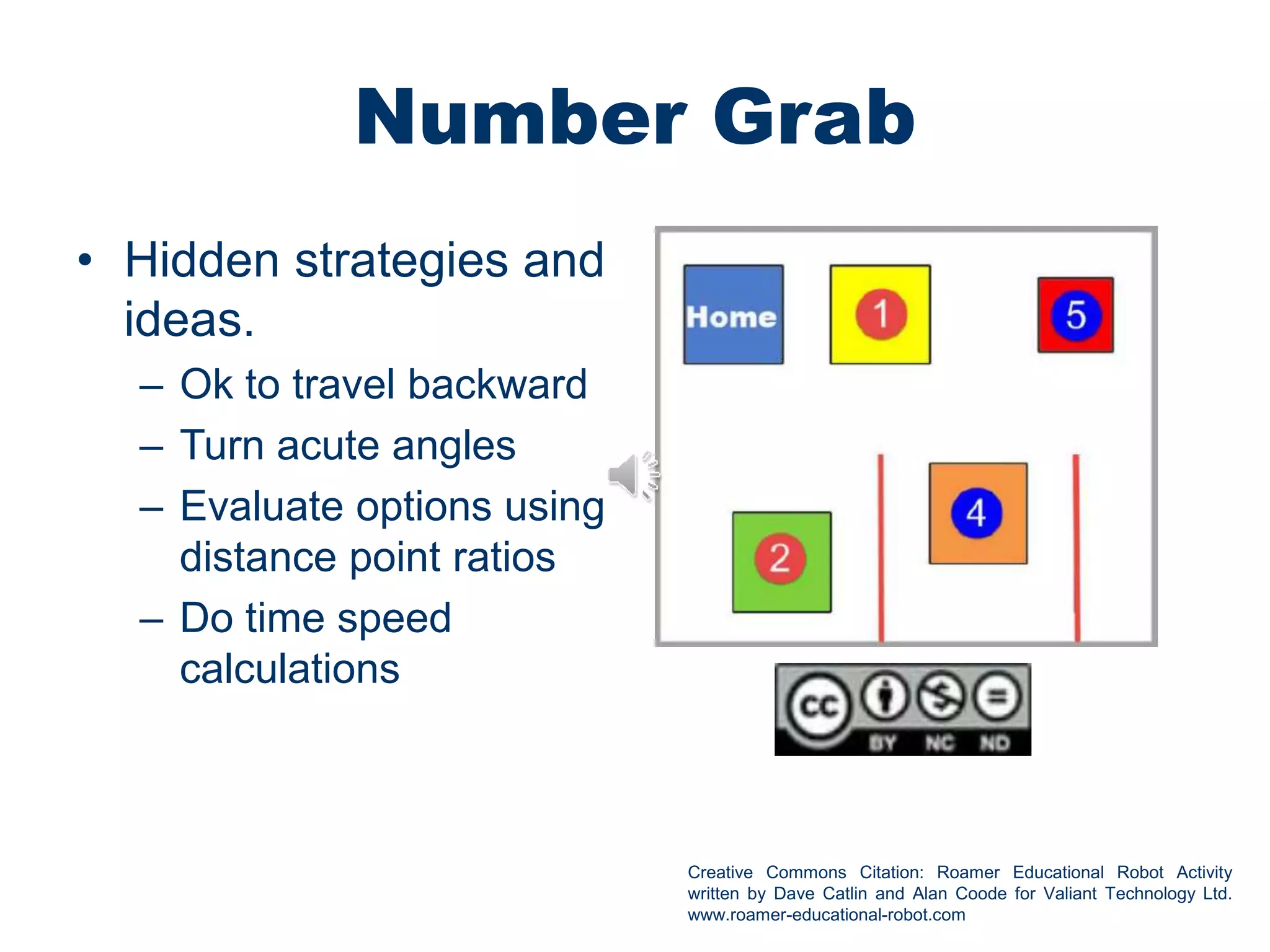
This document discusses using educational robots to facilitate learning intentions and assessment. It provides the following key points:
1. Learning intentions should focus on what students are learning rather than what they have to do. They work best when negotiated with students.
2. Engaging students through discussion and effective questioning before setting learning intentions helps students take ownership of their learning.
3. Learning intentions are not always necessary or possible to establish at the start of a lesson. They may need to change based on how the lesson is going. The goal is improving student learning.