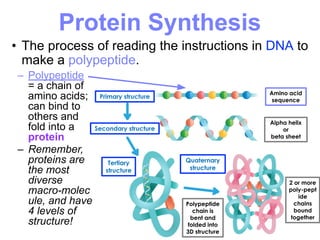
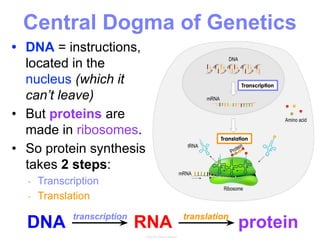
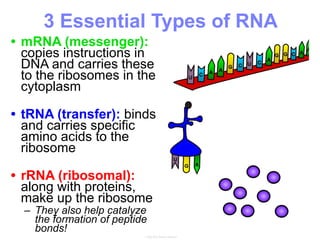
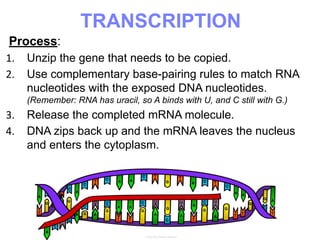
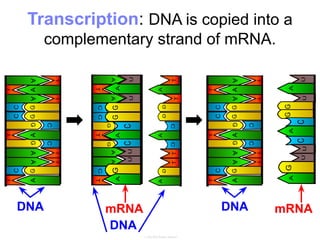
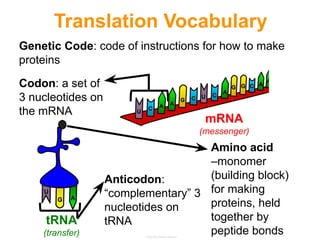
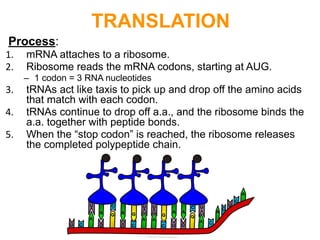
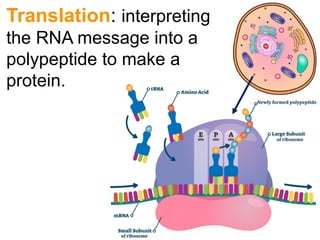
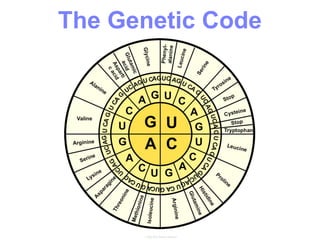
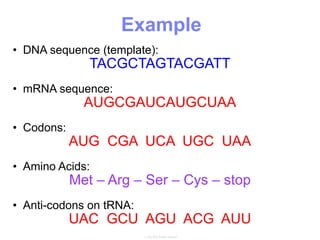
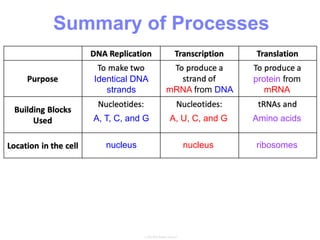
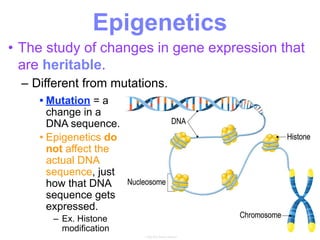
This document summarizes the process of protein synthesis, which occurs in two main steps - transcription and translation. In transcription, DNA in the nucleus is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) using complementary base pairing. The mRNA then exits the nucleus and binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. In translation, the mRNA is read by the ribosome, which uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to translate the mRNA codons into amino acids and assemble them into a polypeptide chain. Although all cells contain the same DNA, gene expression is regulated at the transcriptional and translational levels, allowing different proteins to be produced in different cell types.