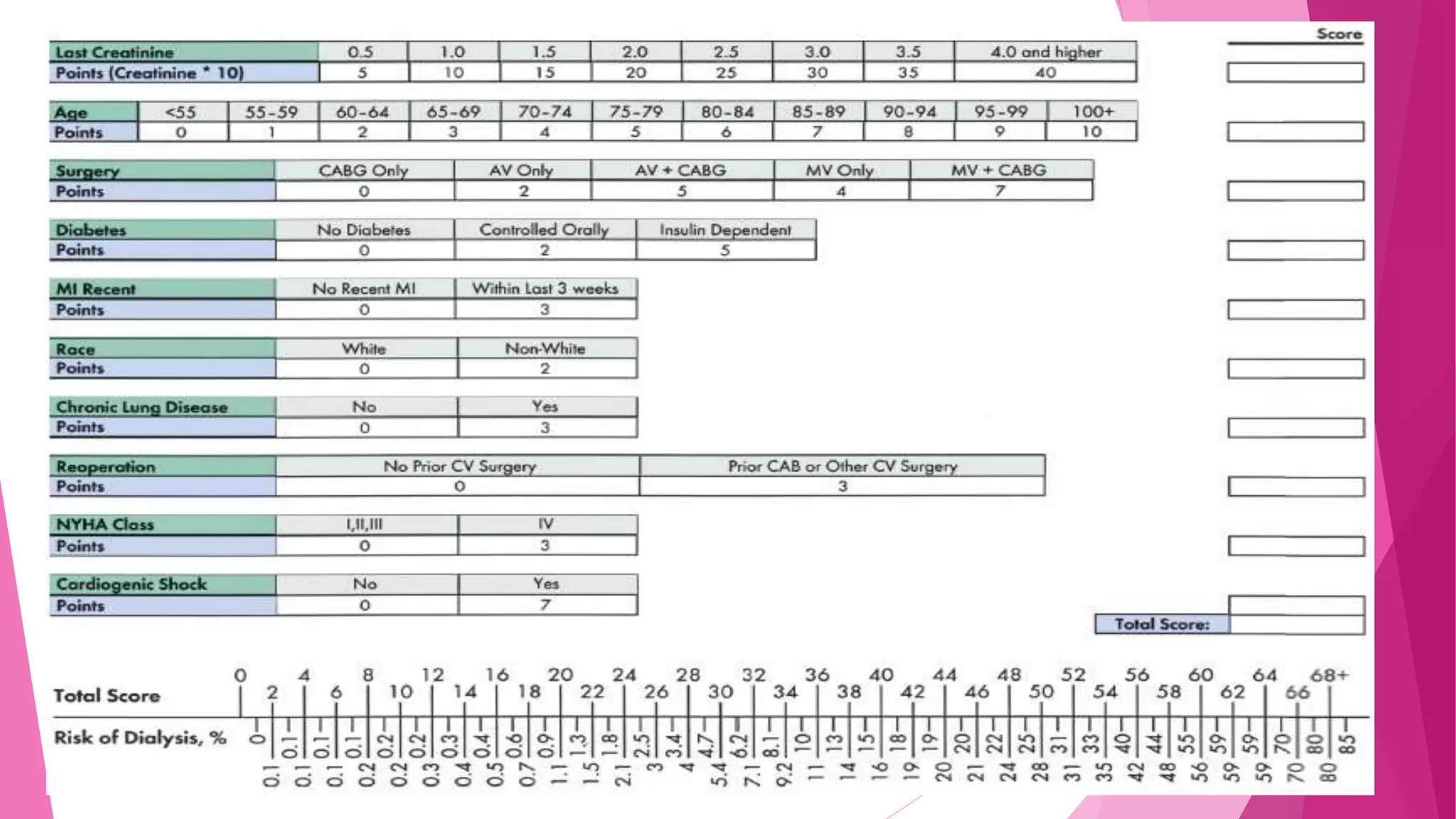
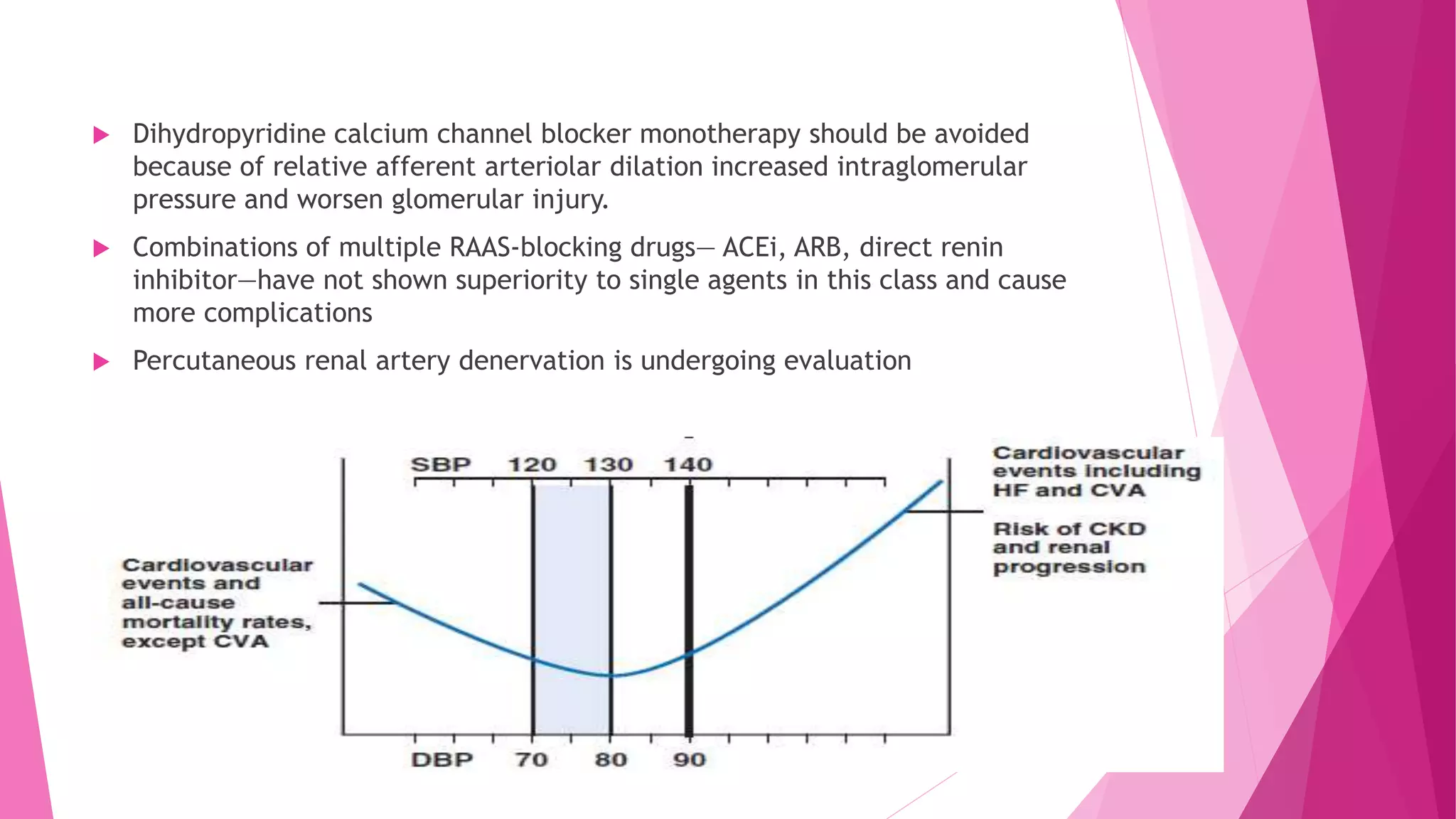
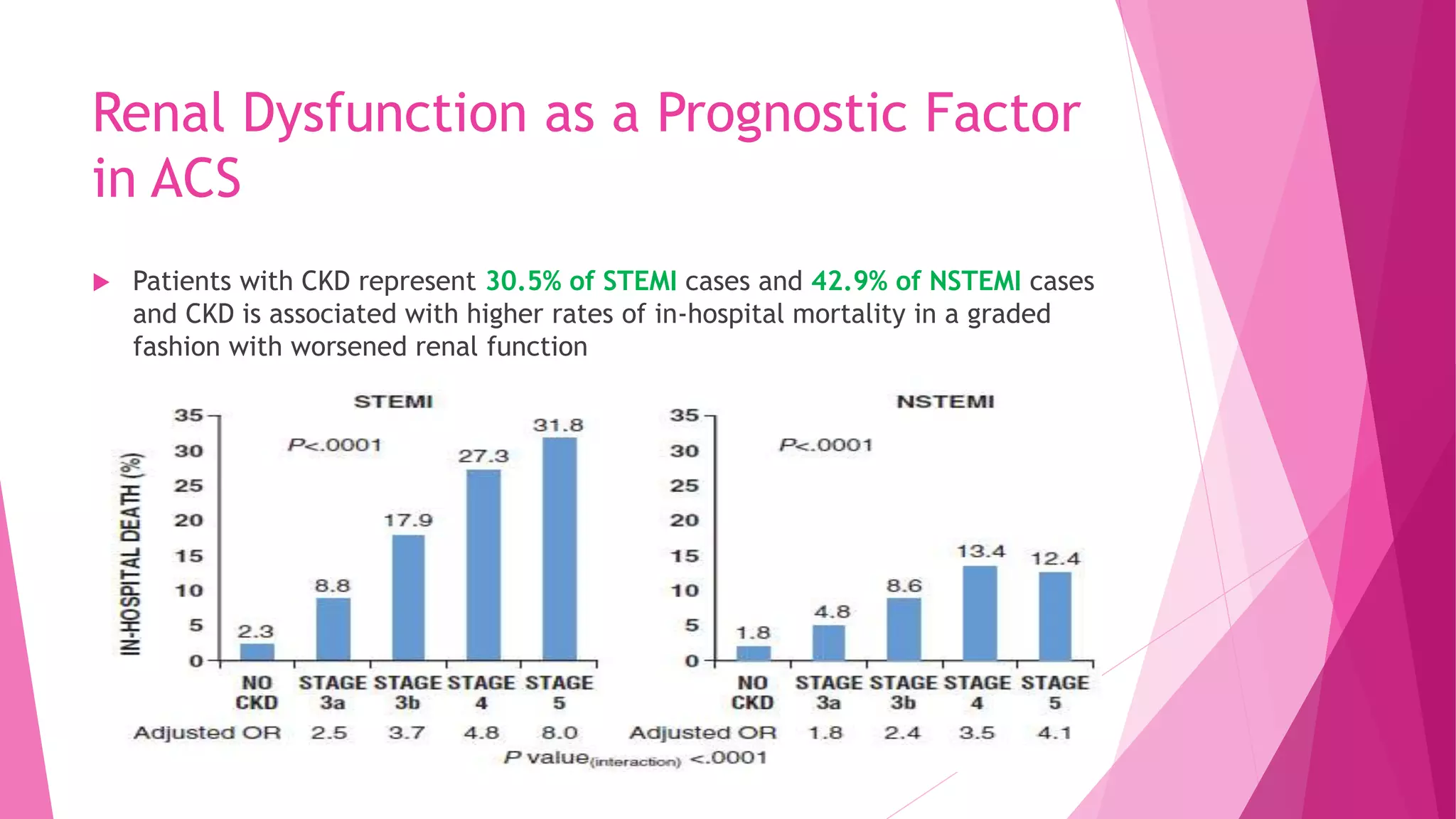
