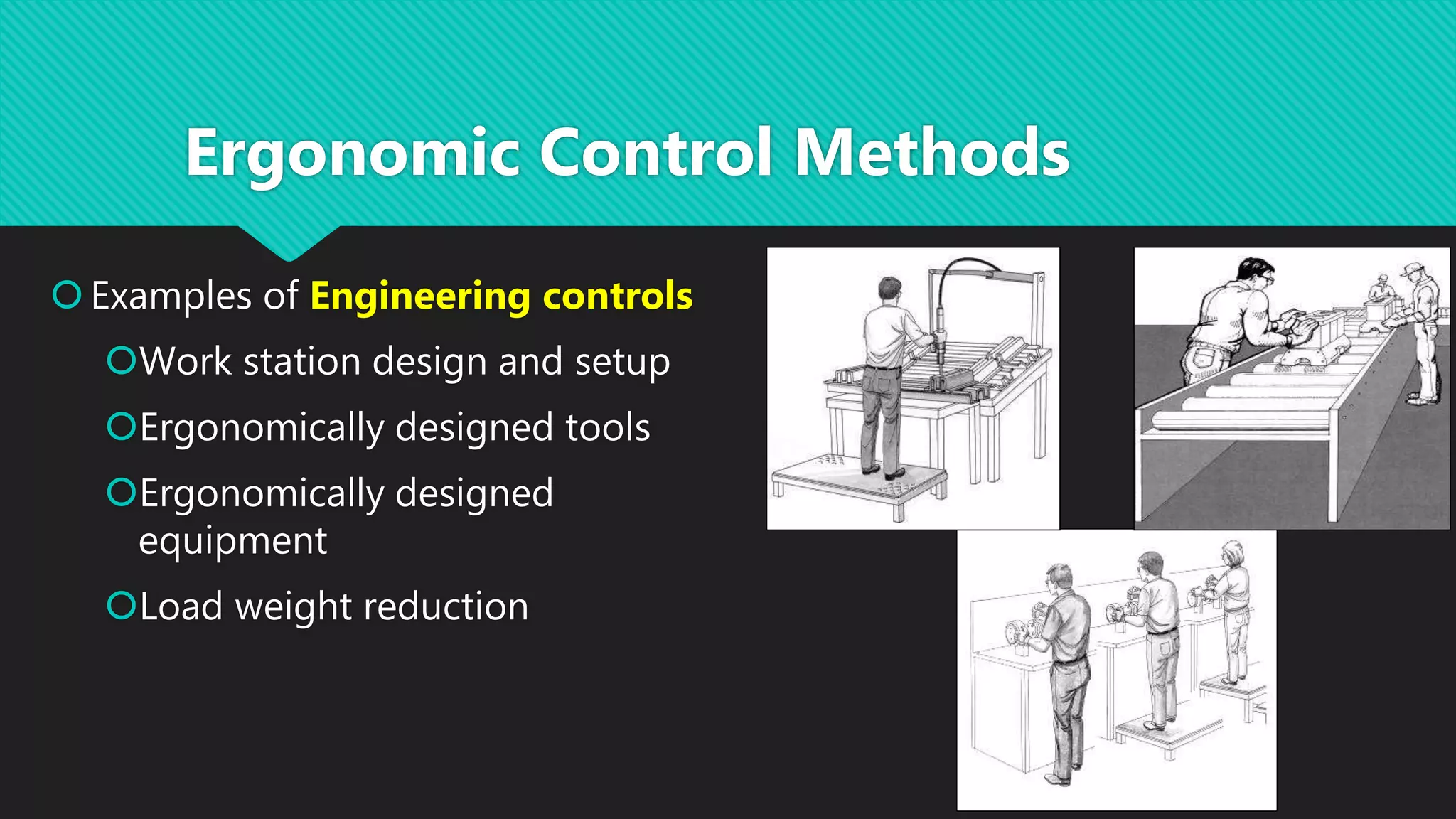
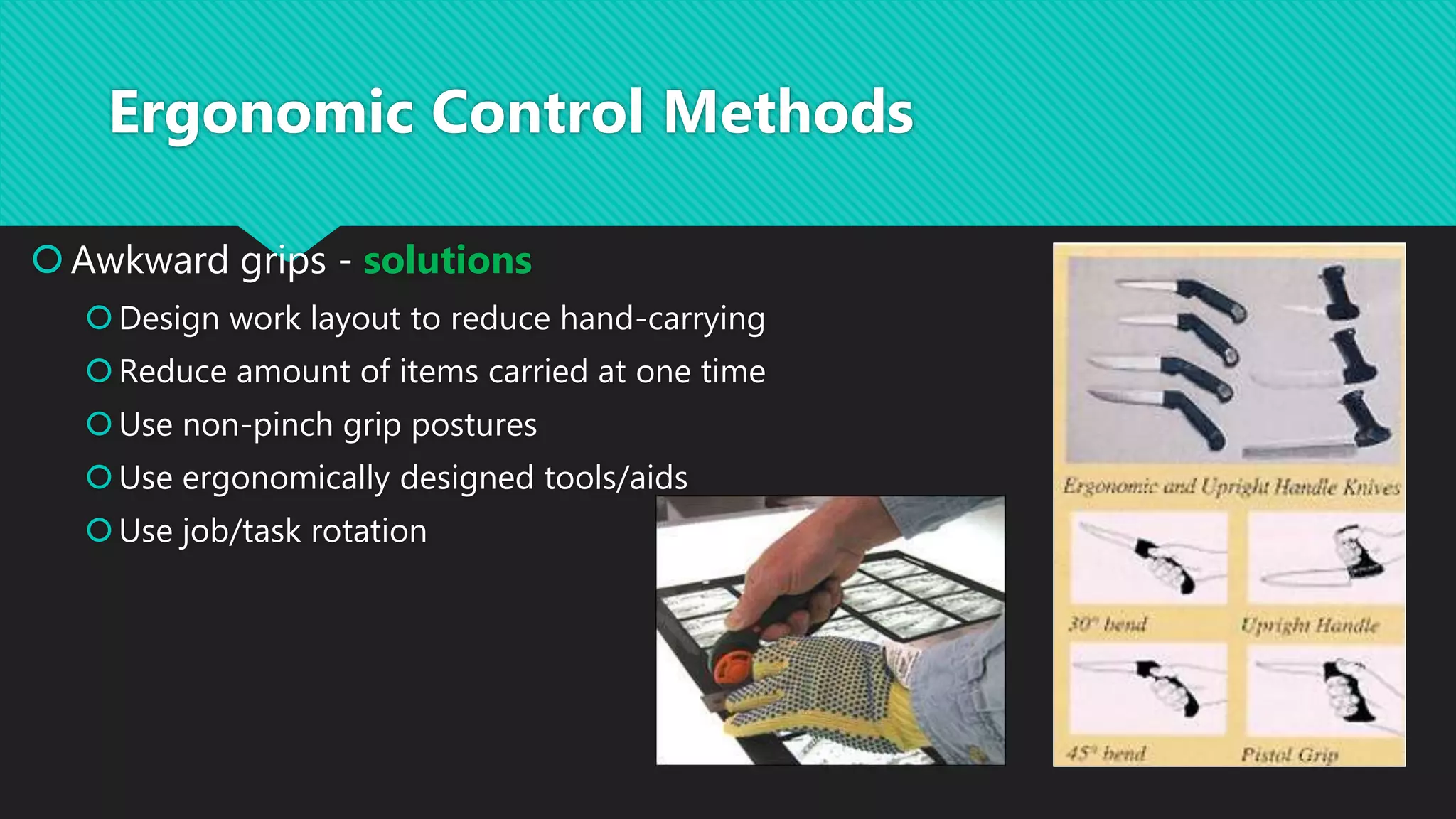
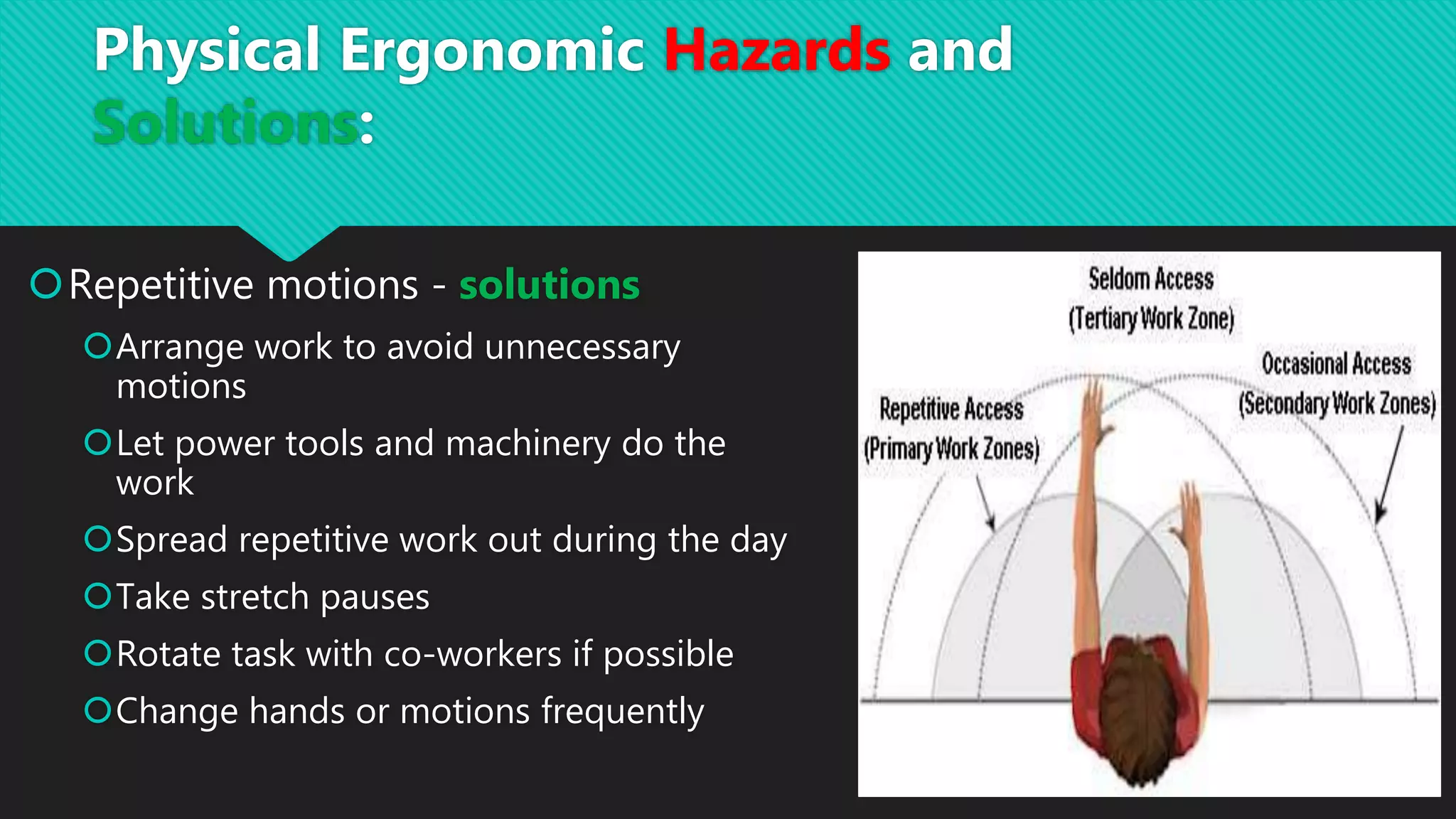
This document discusses methods for controlling musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) hazards, including engineering controls, administrative controls, personal protective equipment, and ergonomic design of tasks, workplaces, and tools. It provides examples of controls such as redesigning tools to enable neutral postures, job rotation systems, padding surfaces, and vibration-reducing gloves. Hazards discussed include repetitive motions, awkward postures, heavy lifting, and vibration. Corresponding solutions focus on workstation design, automation, task variation, and proper lifting techniques.