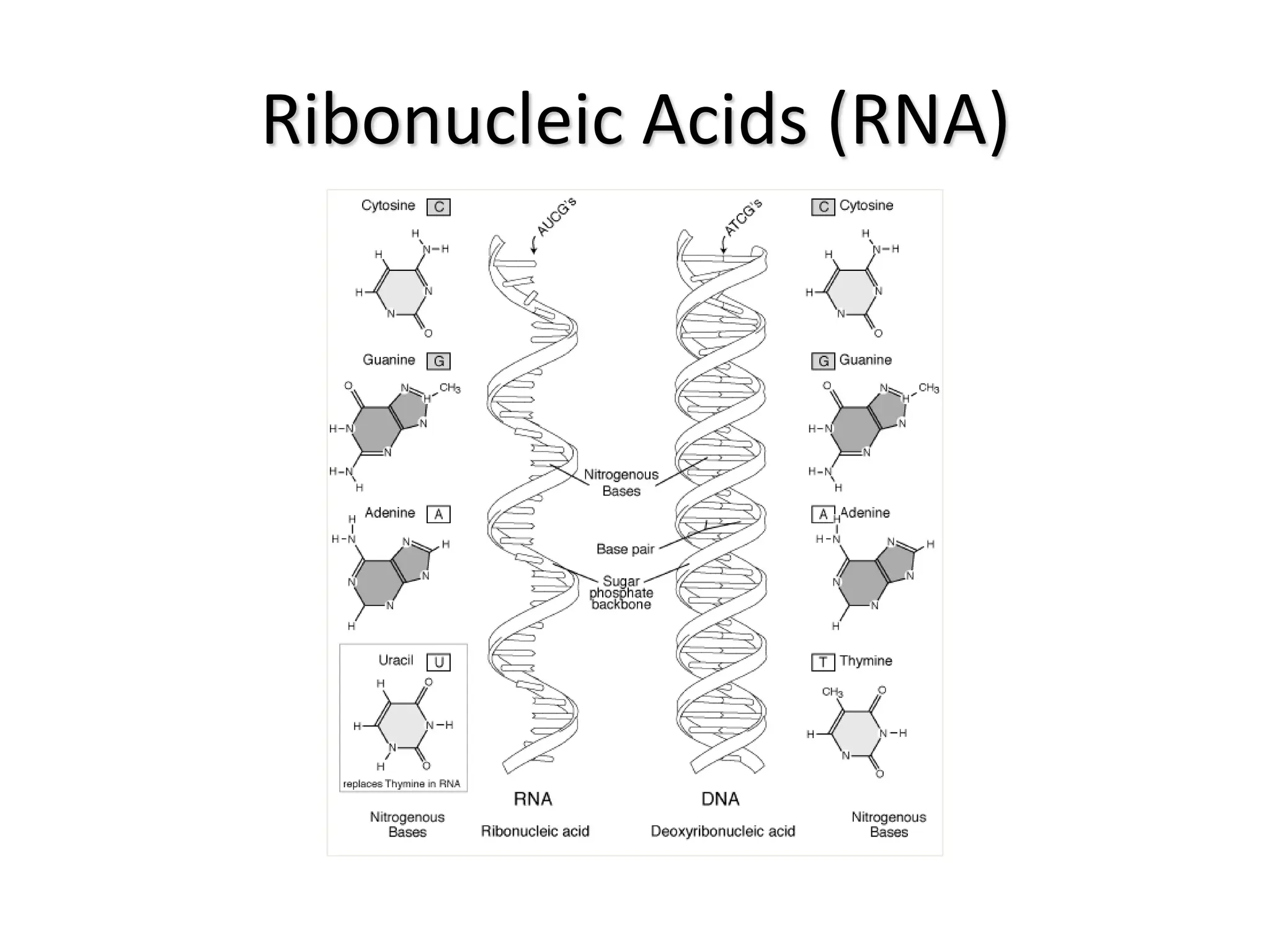
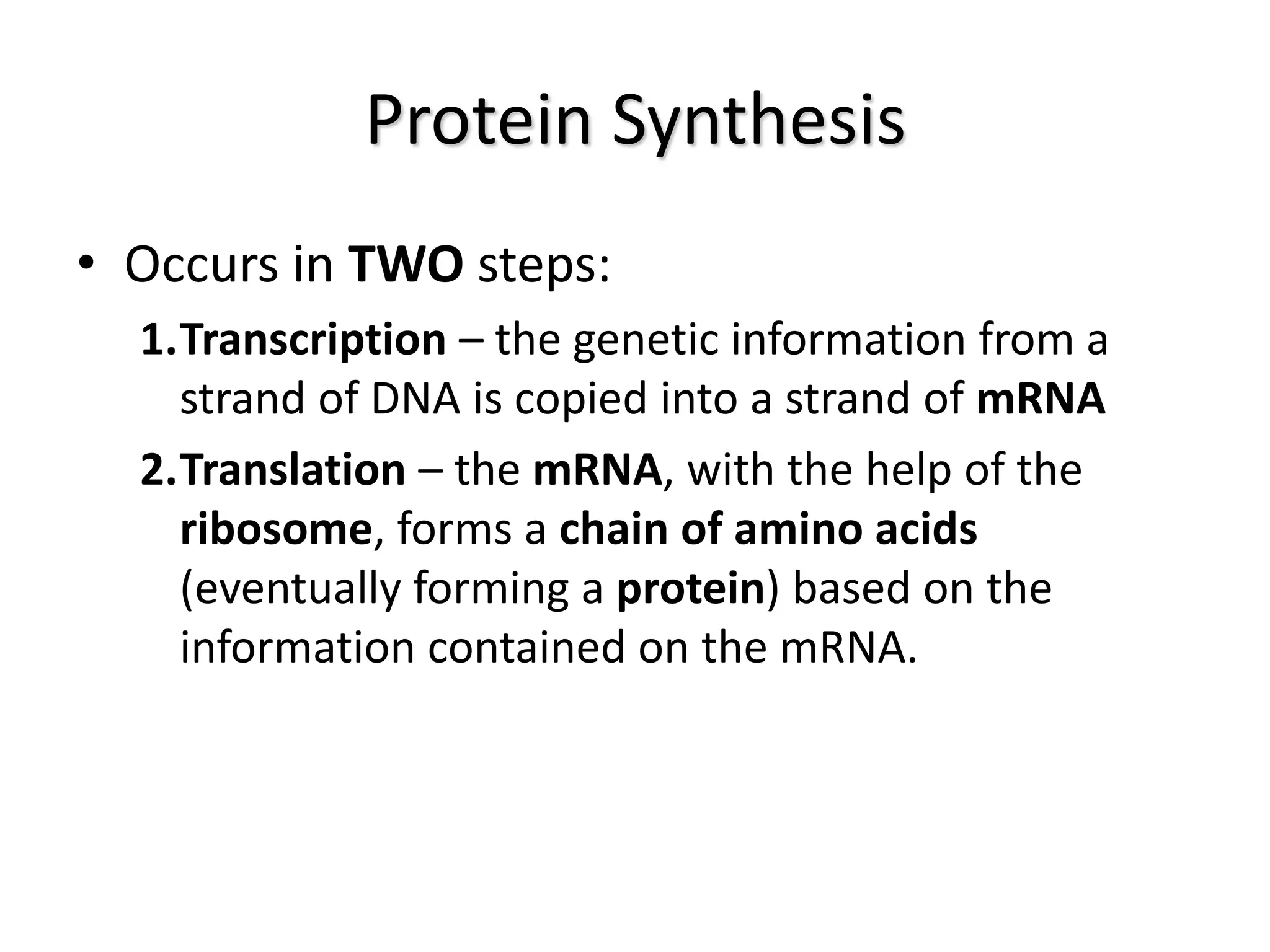
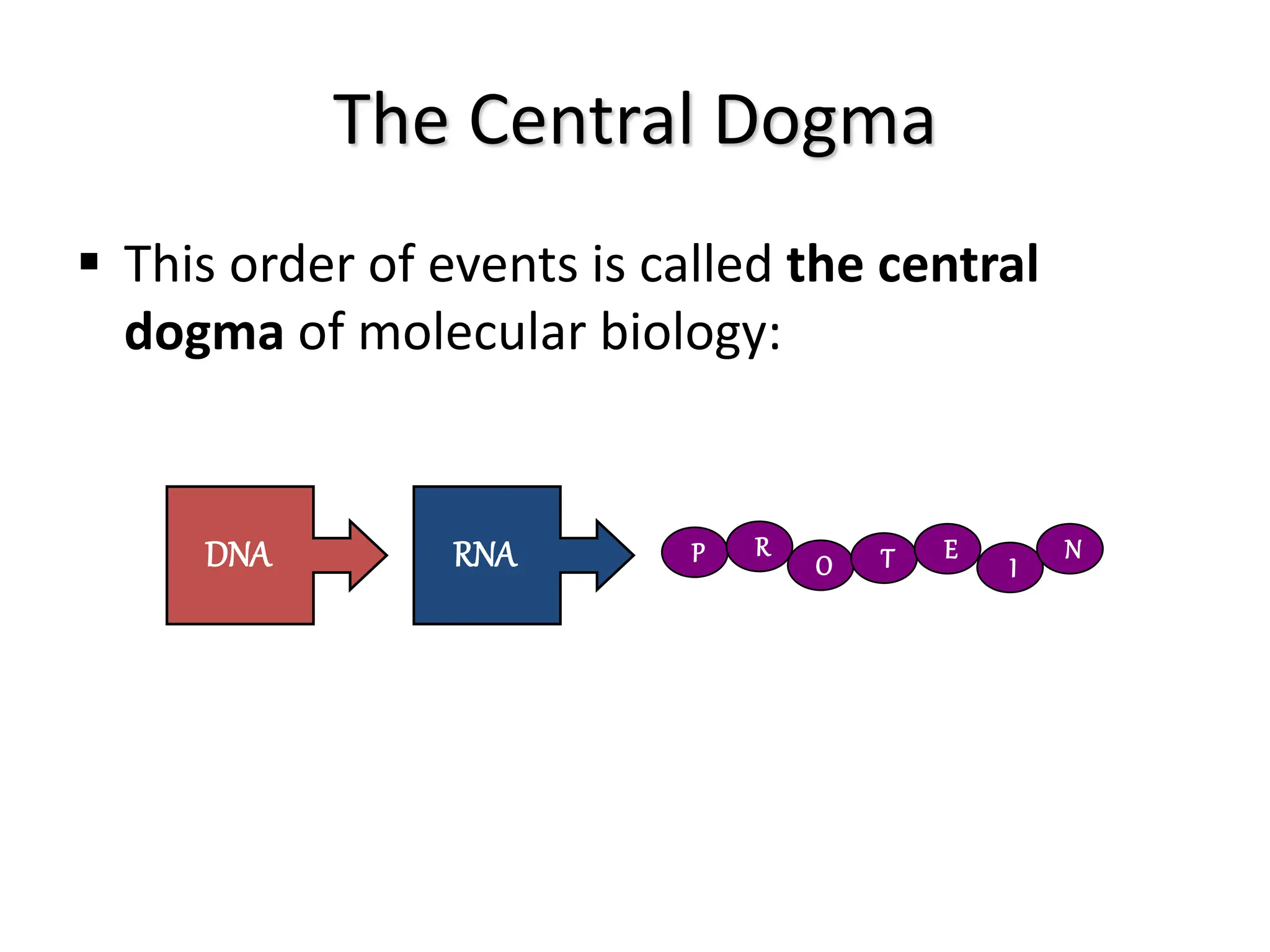
