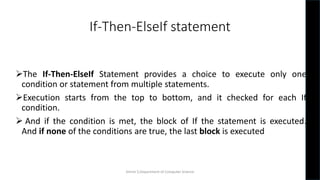
The document discusses different types of statements and loops in Visual Basic. It describes declaration statements, executable statements, and assignment statements. It then explains various conditional/control statements like If-Then, If-Then-Else, If-Then-ElseIf, and Select Case statements. It provides syntax and examples for each. The document also discusses different types of loops like Do, For-Next, For Each, While, and With loops. It provides the syntax and examples of Do While and For-Next loops.






![If-Then Statement
• The If-Then Statement is a control statement that defines one or
more conditions, and if the particular condition is satisfied, it
executes a piece of information or statements.
If condition Then
[Statement or block of Statement]
End If
Simmi S,Department of Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1lecture4vp-231129084243-8c017742/85/Conditional-Statements-Loops-8-320.jpg)






![Select Case Statement
Syntax:
Select Case [variable or expression]
Case value1 'defines the item or value that you want to match.
//define a statement to execute
Case value2 'defines the item or value that you want to match.
// Define a statement to execute
Case Else
// Define the default statement if none of the conditions is true.
End Select
Simmi S,Department of Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1lecture4vp-231129084243-8c017742/85/Conditional-Statements-Loops-16-320.jpg)



![Do Loop
In VB.NET, Do While loop is used to execute blocks of statements in the
program, as long as the condition remains true
Do [ { While | Until } condition ]
[ statements ]
Loop
' -or-
Do
[ statements ]
Loop [ { While | Until } condition ]
Simmi S,Department of Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1lecture4vp-231129084243-8c017742/85/Conditional-Statements-Loops-20-320.jpg)
![Do
[ Statements to be executed]
Loop While Boolean_expression
or
Do
[Statement to be executed]
Loop Until Boolean_expression
Simmi S,Department of Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1lecture4vp-231129084243-8c017742/85/Conditional-Statements-Loops-21-320.jpg)


![For Next Loop
• A For Next loop is used to repeatedly execute a sequence of code or a
block of code until a given condition is satisfied. A For loop is useful in
such a case when we know how many times a block of code has to be
executed.
• Syntax
For variable_name As [ DataType ] = start To end [ Step step ]
[ Statements to be executed ]
Next
Simmi S,Department of Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1lecture4vp-231129084243-8c017742/85/Conditional-Statements-Loops-24-320.jpg)
![For Next Loop
• For: It is the keyword that is present at the beginning of the definition.
• variable_name: It is a variable name, which is required in the For loop
Statement..
• [Data Type]: It represents the Data Type of the variable_name.
• start To end: The start and end are the two important parameters
representing the initial and final values of the variable_name..
• Step: A step parameter is used to determine by which the counter value of a
variable is increased or decreased after each iteration in a program. If the
counter value is not specified; It uses 1 as the default value.
• Statements: A statement can be a single statement or group of statements
that execute during the completion of each iteration in a loop.
• Next: In VB.NET a Next is a keyword that represents the end of the For loop's
Simmi S,Department of Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1lecture4vp-231129084243-8c017742/85/Conditional-Statements-Loops-25-320.jpg)

![For Each Loop
In the VB.NET, For Each loop is used to iterate block of statements in an array
or collection objects. Using For Each loop, we can easily work with collection
objects such as lists, arrays, etc., to execute each element of an array or in a
collection.
For Each var_name As [ DataType ] In Collection_Object
[ Statements to be executed]
Next
Simmi S,Department of Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1lecture4vp-231129084243-8c017742/85/Conditional-Statements-Loops-27-320.jpg)


