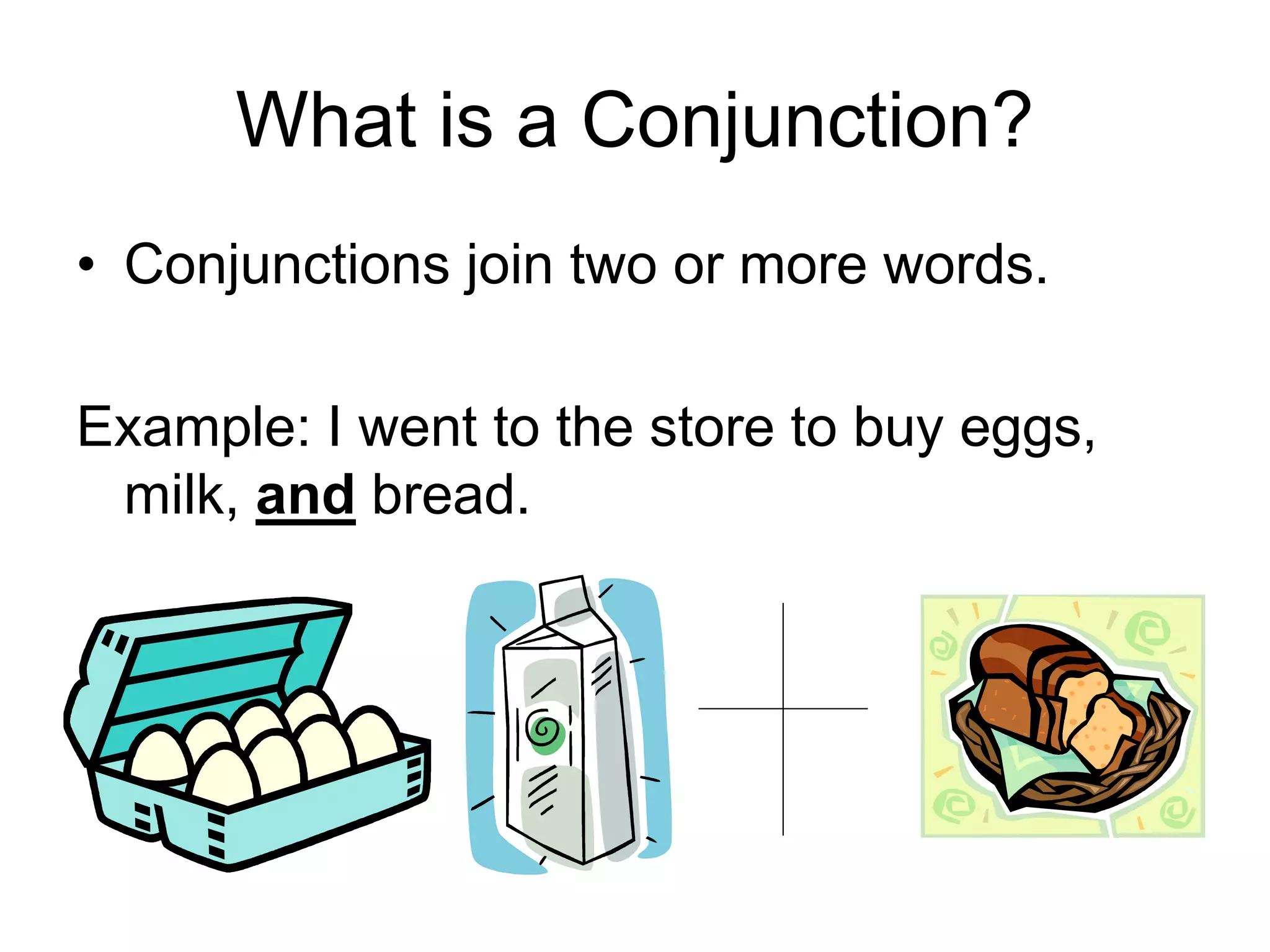
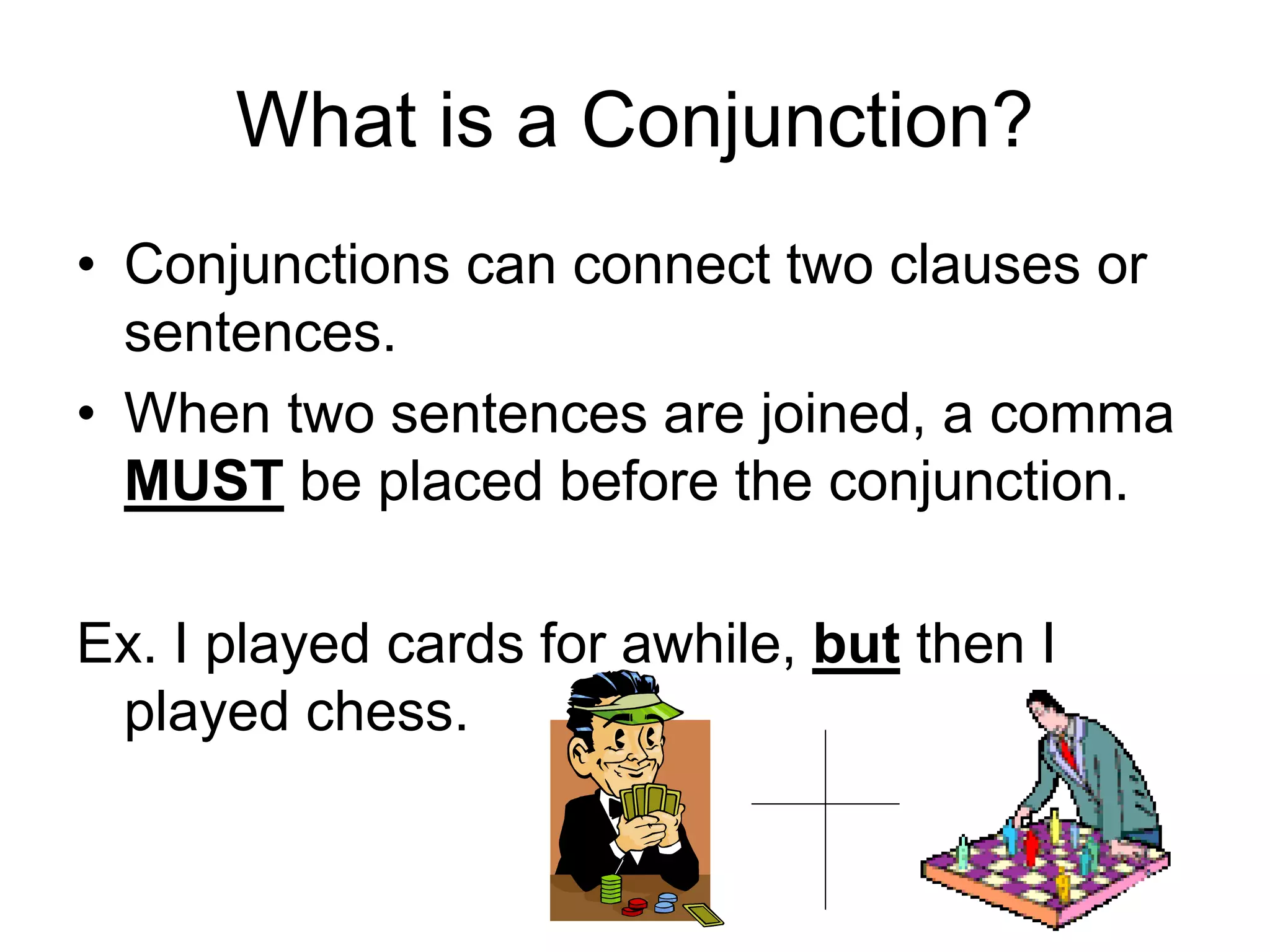
1. The document discusses different types of conjunctions and interjections. It defines conjunctions as words that join other words, phrases, or clauses.
