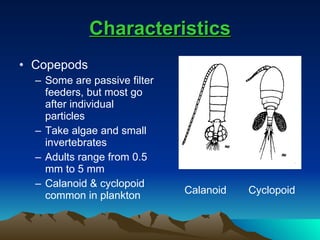
Copepods are microscopic crustaceans that are an important link in the food chain. They undergo multiple molting stages from nauplius larvae to adult, and reproduction is sexual. Common types include calanoid and cyclopoid copepods, which are found globally in aquatic environments. Copepods feed on algae and small invertebrates and are themselves an important food source for many marine organisms. Their distribution and pigmentation are affected by environmental factors like water temperature.