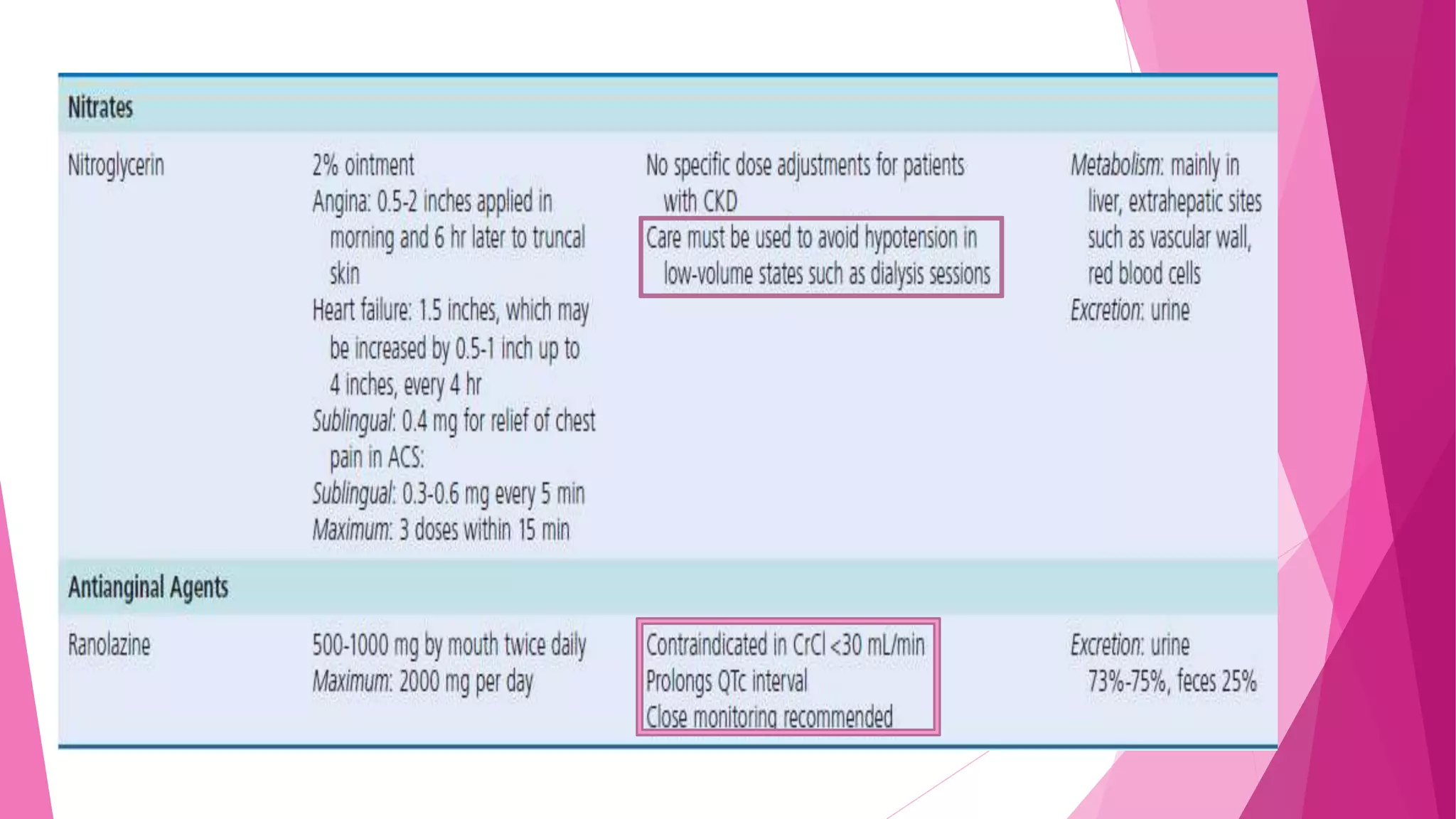
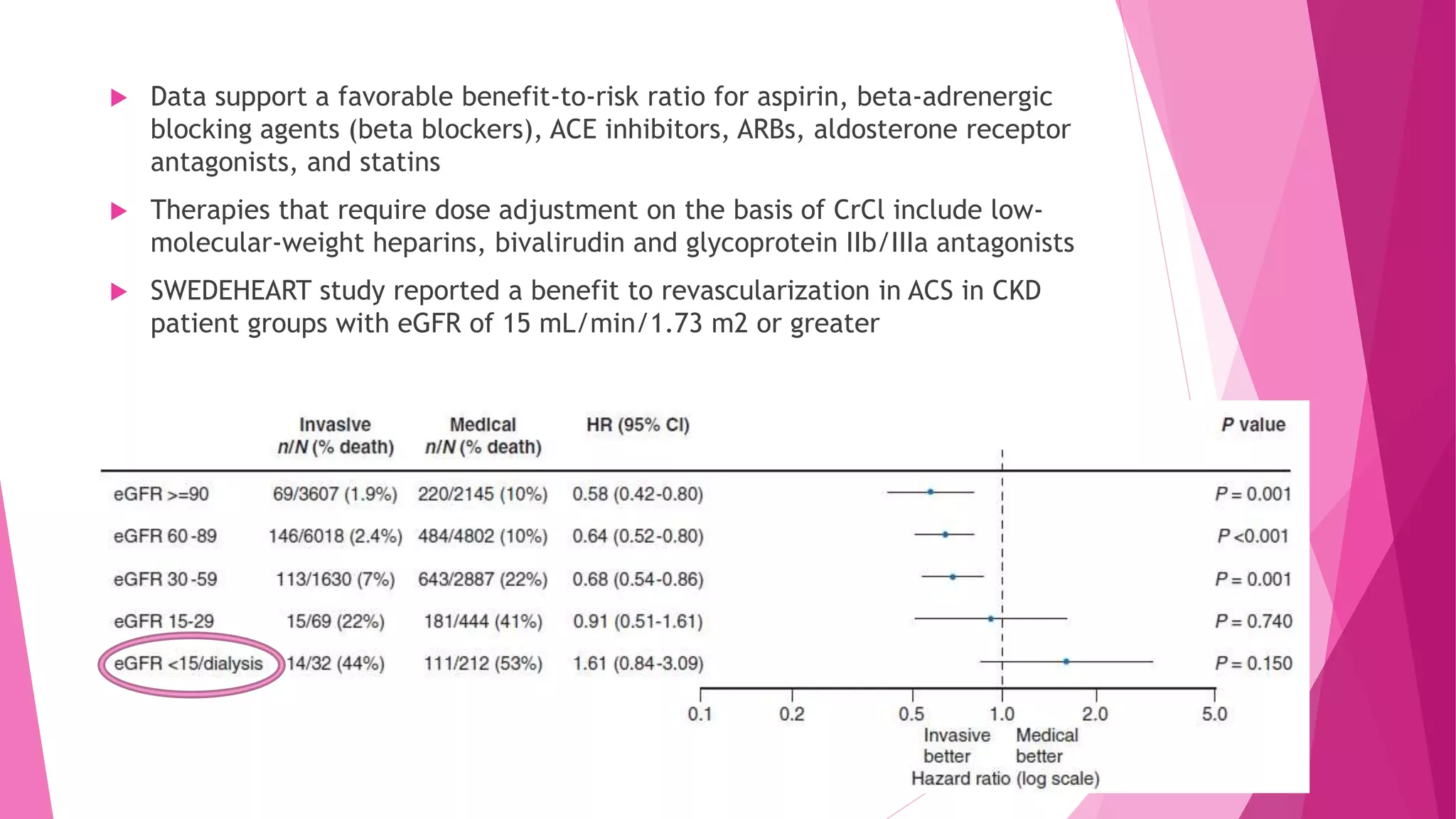
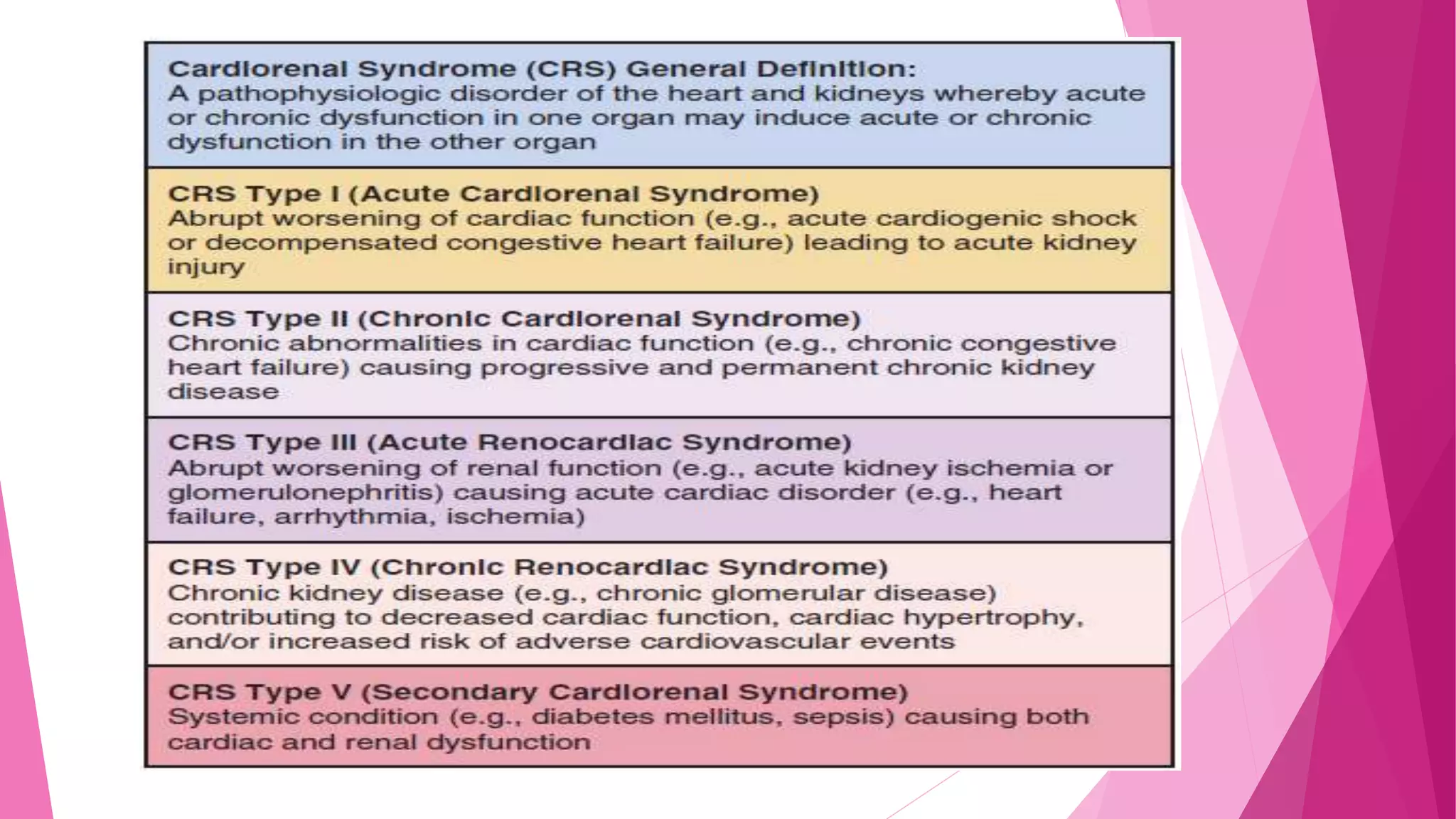