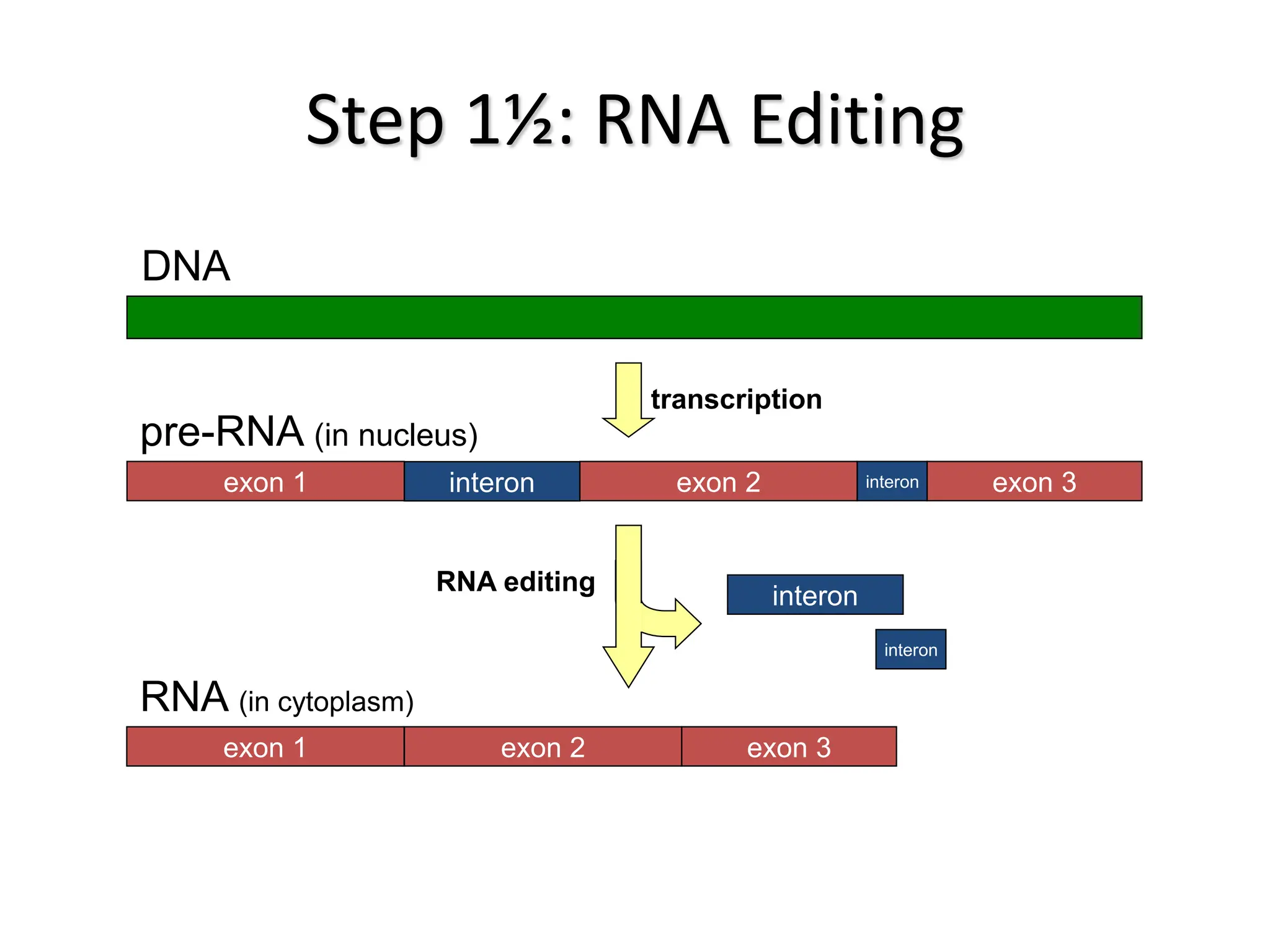
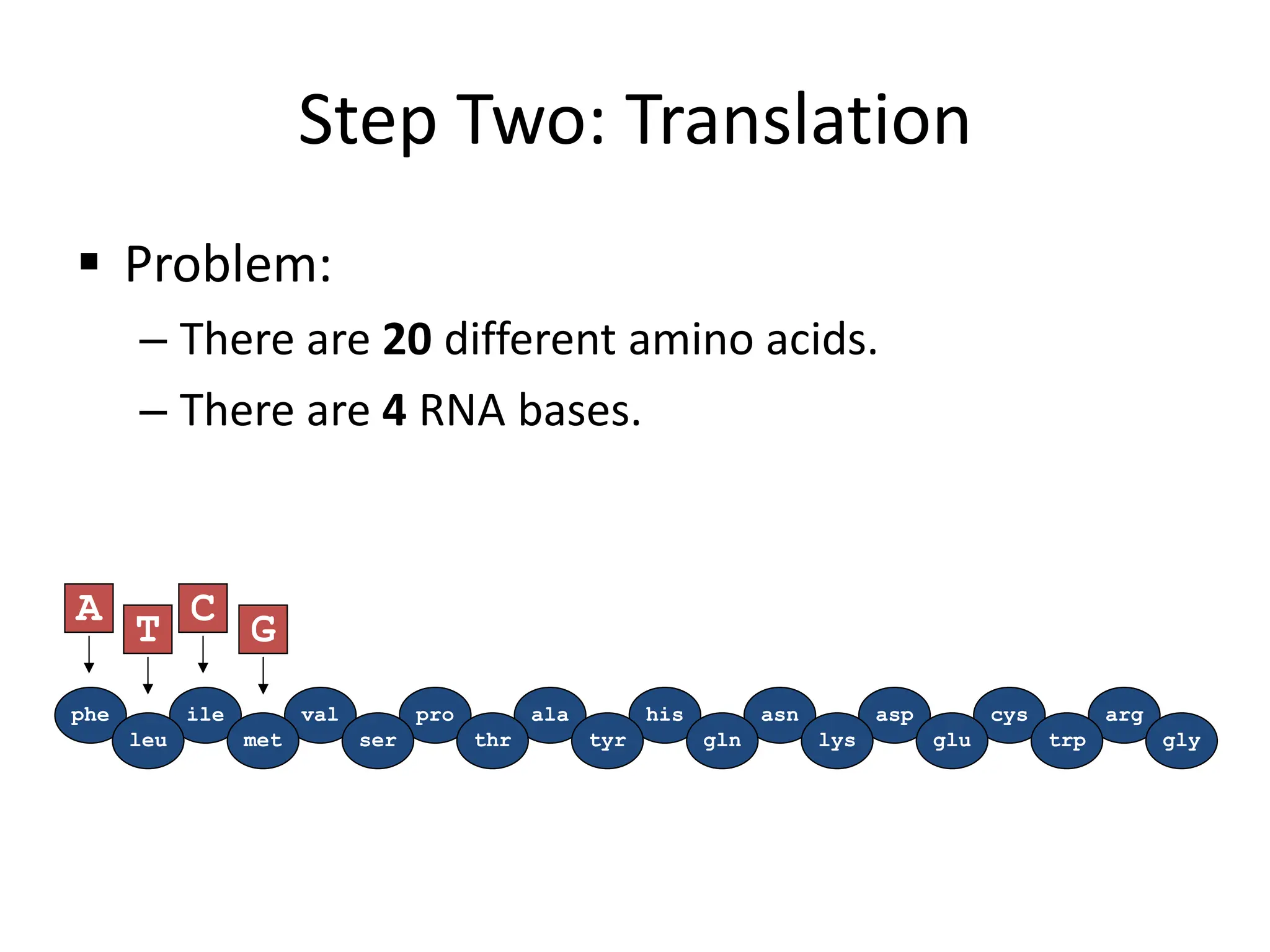
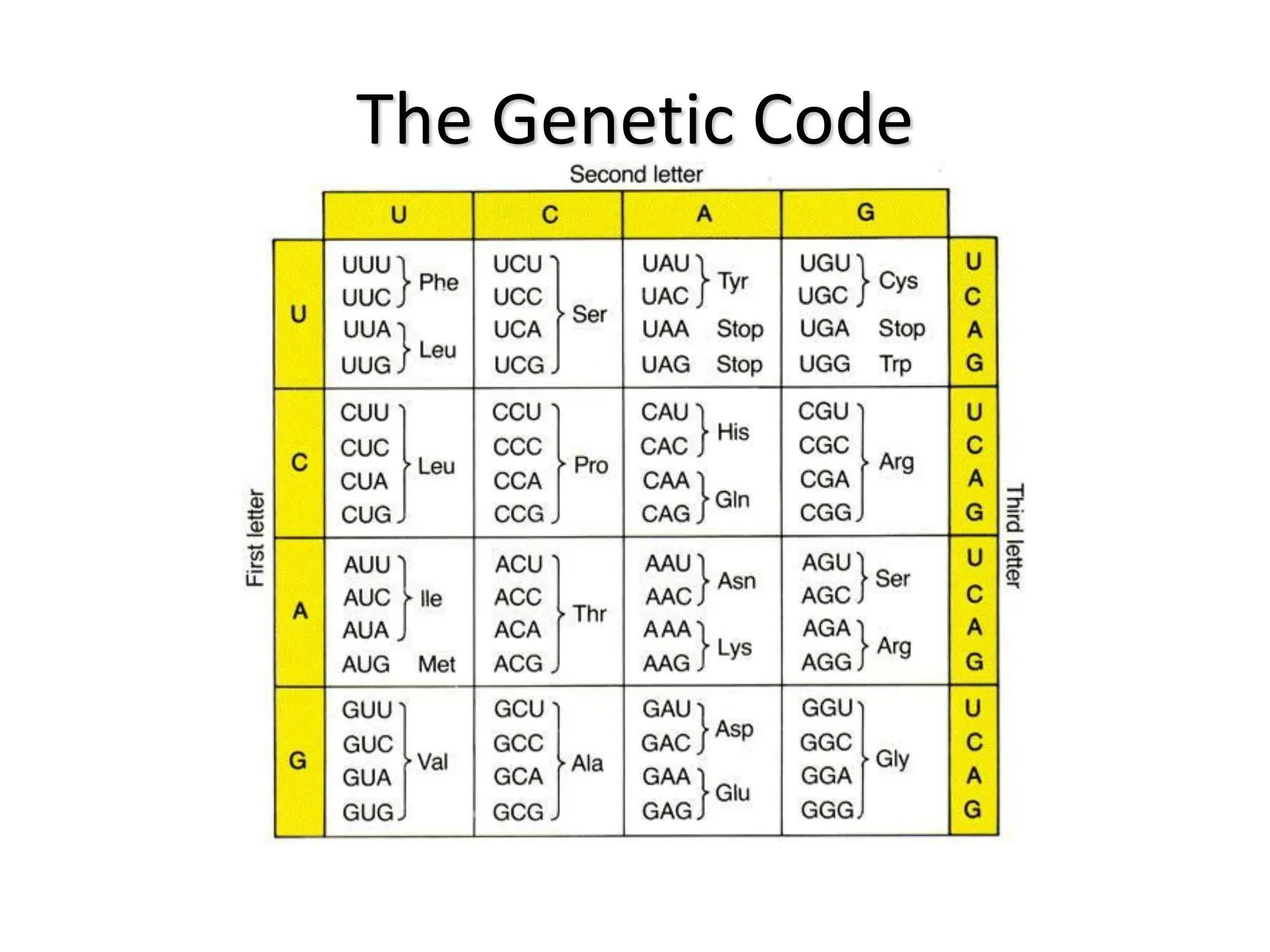
