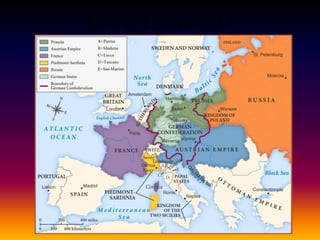
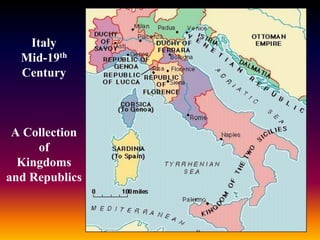
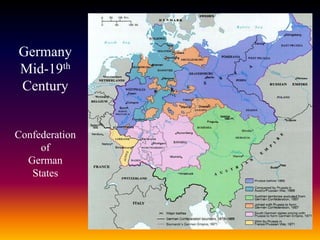
This document summarizes the rise of conservatism, liberalism, and nationalism in Europe during the 19th century. It discusses how conservatism opposed the liberal and nationalist uprisings inspired by the French Revolution, seeking to preserve the status quo through a balance of power. Liberalism emerged advocating individual freedoms and rights. Nationalism grew as peoples sought self-governance based on shared identities. The revolutions of 1848 briefly spread liberal and nationalist ideals before being crushed by conservative forces, though changes were still underway in places like France under Napoleon III and in the unifications of Italy and Germany.