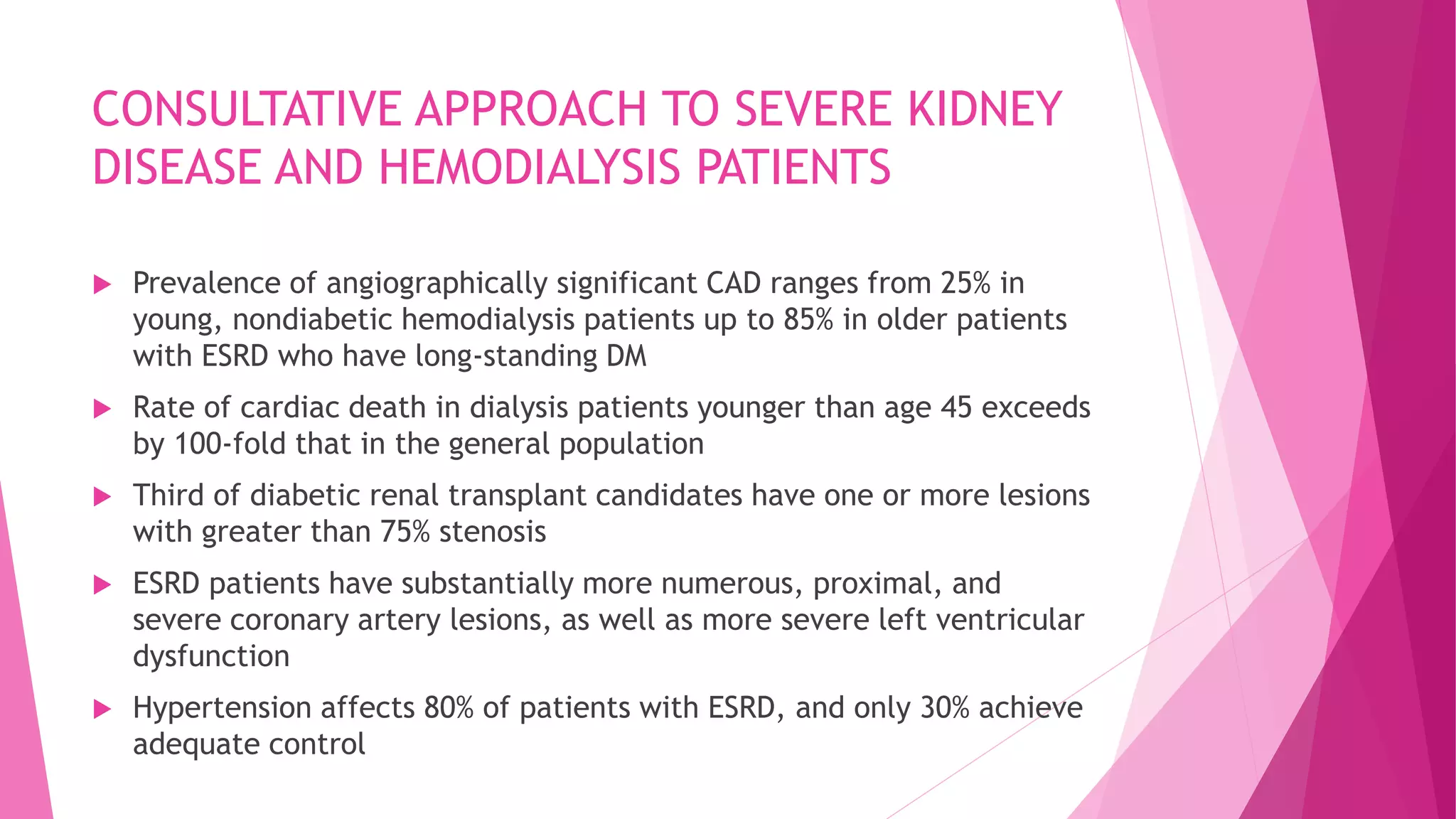
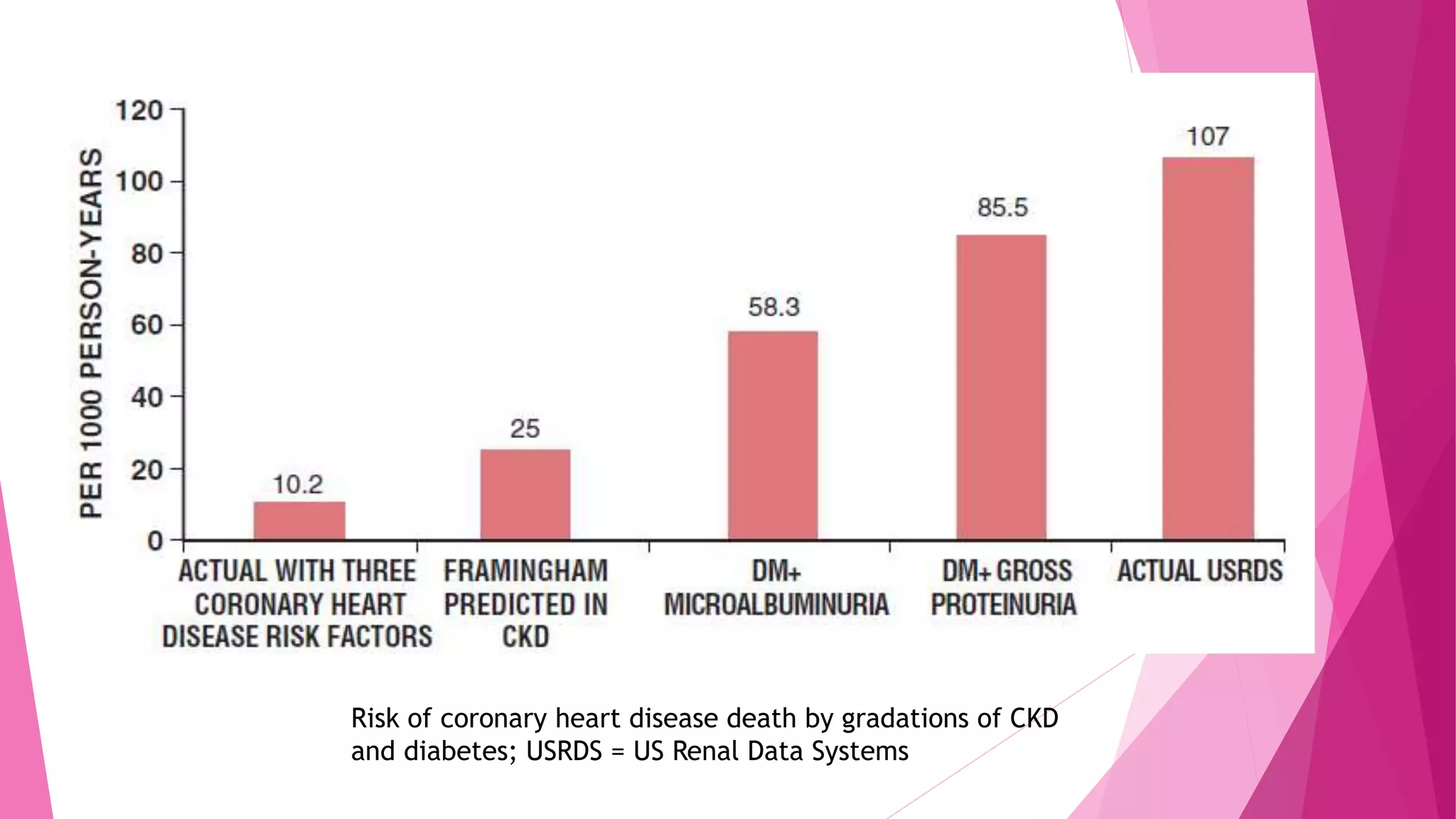
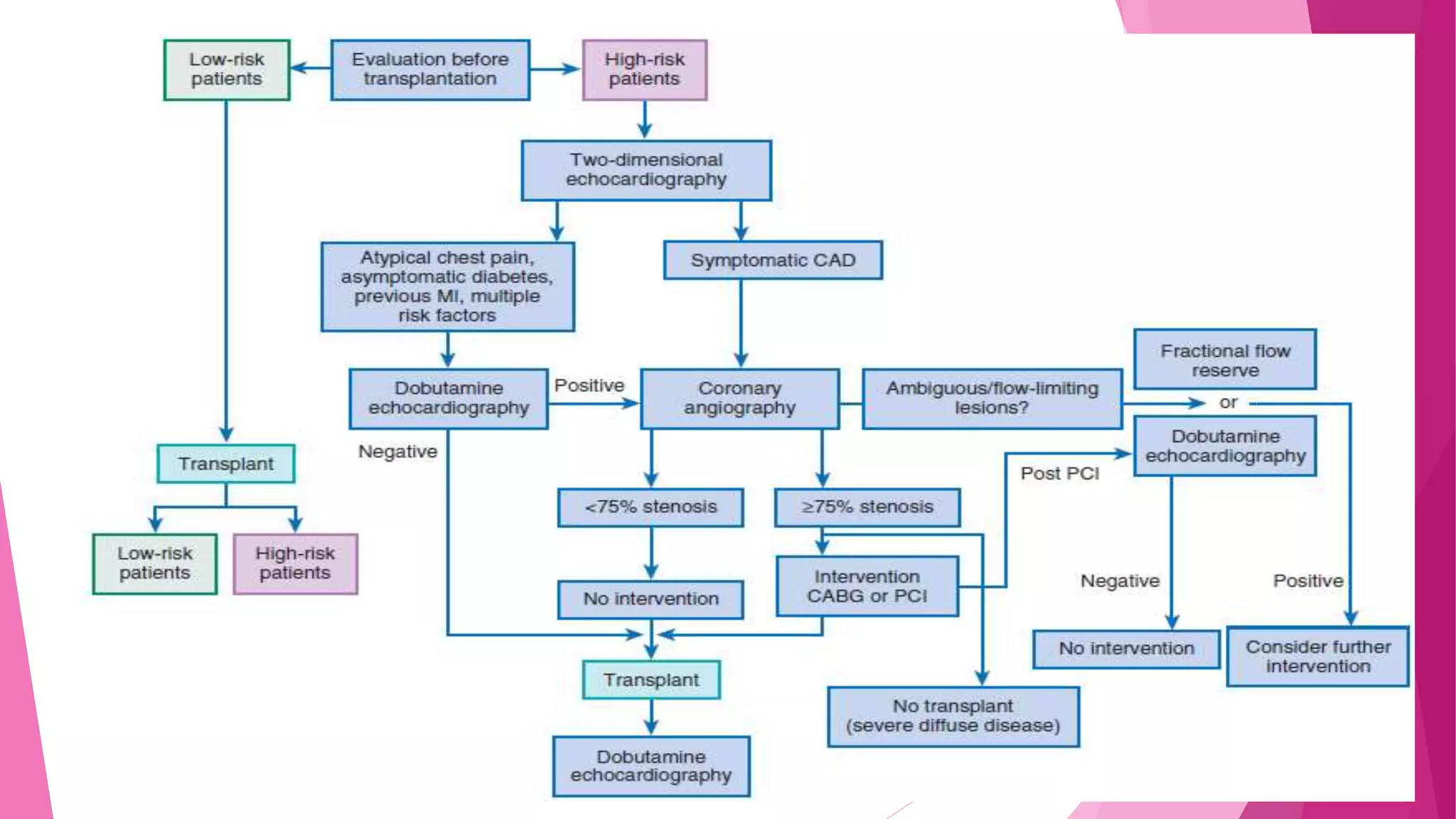
This document discusses the relationship between renal disease and cardiovascular illness. Some key points:
- The kidneys and heart communicate extensively through hormones and the sympathetic nervous system. Renal dysfunction increases cardiovascular risk.