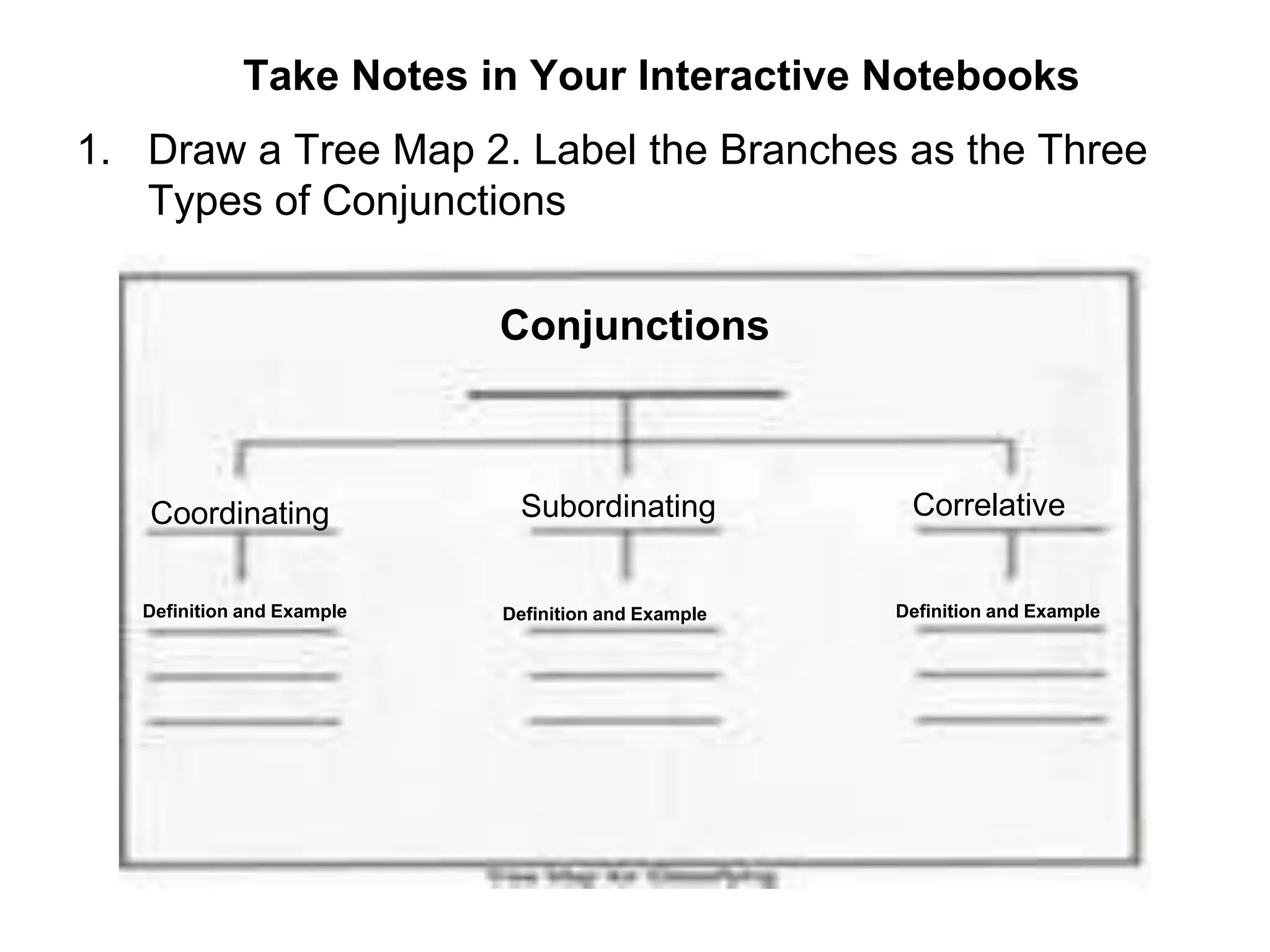
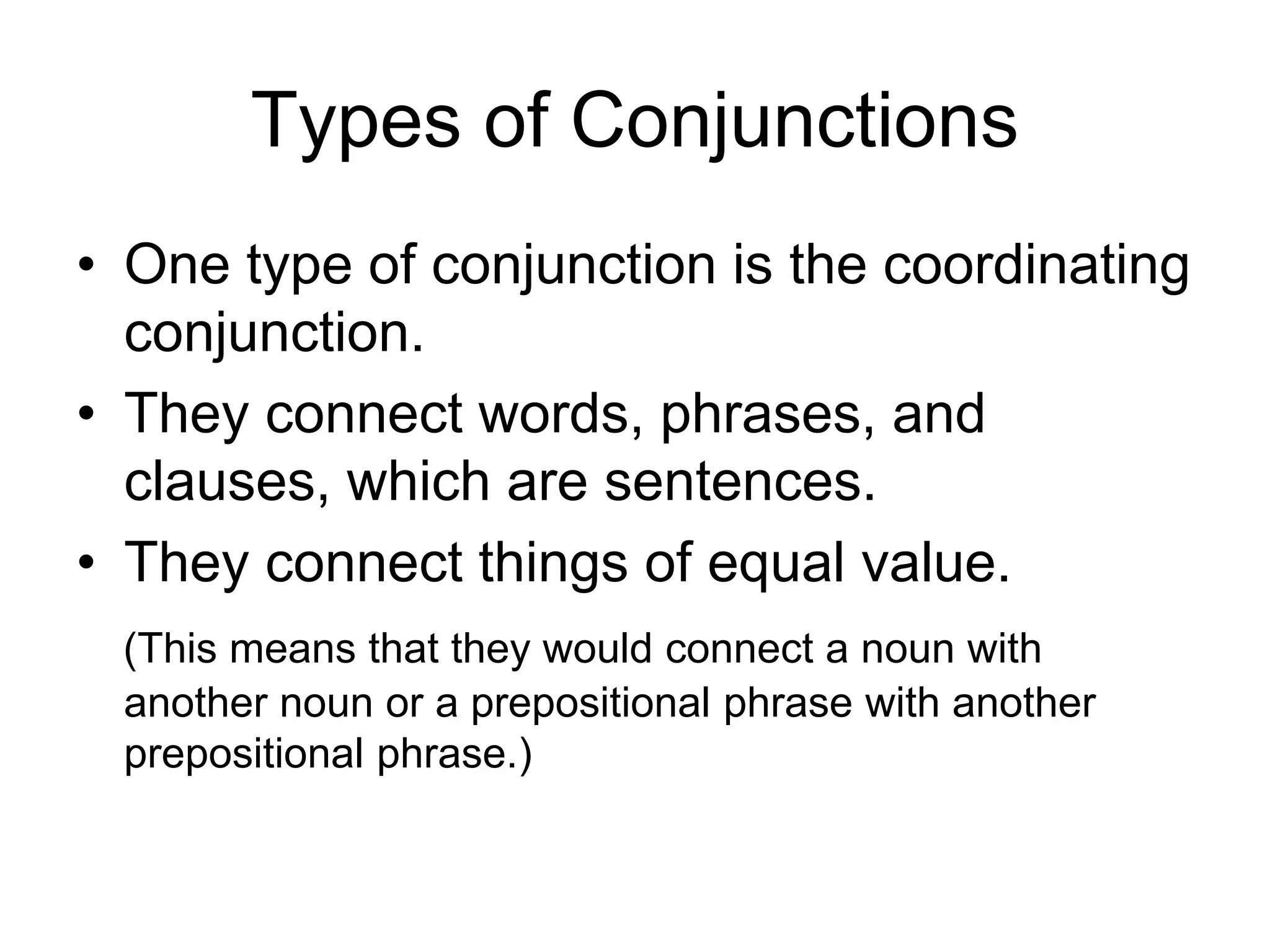
