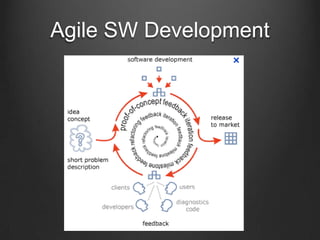
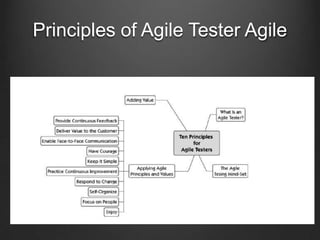
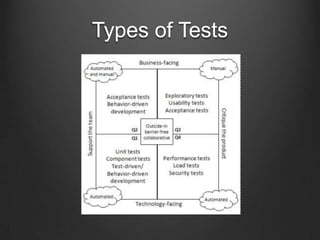
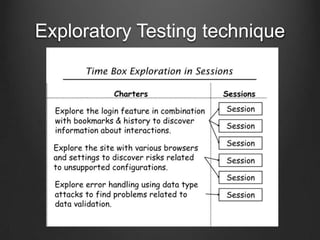
The document discusses agile testing practices and principles. It emphasizes that agile testing focuses on quality over speed, with the whole team sharing responsibility for quality. Agile testers work collaboratively with developers to ensure software meets customer needs. Exploratory testing and test automation are recommended techniques. Continuous integration with Jenkins is presented as a way to get early feedback and detect defects.