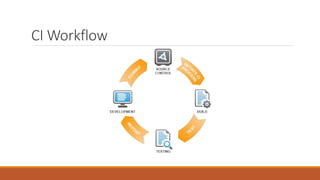
This document discusses continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD). CI involves integrating code changes frequently through automated builds and testing to detect errors early. CD takes CI a step further by making software deployable at any time through automated testing and deployment. The document outlines the key aspects of CI like continuous building, testing and inspection. It provides examples of tools like Git, Jenkins and best practices for implementing CI on projects like Hybris. Continuous deployment aims to enable fast feedback through automated testing and deployment of any version of software.