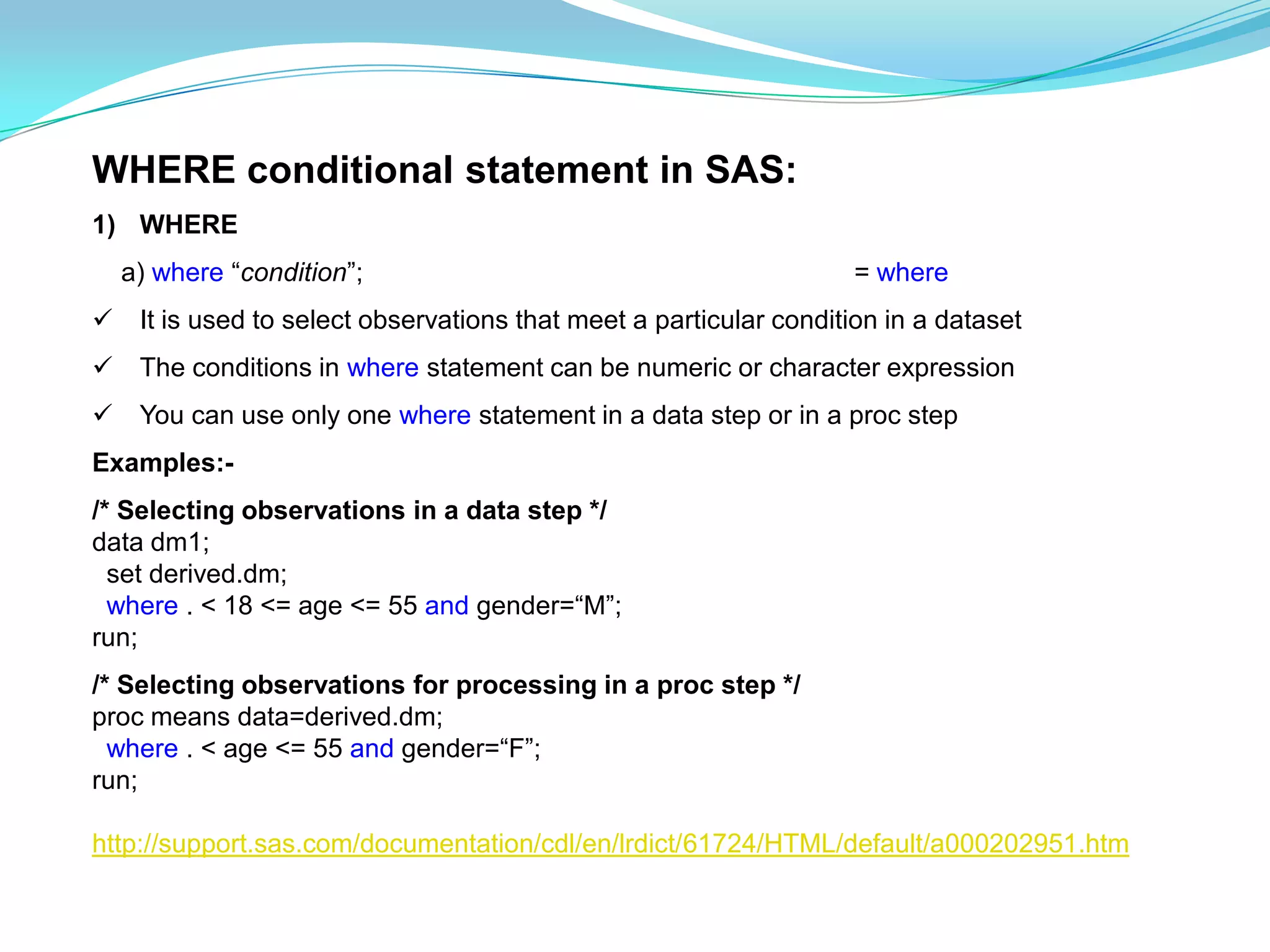
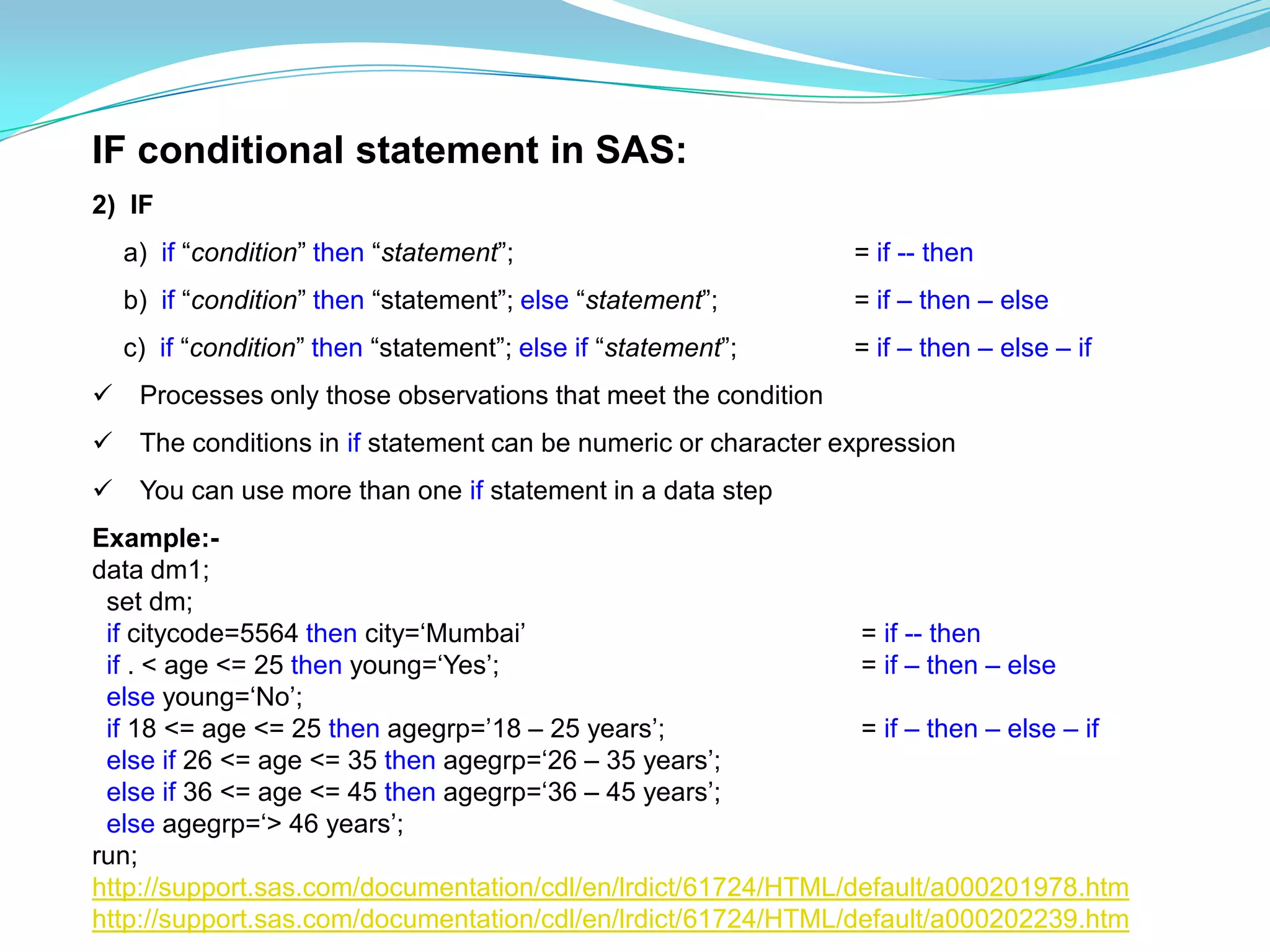
The document discusses the different types of conditional statements in SAS including WHERE, IF, and DO statements. WHERE is used to select observations based on a condition. IF processes observations that meet a condition and can have multiple statements. DO specifies a group of statements to be executed, including do loops that execute statements repetitively until or while a condition is true.