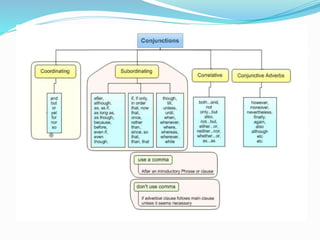
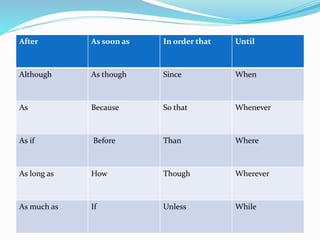
This document discusses different types of conjunctions in English: coordinating, correlative, and subordinating. It provides examples of each. Coordinating conjunctions connect words or phrases of equal grammatical rank, with examples given of the FANBOYS conjunctions - for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so. Correlative conjunctions join sentence elements in pairs and include both/and, either/or, neither/nor. Subordinating conjunctions introduce subordinate clauses and indicate time or place, with examples like after, although, as, before, until, when, where. Care must be taken as some conjunctions can function as both subordinating conjunctions and prepositions.