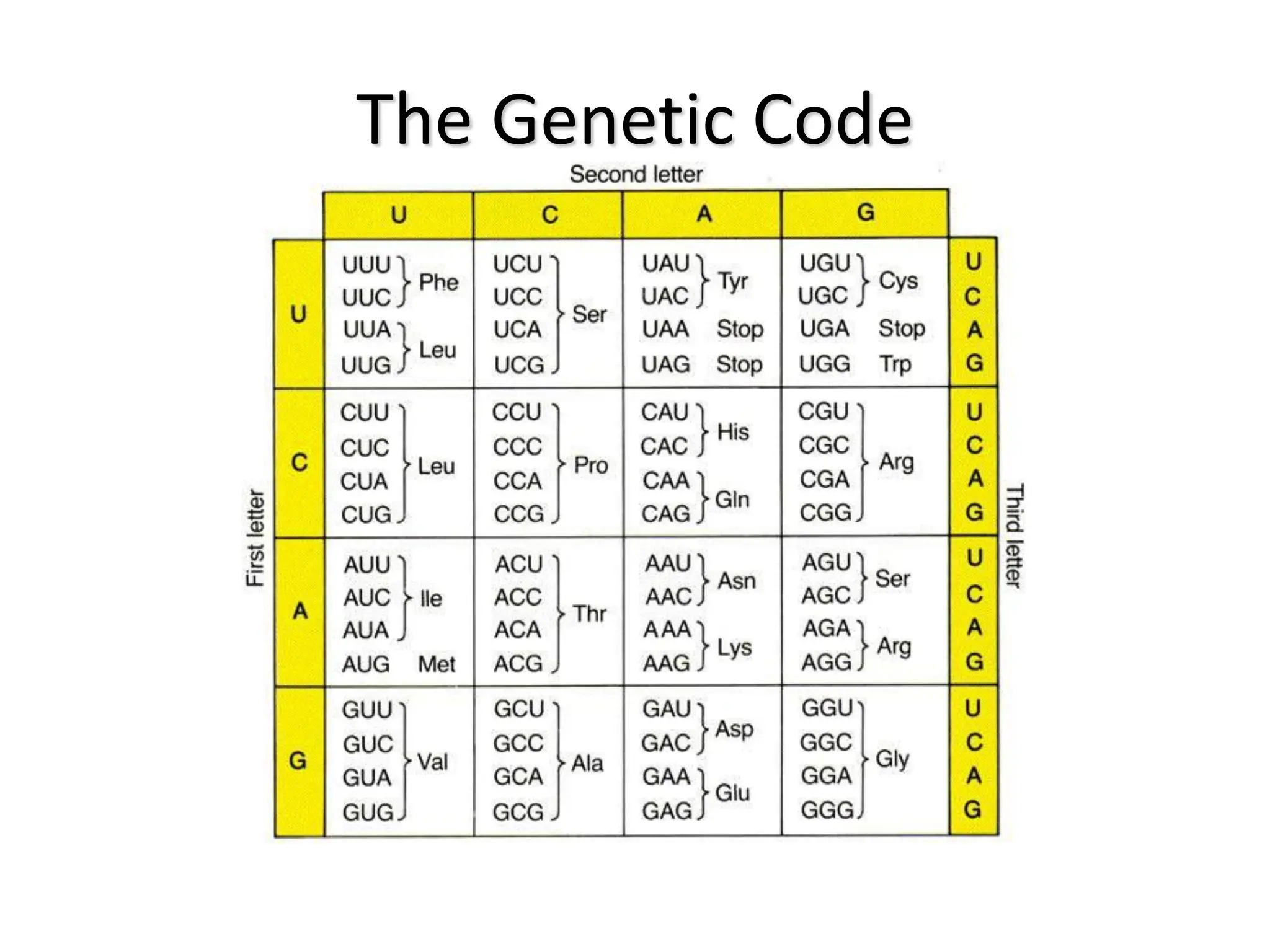
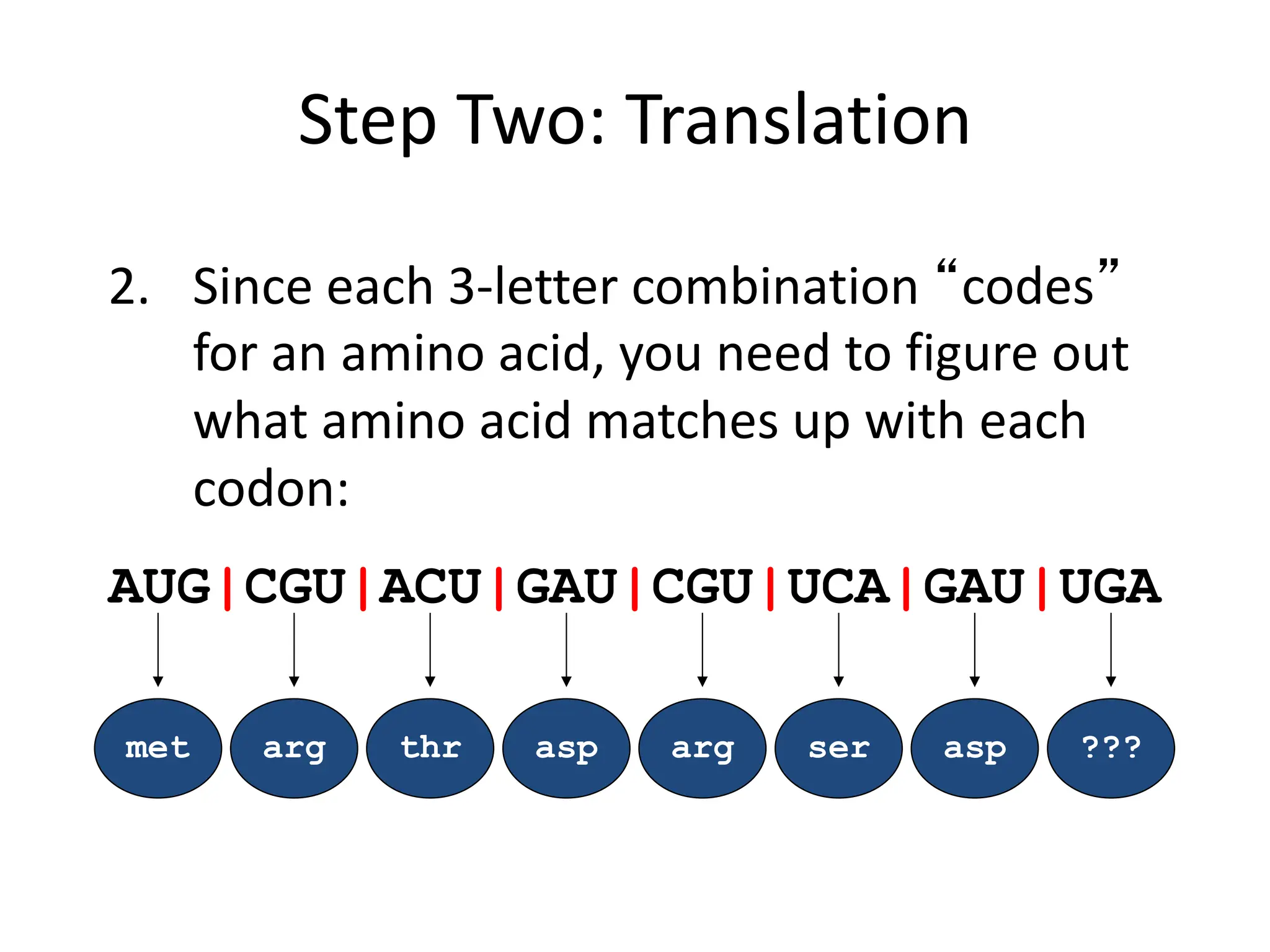
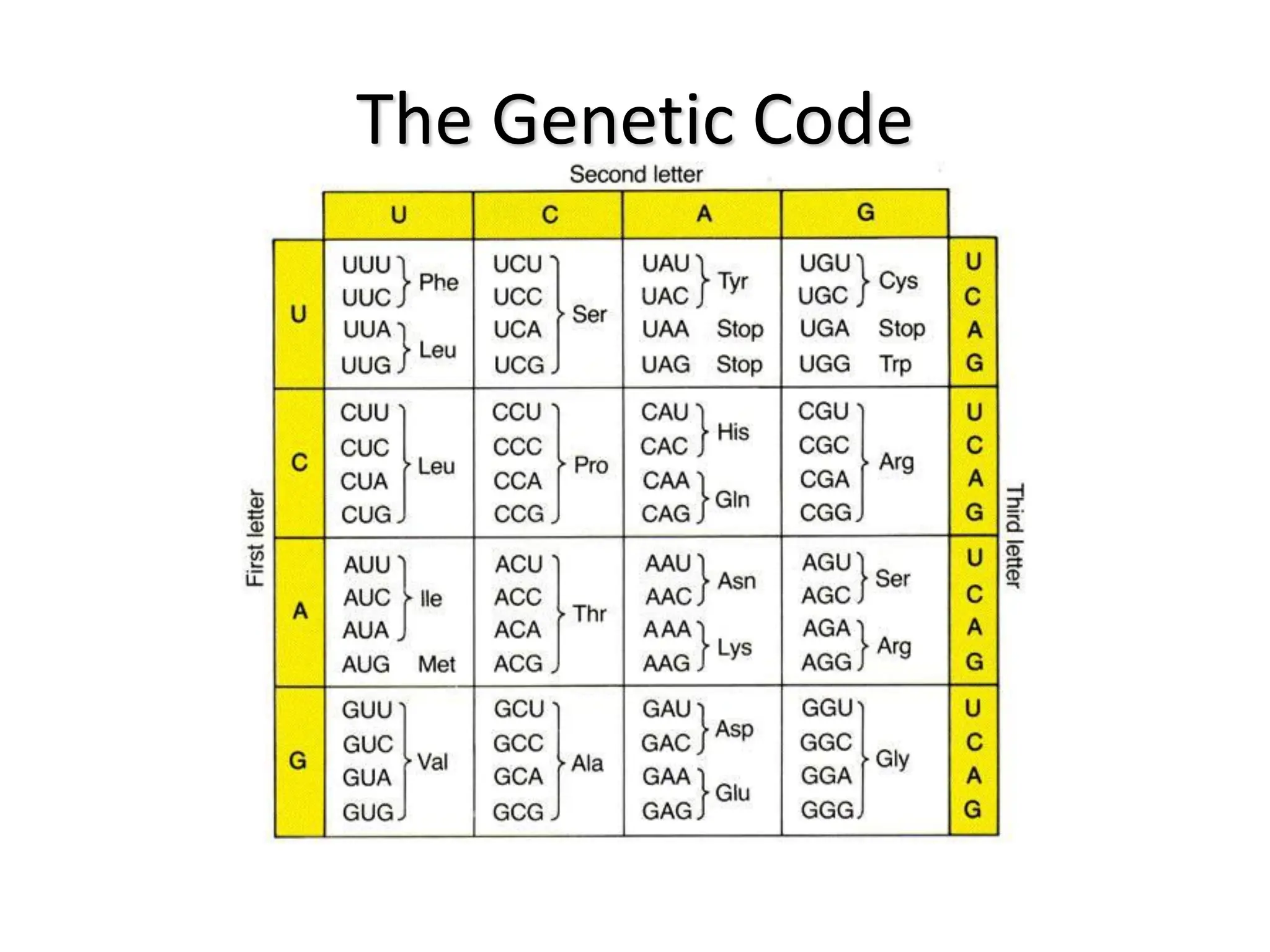