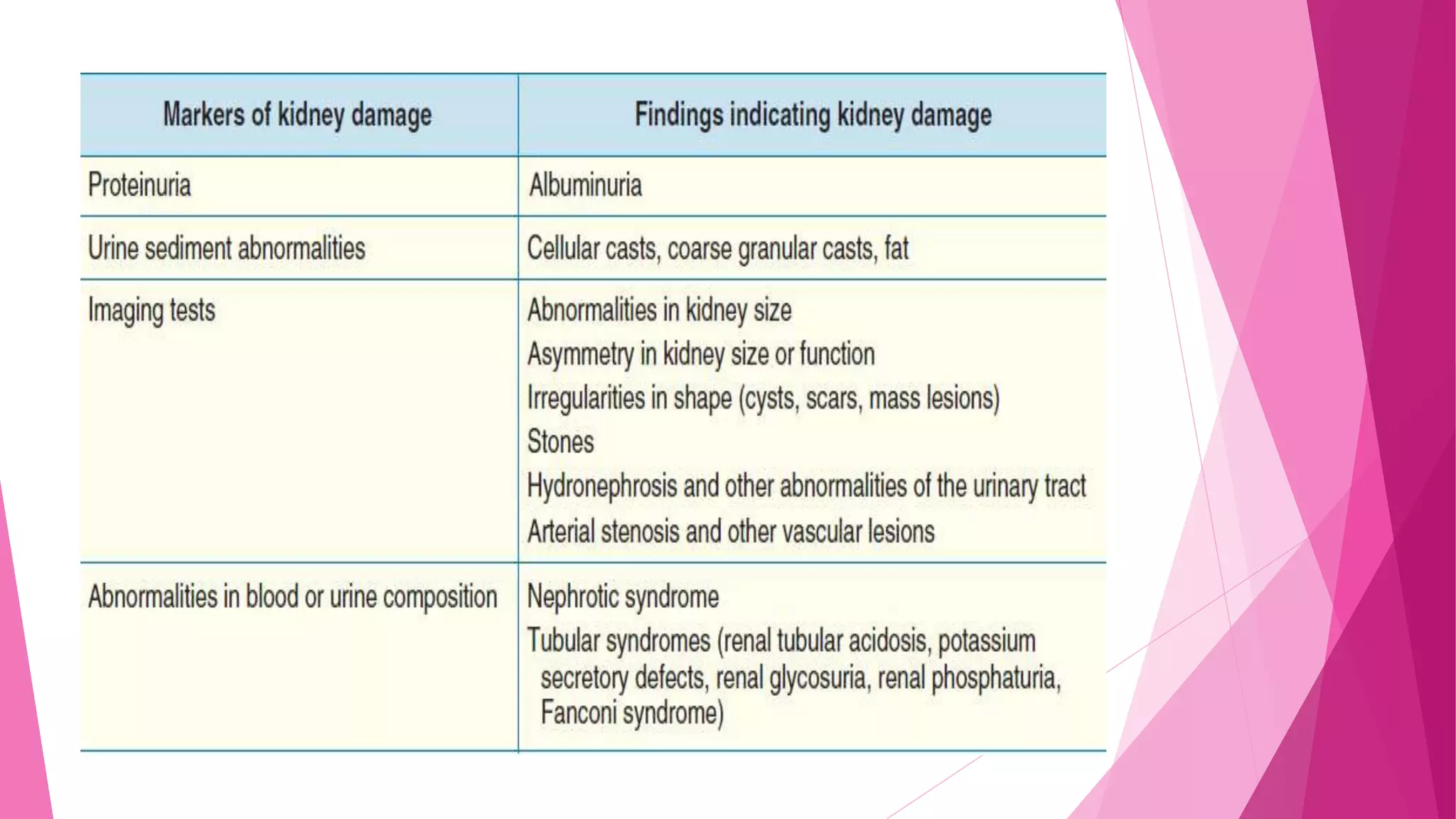
- Risk rises when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) drops below 60 mL/min/1.73m2. Microalbuminuria also predicts increased CVD risk regardless of diabetes status.
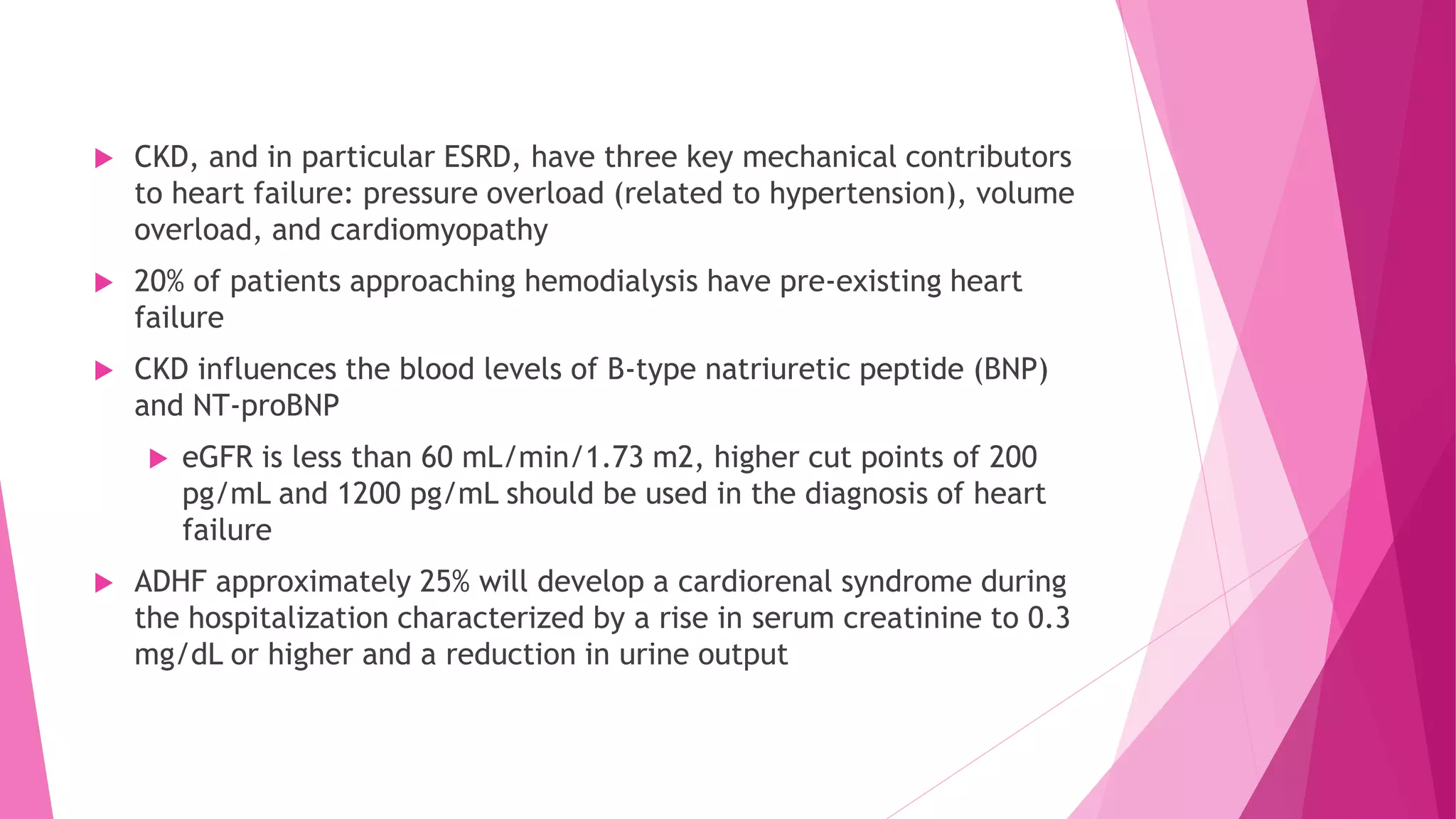
- Anemia due to chronic kidney disease is linked to worse heart failure outcomes and increased mortality. Treatment of anemia has risks that may outweigh benefits.
