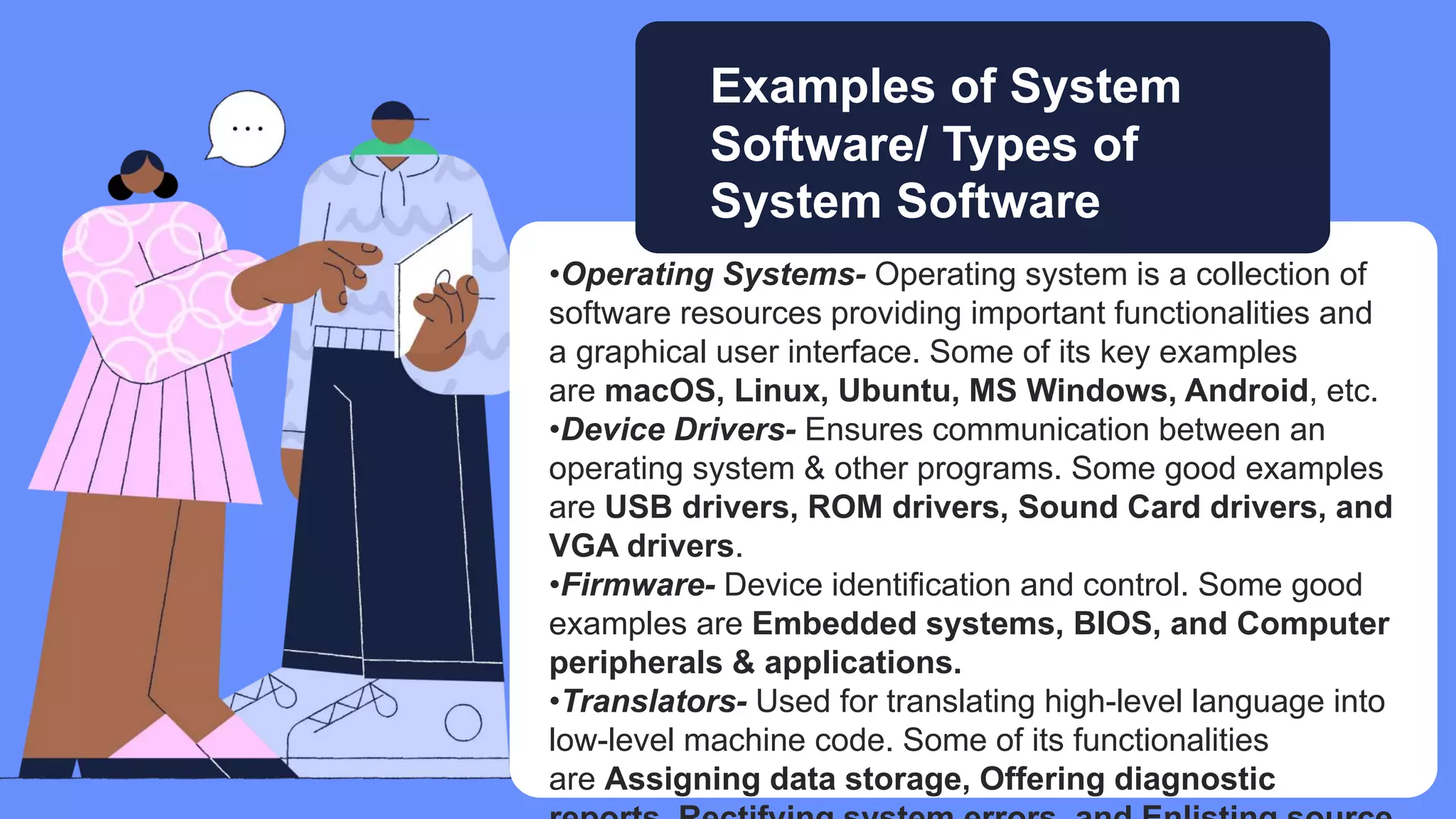
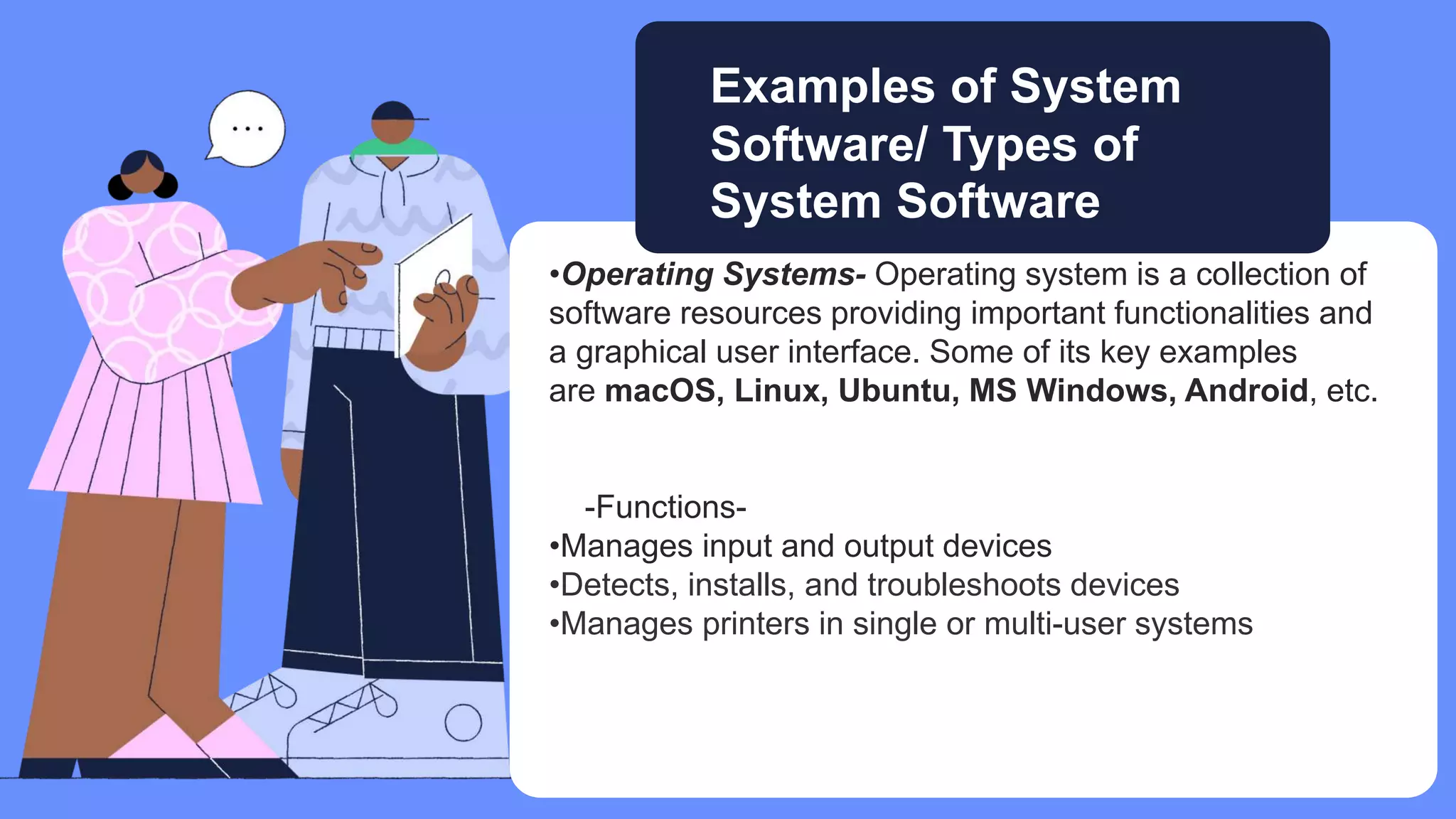
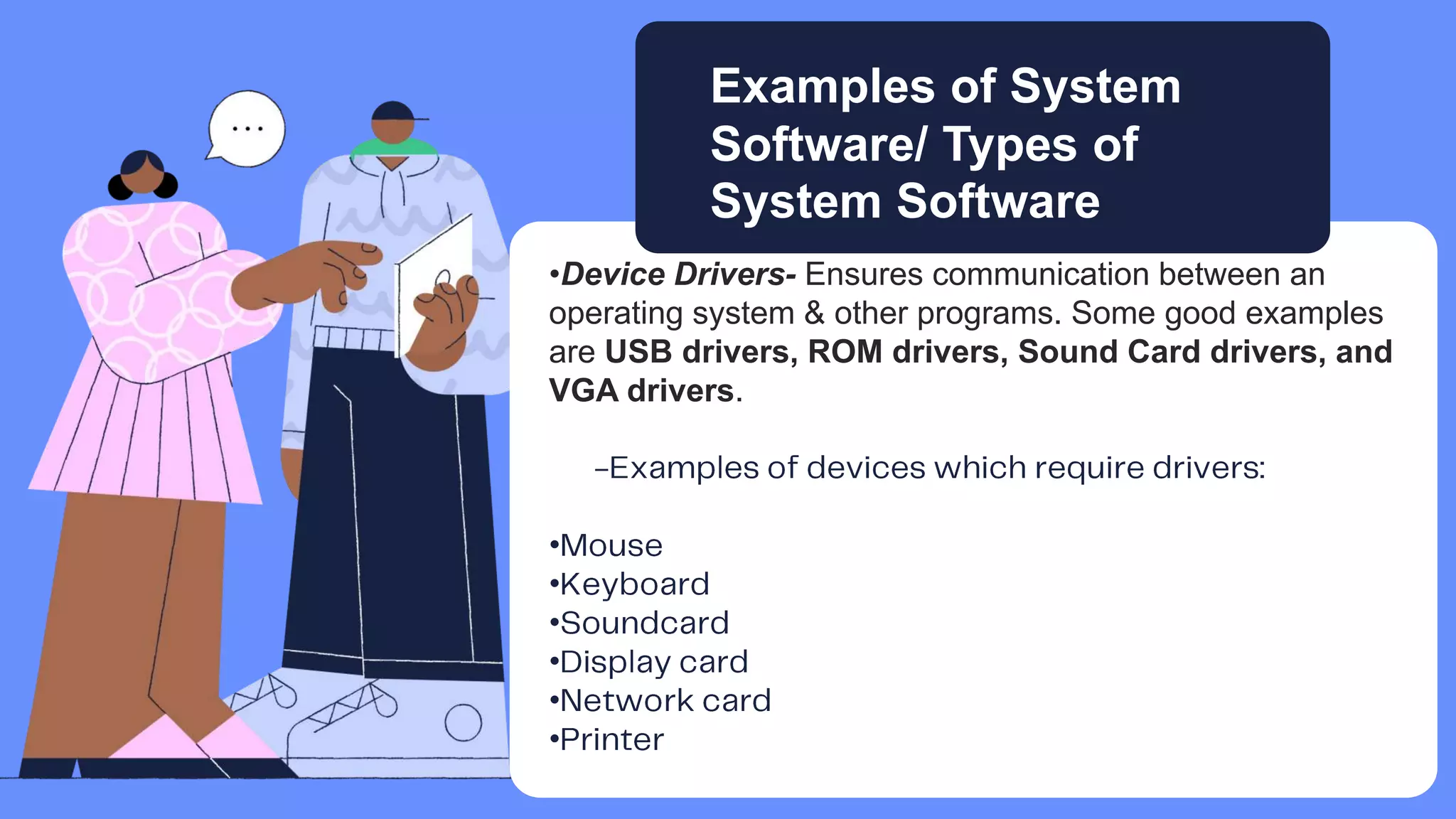
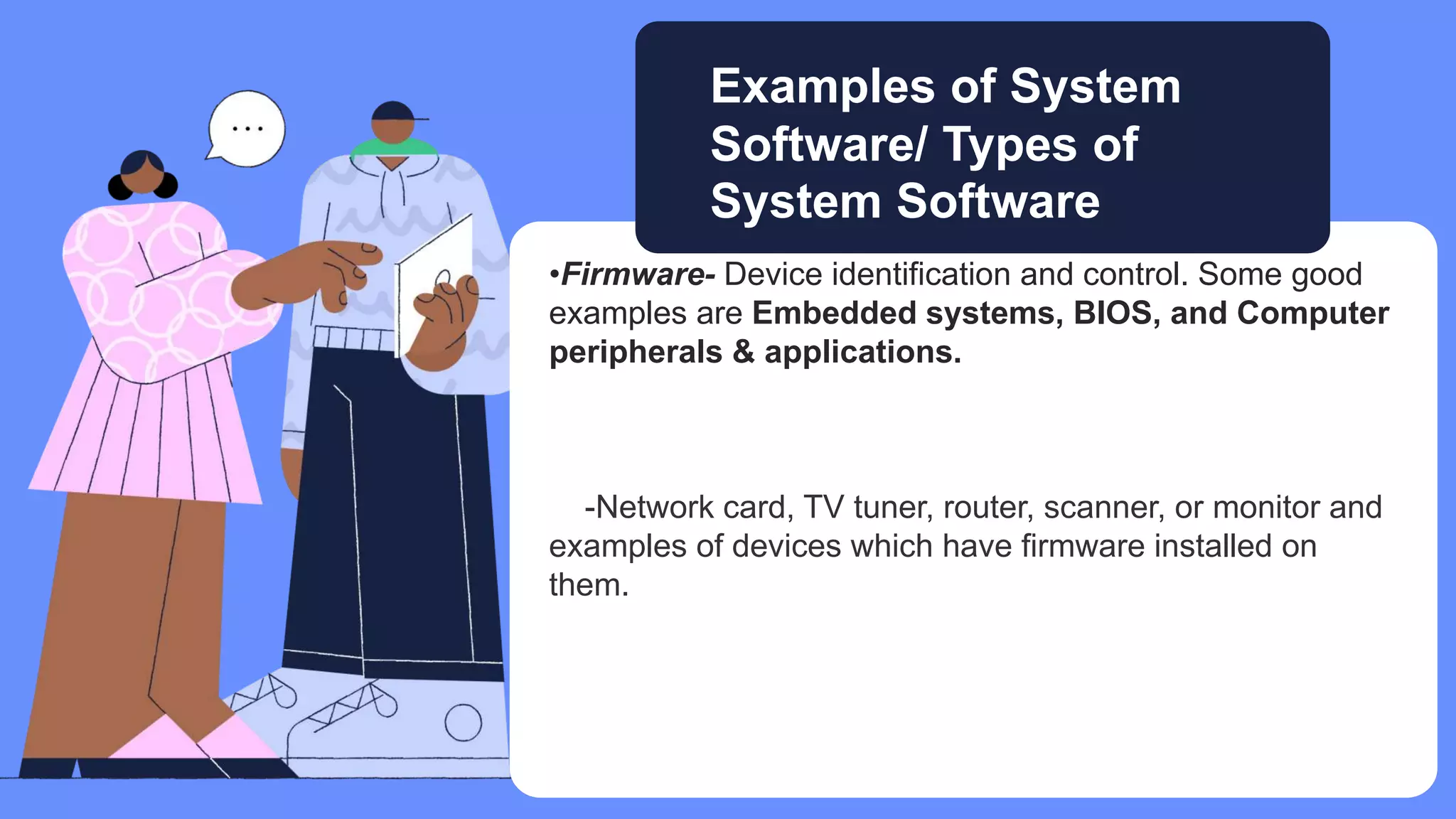
