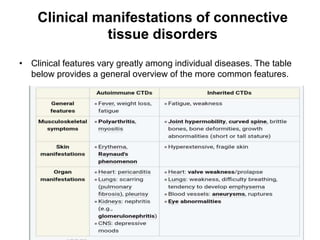
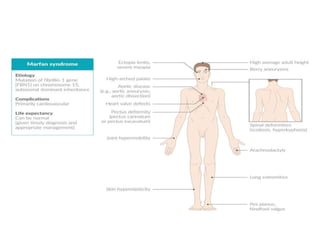
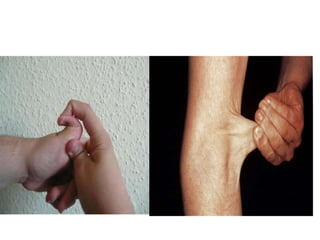
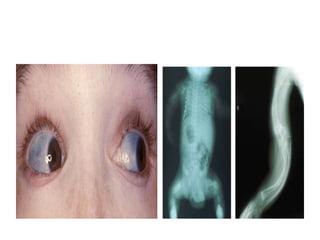
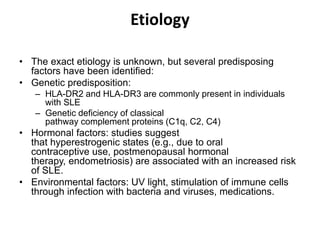
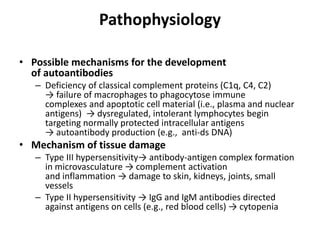
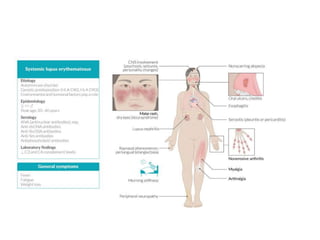
Connective tissue disorders are conditions that affect connective tissue and can be inherited or autoimmune in nature. The document discusses several common connective tissue disorders including Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, osteogenesis imperfecta, scurvy, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren syndrome, and mixed connective tissue disease. Each disorder is summarized with key details on etiology, clinical features, and prognosis when available.



![Inherited connective tissue diseases
• Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
• Marfan syndrome
• Osteogenesis imperfecta
• Alport syndrome
• Loeys-Dietz syndrome [1]
– Autosomal dominant inheritance
– Features shared with Marfan syndrome: marfanoid
habitus, increased risk of ascending aortic
aneurysms and aortic dissection
– Distinct features: hypertelorism, bifid uvula, cleft palate,
easy bruising and keloids, arterial tortuosity (winding
course of arteries)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/connectivetissuedisorder-200313102959/85/Connective-tissue-disorder-5-320.jpg)