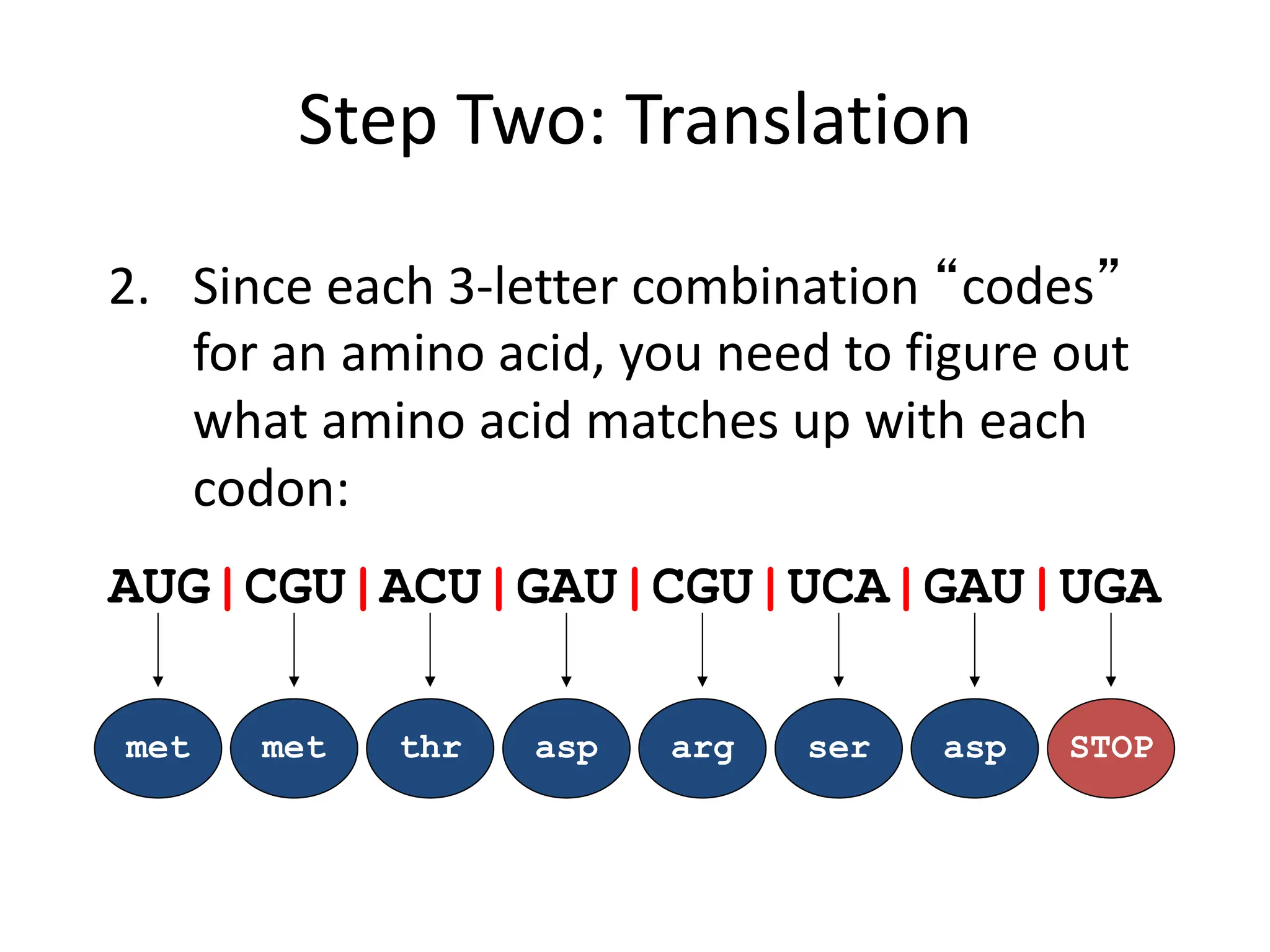
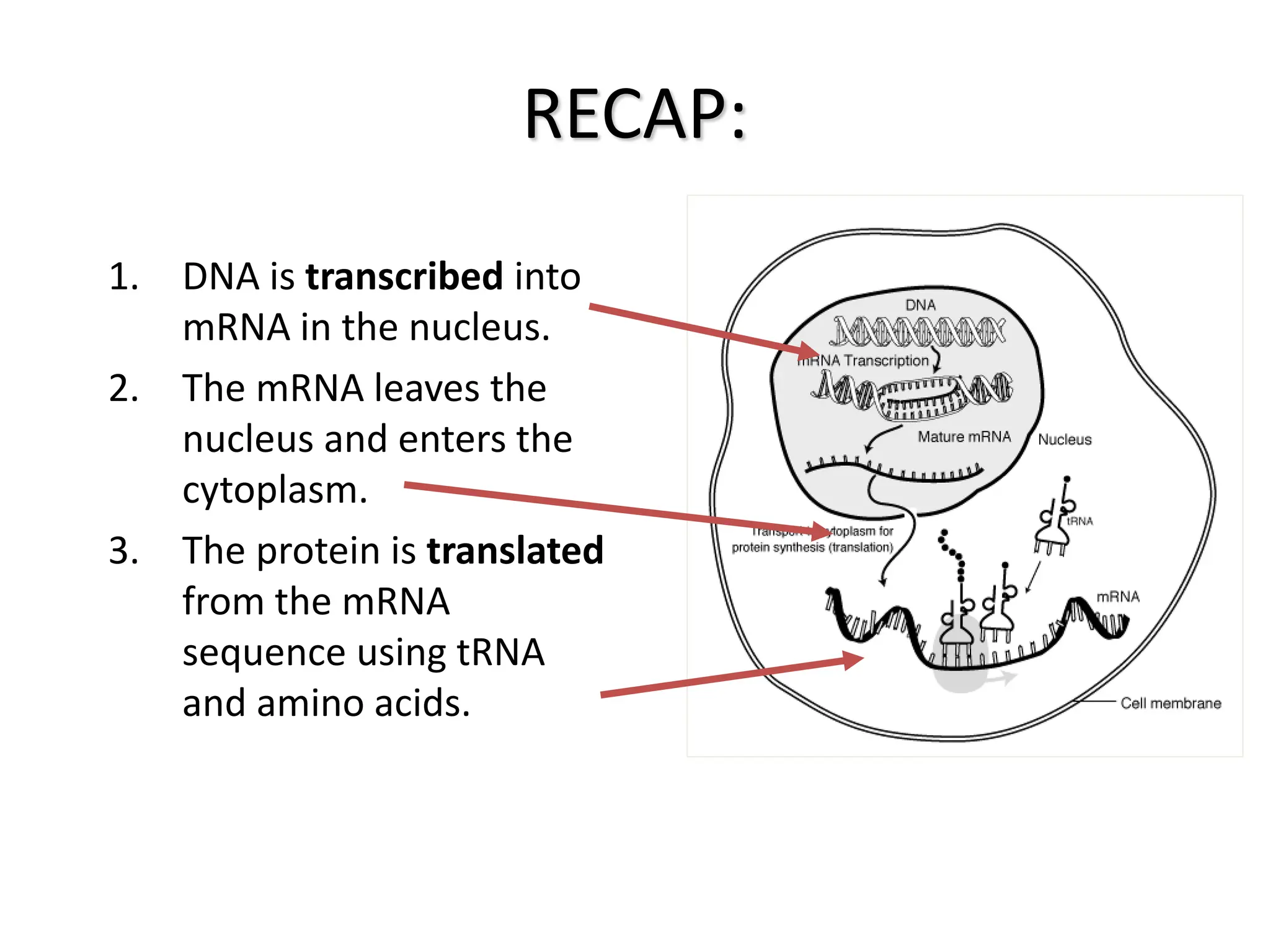
Protein synthesis is a multi-step process where DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus, which is then transported to the cytoplasm and translated into a protein based on the mRNA sequence. Specifically, transcription involves RNA polymerase copying the DNA sequence into mRNA. The mRNA is then edited before being translated by ribosomes into a protein chain through codon-anticodon base pairing between mRNA and tRNA, which brings amino acids in the specified order.