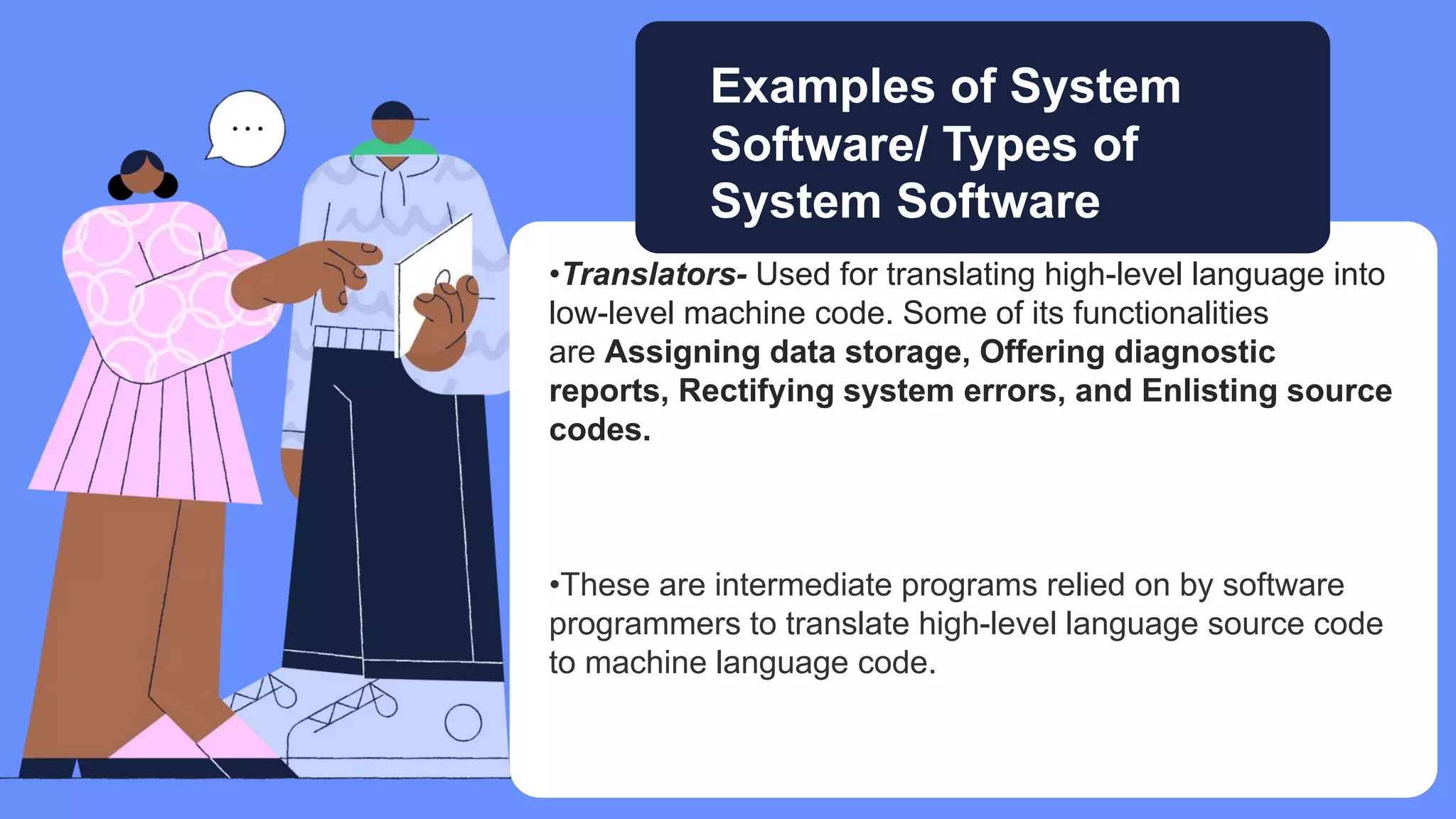
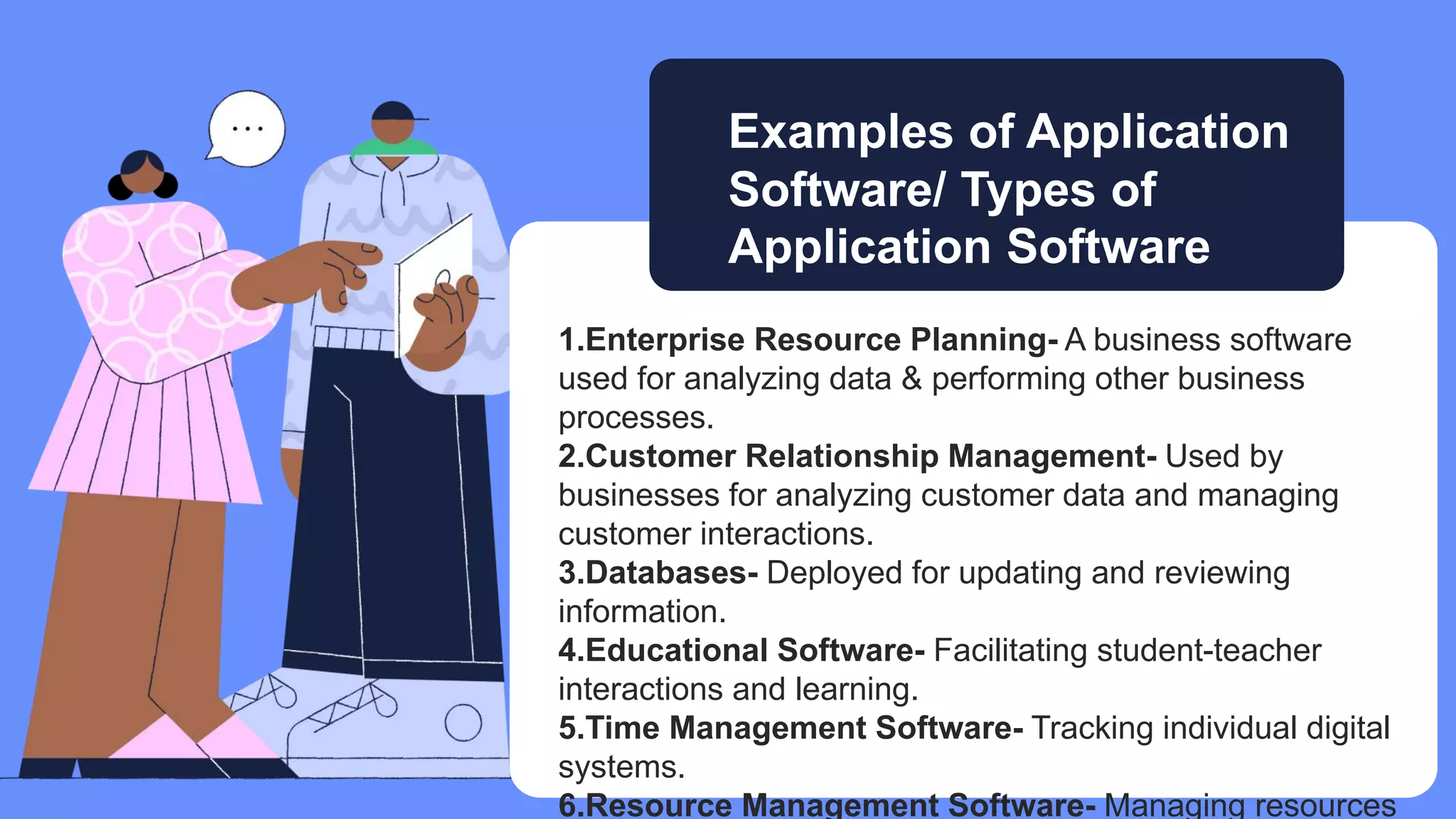
Five elements are needed for cooperative learning: a common goal, interdependence, interaction, individual accountability, and social skills. Cooperative learning encourages active learning and motivation, increases academic performance, promotes literacy and language skills, and improves teacher effectiveness. Studies show that students in computer groups interact and help each other, contradicting fears that computers isolate students. Cooperative learning can be implemented online or in classrooms, synchronously or asynchronously, by assigning mixed-ability teams, establishing interdependence, teaching social skills, ensuring accountability, and helping groups process information.