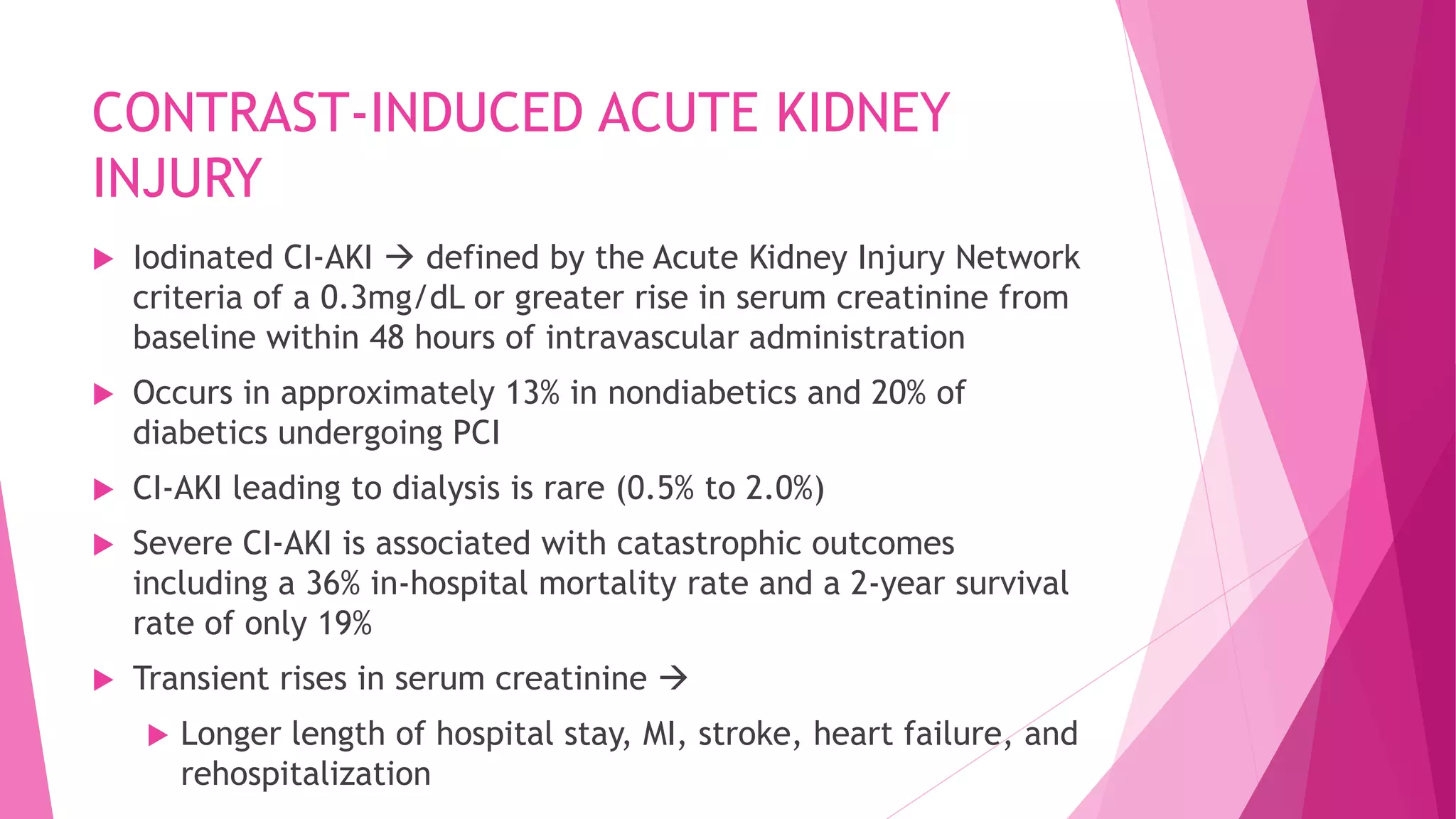
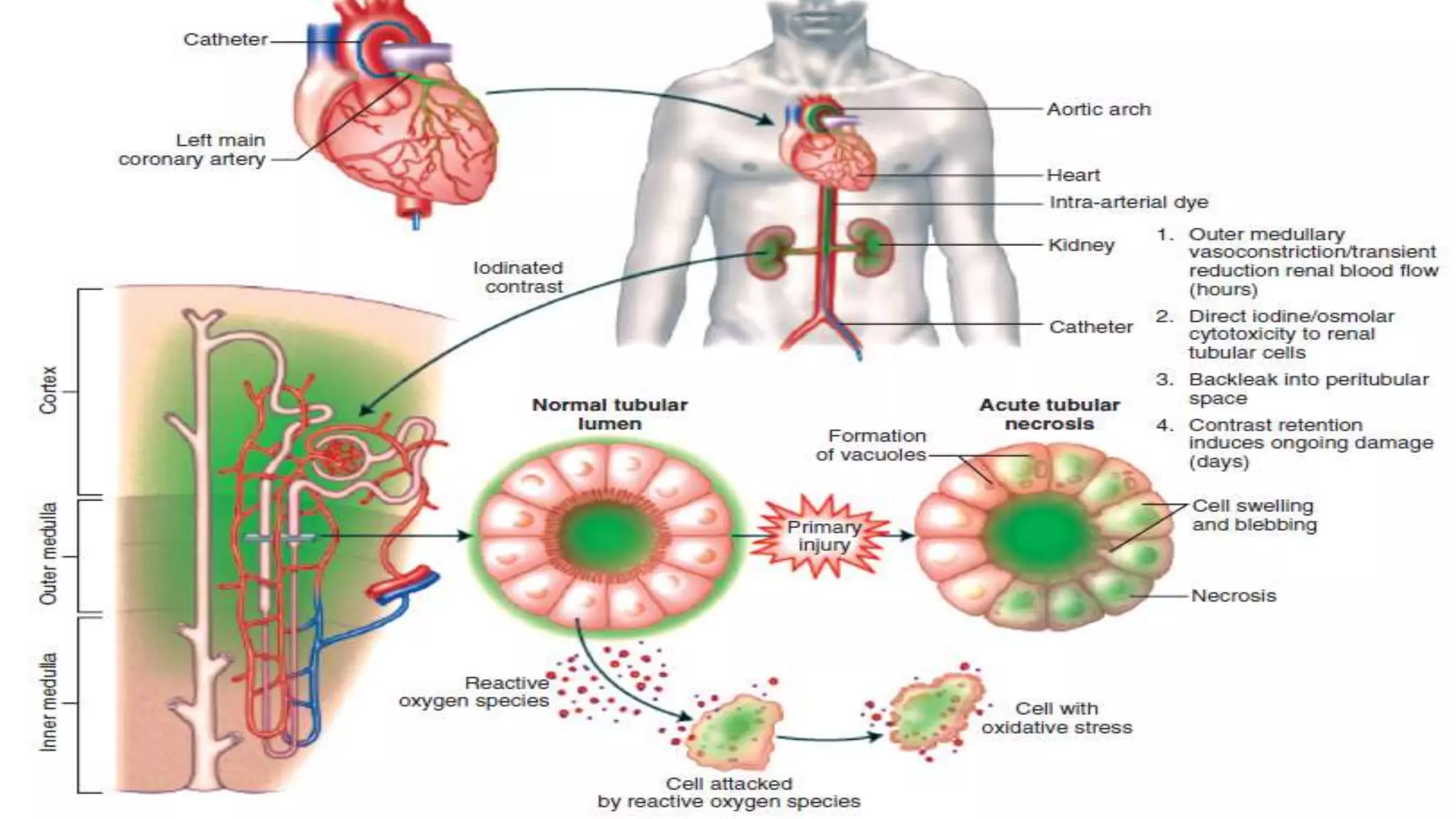
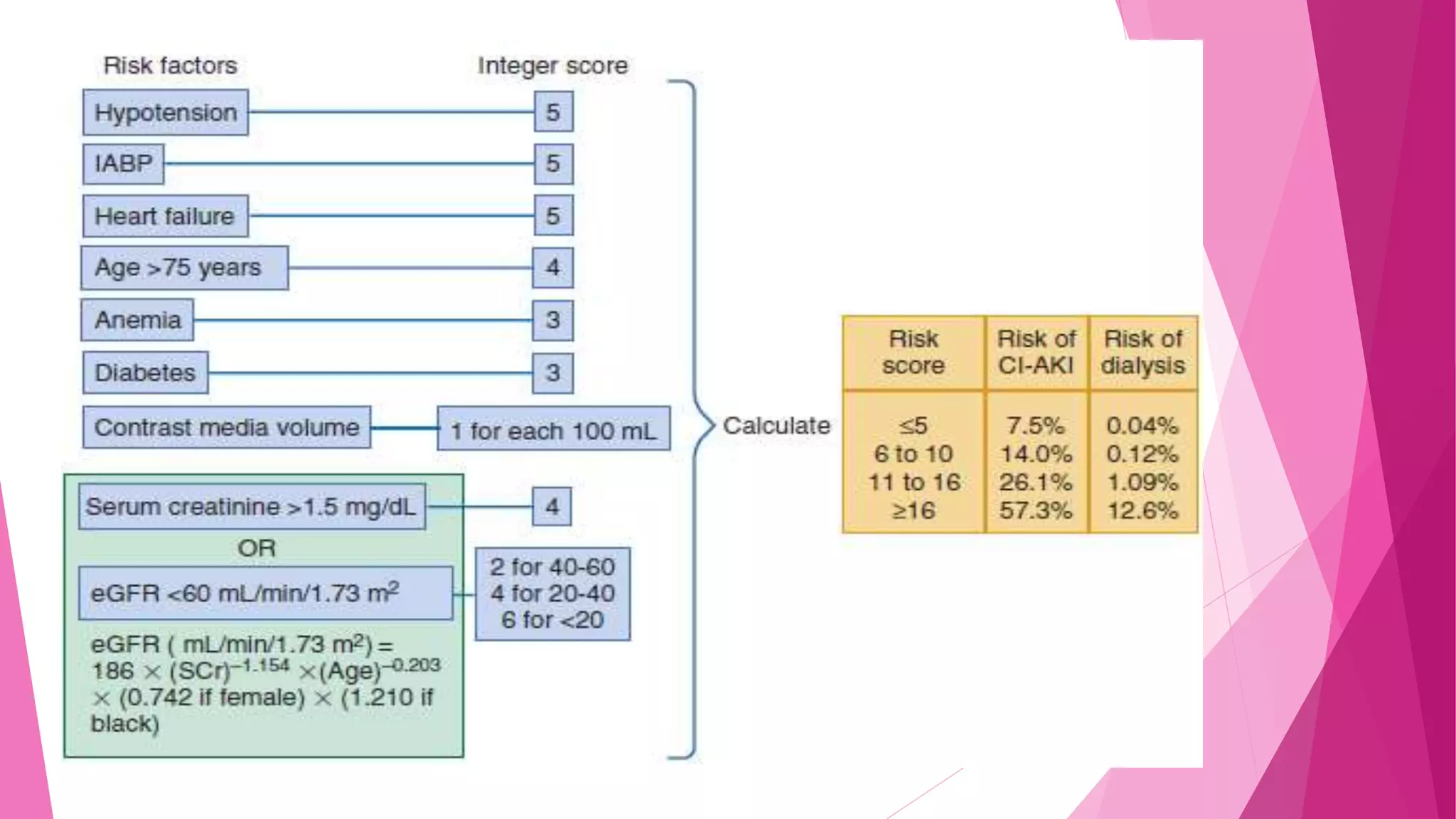
- Contrast-induced acute kidney injury is a risk for those with an eGFR <60 undergoing imaging with iodinated contrast