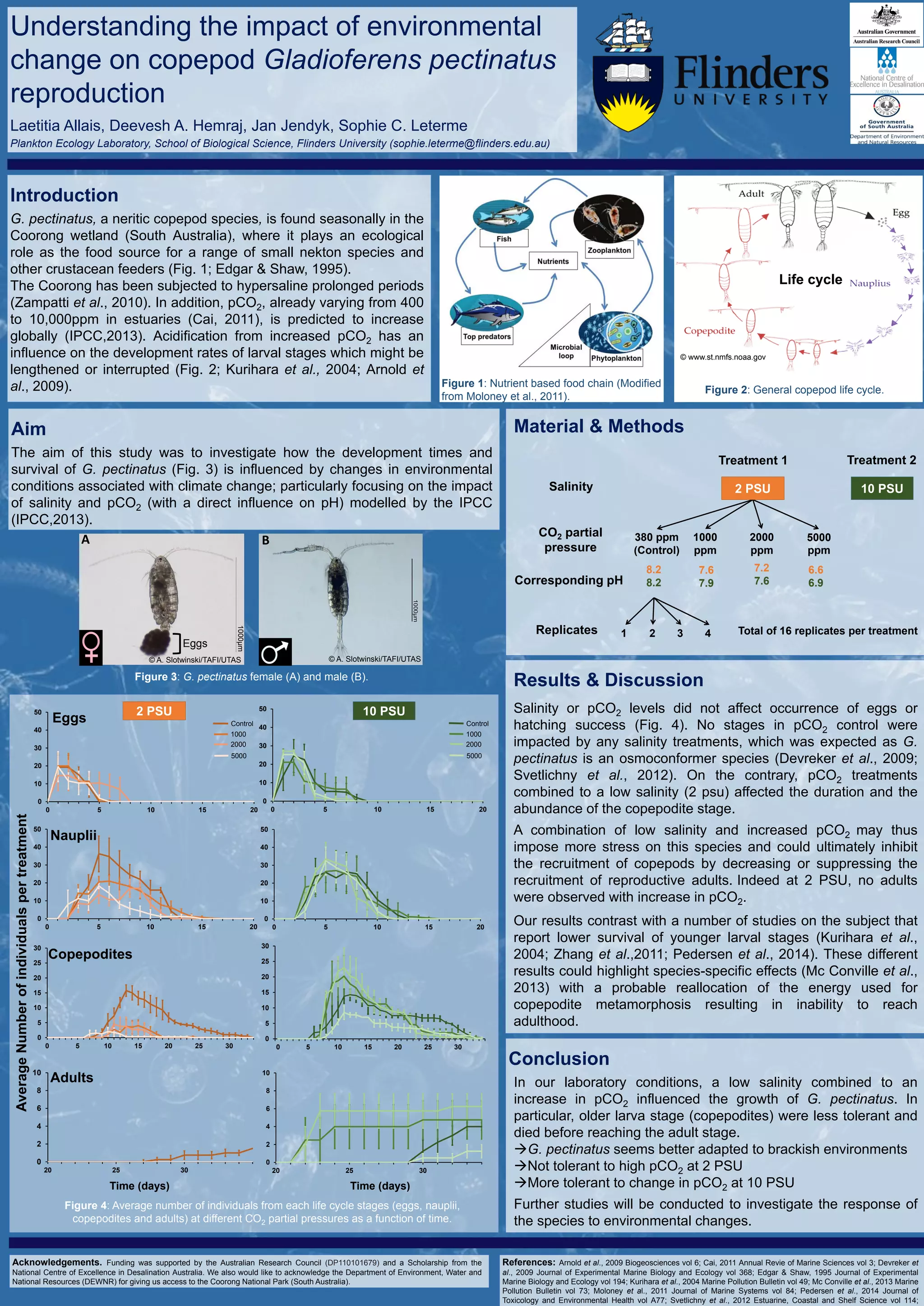
This study investigated the impact of low salinity and increased carbon dioxide (CO2) levels on the reproduction of the copepod Gladioferens pectinatus. The researchers found that a combination of low salinity (2 psu) and high CO2 (2000 and 5000 ppm) negatively affected the copepodite stage, preventing them from reaching adulthood. However, eggs and nauplii were not impacted. The species seemed more tolerant of changes in salinity and CO2 at higher salinity (10 psu). The results suggest the species has difficulty adapting to multiple environmental stressors.