Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times






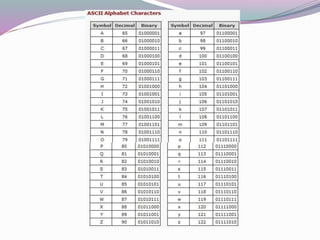












This document discusses units of measurement for digital information storage. It defines the bit as the smallest unit, with a byte equal to 8 bits that can represent a character. A kilobyte is equal to either 1,000 or 1,024 bytes depending on notation, while a megabyte is roughly 1,000 kilobytes. Examples are given for how many bytes or megabytes would be needed to store different amounts of text information.


