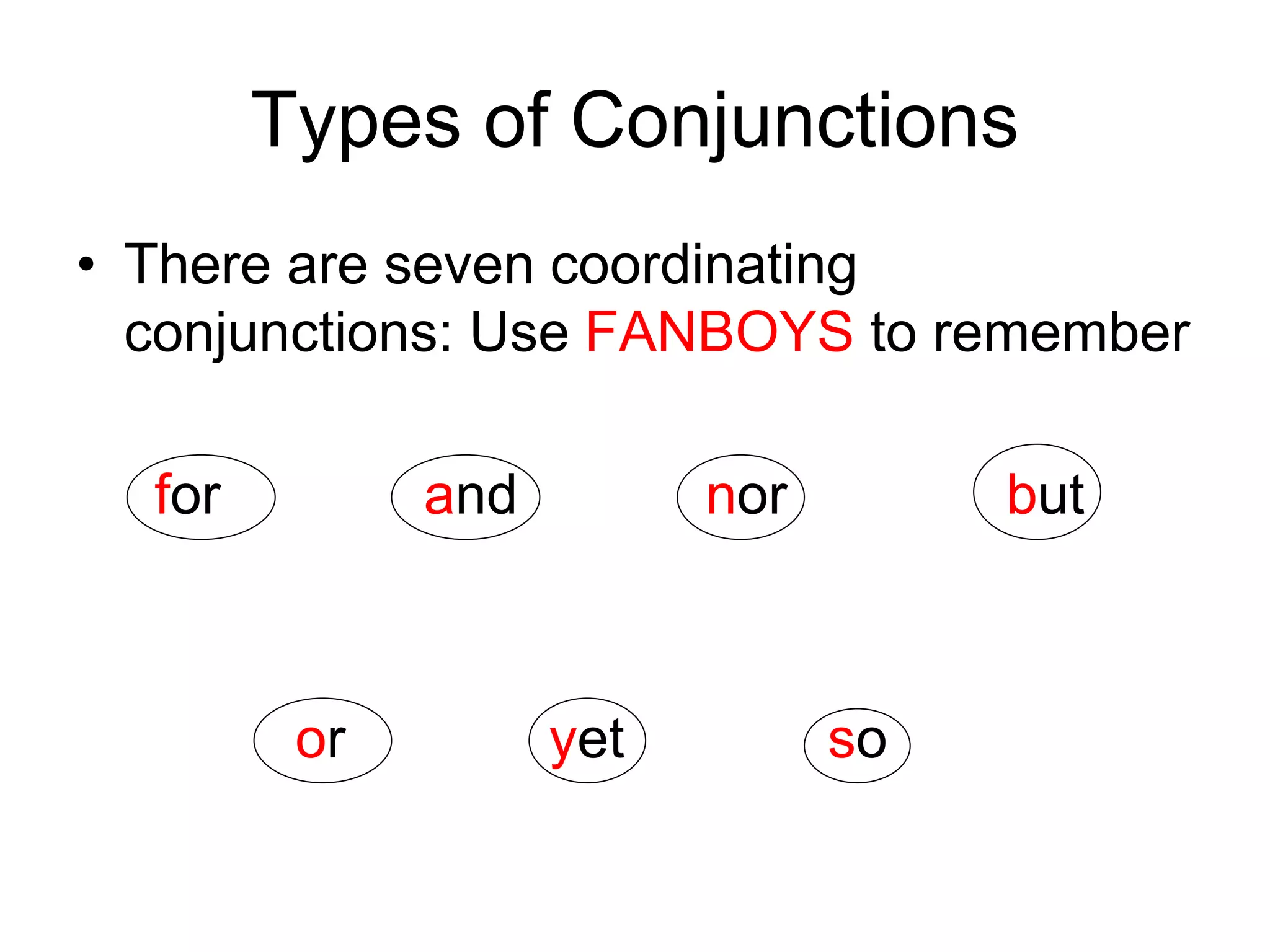
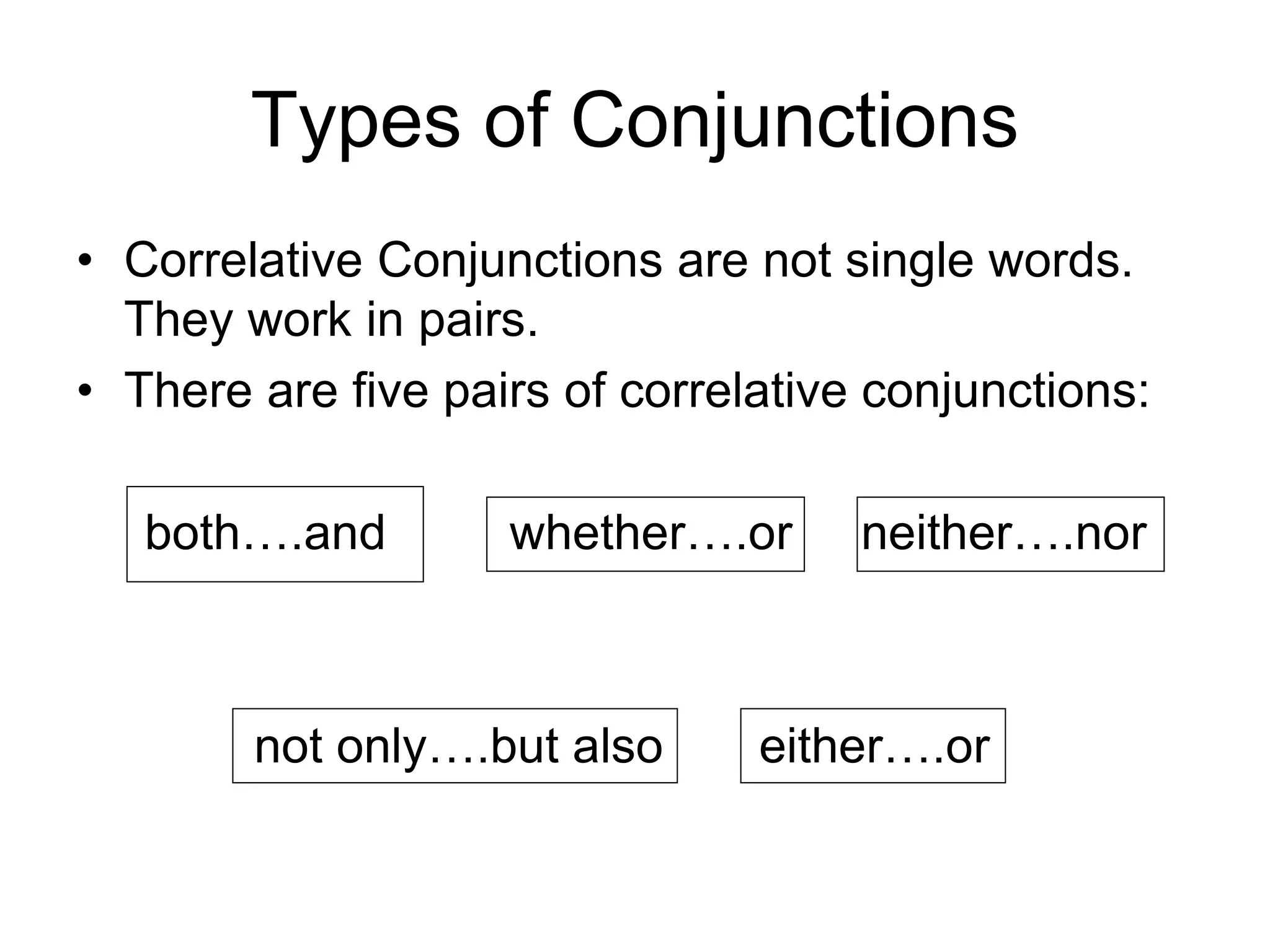
2. There are three main types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions. Coordinating conjunctions connect equal grammatical elements, while subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses.
