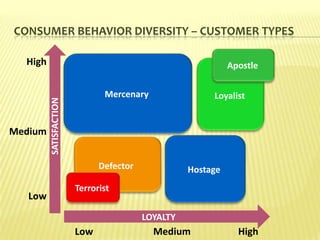
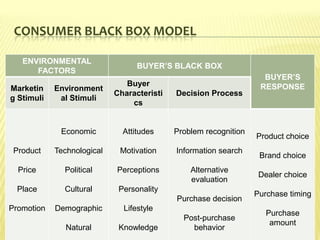
This document provides an introduction to consumer behavior and its significance for marketing. It discusses key concepts like understanding consumer needs, customer orientation, and customer value. It notes that consumer behavior is complex due to the diversity of consumer needs, influences, and roles in purchase decisions. Marketers must understand these differences to segment consumers and address specific groups through tailored products and marketing mixes. A deep understanding of consumer behavior is crucial for identifying market opportunities and making effective marketing strategy decisions.