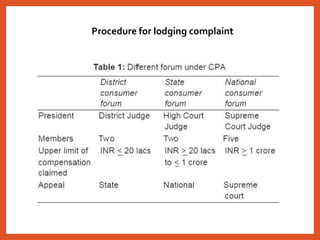
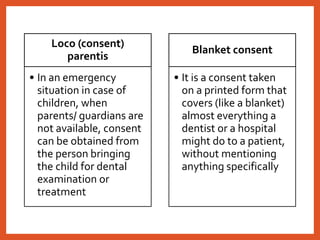
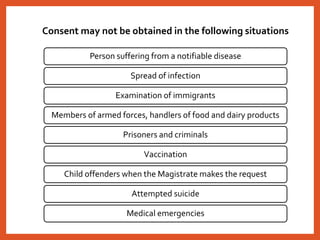
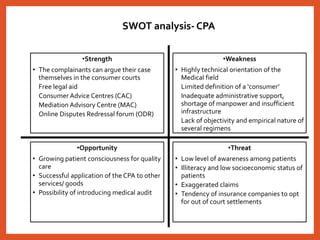
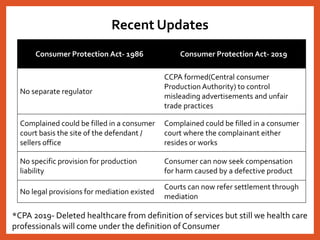
The Consumer Protection Act was introduced in 1986 to better protect consumers in India. It established a three-tier system for consumer dispute redressal at the district, state and national levels to provide simple and speedy remedies to consumer complaints. The act defines consumers and covers goods and services, including healthcare. It aims to make consumers aware of their rights and provides recourse in the form of consumer courts. Recent amendments in 2019 have strengthened provisions regarding product liability, mediation and regulation of misleading advertisements. Continued awareness among healthcare professionals about their obligations under this legislation is important.