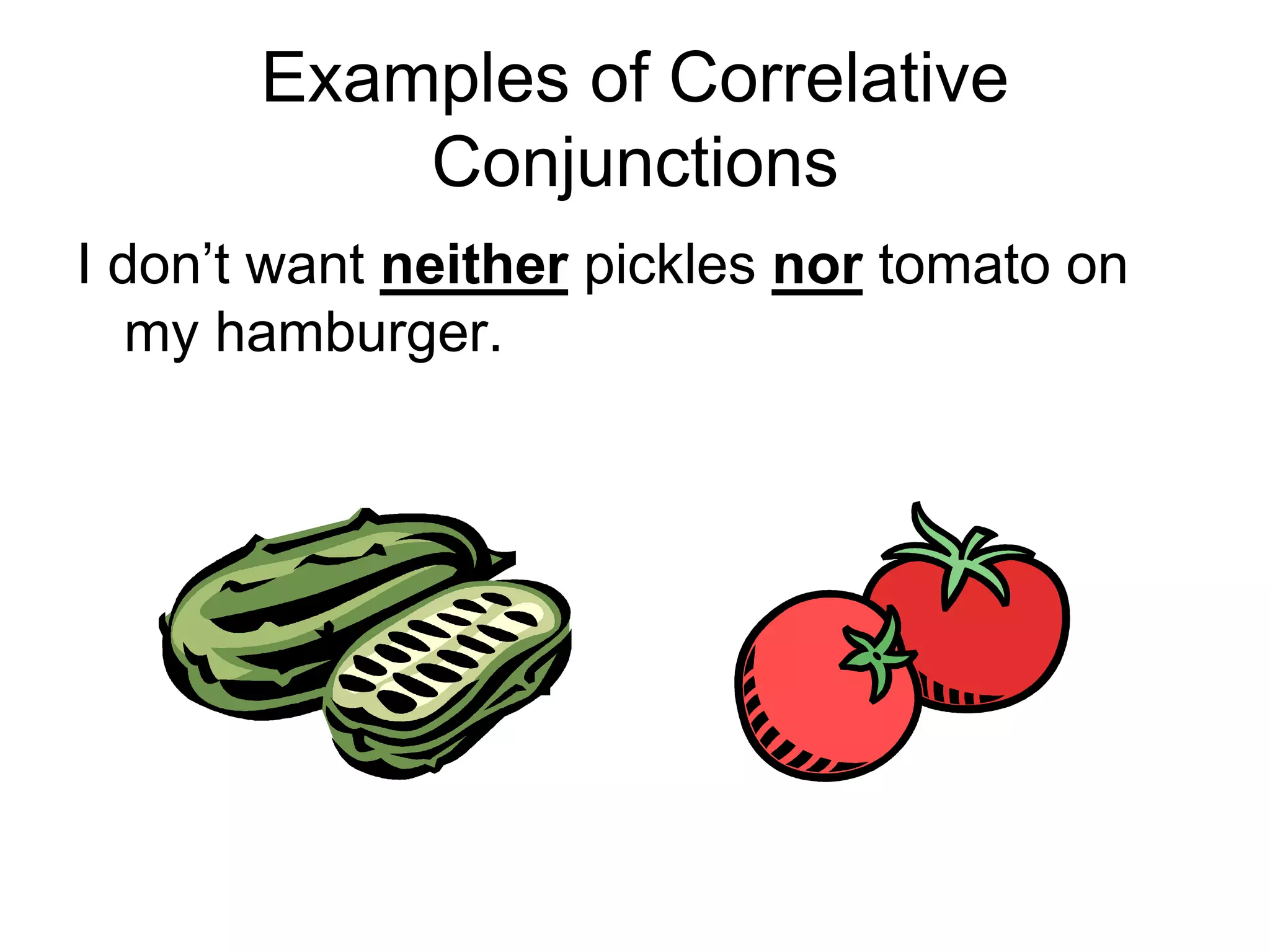
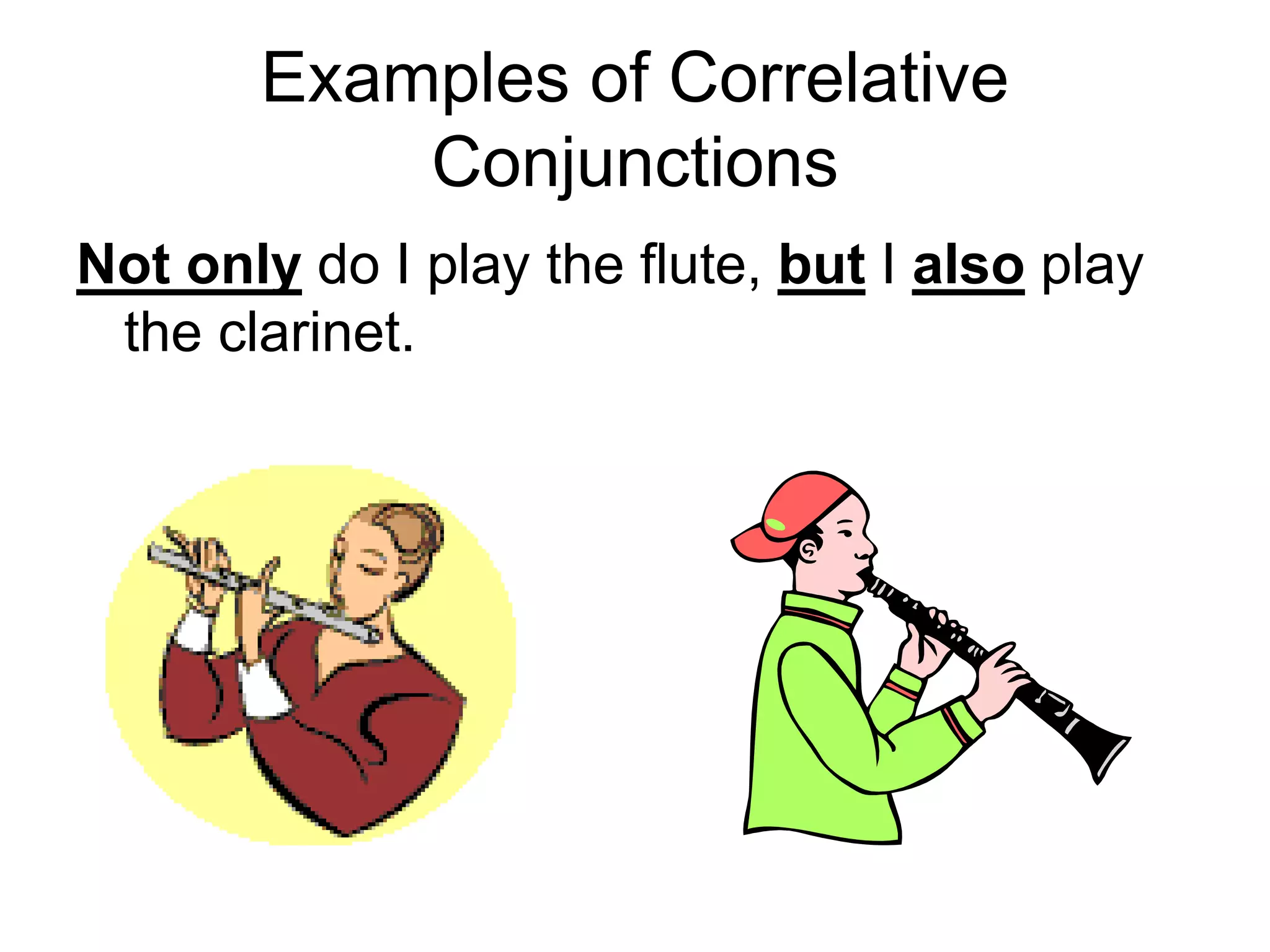
3. The document provides examples of each type of conjunction and explains how they are used and punctuated in sentences. It also defines interjections as words that express emotion and can interrupt sentences.