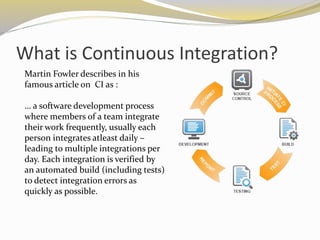
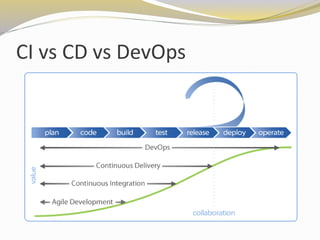
This document discusses continuous integration (CI), continuous delivery (CD), and DevOps. It defines CI as integrating code changes frequently, such as daily, and verifying them through automated builds and tests. CD builds on CI by making software deployable at any time by prioritizing deployments over new features and enabling anyone to deploy any version on demand. For developers, CD provides immediate feedback and the ability to test in production-like environments. For system admins, CD allows automating environments for developer testing. For businesses, CD lowers deployment risks and improves market responsiveness.