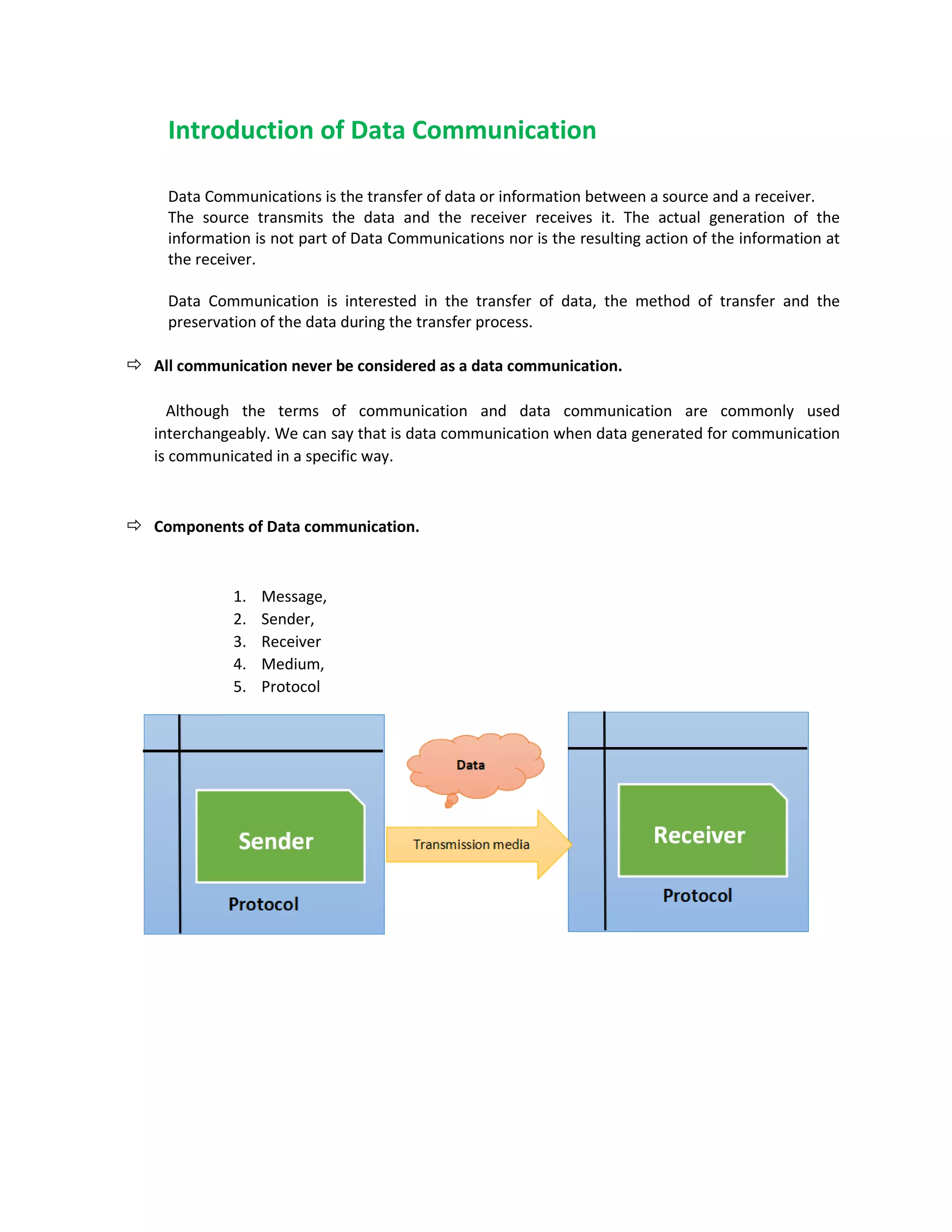
Data communication involves the transfer of data between a source and receiver. It focuses on how the data is transferred and preserved during transmission. There are five main components: a message, sender, receiver, medium, and protocol.
The TCP/IP model defines four layers - application, transport, internet, and network interface - that work together to transmit data across networks. The transport layer ensures reliable and error-free delivery of data between processes running on different devices. It includes protocols like TCP that provide features like flow control, error checking, and retransmission.
Data modulation converts analog and digital signals so they can be transmitted over different mediums. Common analog modulation techniques are amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation, which vary