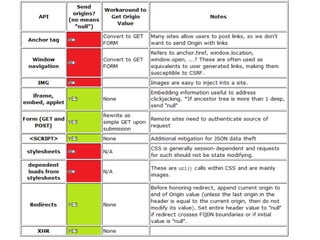
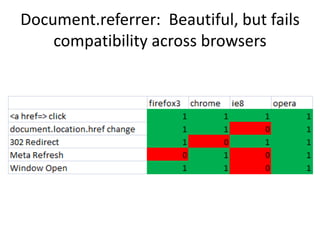
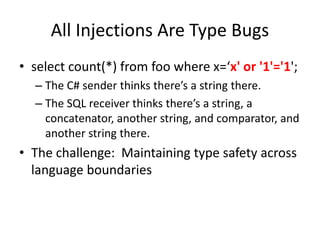
The document discusses securing web applications. It argues that traditional approaches like blaming developers or banning third-party cookies are not effective solutions. Adding random tokens manually to URLs is difficult for developers. Using the referer header is unreliable due to inconsistencies across browsers and plugins. The origin header has similar problems. The document proposes an "interpreter suicide" approach where JavaScript detects cross-site navigation and prevents further execution to block attacks. This provides a client-side way to enforce session context without requiring manual token management.

















![Tokens Are Actually Really Hard
• [All] application local URLs have to be rewritten for using
the randomizer object. While standard HTML forms and
hyperlinks pose no special challenge, prior existing
JavaScript may be harder to deal with. All JavaScript
functions that assign values to document.location or open
new windows have to be located and modified. Also all
existing onclick and onsubmit events have to be rewritten.
Furthermore, HTML code might include external referenced
JavaScript libraries, which have to be processed as well.
Because of these problems, a web application that is
protected by such a solution has to be examined and tested
thoroughly.
– http://www.informatik.uni-
hamburg.de/SVS/papers/2006_esorics_SessionSafe.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confidenceweb-101128063554-phpapp02/85/Confidence-web-18-320.jpg)

























![One Design
• SessionID “Supercookie”, emitted on requests from:
– Same-site nav
– Top-level nav
– Bookmarks
– “Friend sites”
• API
– window.getSessions([domain]) and
window.setSessionId([string], [domain])
• Google can declare a session ID context for Pandora
• Pandora can see all sessions that are live, from all sources
– window.addSessionFriend(domain) allows/accepts session IDs
from a named domain
– window.atomicnavigate(domain) should do the equivalent of
interpreter suicide, by design](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confidenceweb-101128063554-phpapp02/85/Confidence-web-46-320.jpg)
![The Simple Implementation
• On login:
– window.setSessionId(“loggedin”);
• Server side check: Just look for a cookie pair,
“_sessionId=loggedin”
• Client side check:
if(window.getSessions()[0]!=‘loggedin’){
window.atomicNavigate(‘login.php’);
• (Gets fancier when accepting SSO cookies, but
not much fancier.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confidenceweb-101128063554-phpapp02/85/Confidence-web-47-320.jpg)





![Insult To Injury
• Escaping encourages the belief that regular
expressions are a good idea
– b(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?).(25[0-
5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?).(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-
9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?).(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-
9][0-9]?)b
• Makes sure that an IP address is valid
– /(<as(?:[^>](?!href))*hrefs*)(&(&[^;]+;)?(?:.(?!3))+(
?:3)?)([^>]+>)/
• Curtis Poe, Author: “I was strutting like a peacock when I
wrote that, followed quickly by eating crow when I ran it. I
never did get that working right. I'm still not sure what I was
trying to do.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confidenceweb-101128063554-phpapp02/85/Confidence-web-54-320.jpg)




















